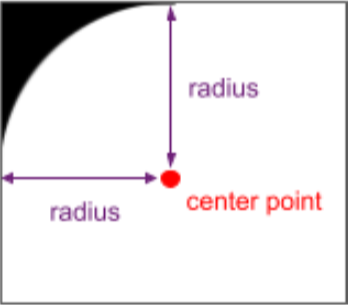
À partir d'Android 12 (niveau d'API 31), vous pouvez utiliser
RoundedCorner et
WindowInsets.getRoundedCorner(int
position) pour obtenir
le rayon et le point central des coins arrondis de l'écran de l'appareil. Ces API
éviter que les éléments d'interface utilisateur de votre application soient tronqués sur les écrans dont les
dans chaque coin. Le framework fournit
getPrivacyIndicatorBounds()
qui renvoie le rectangle limité de tous les micros et caméras visibles
de sécurité.
Lorsqu'elles sont implémentées dans votre application, ces API n'ont aucun effet sur les appareils avec les écrans non arrondis.
Pour implémenter cette fonctionnalité, récupérez les informations RoundedCorner à l'aide de
WindowInsets.getRoundedCorner(int position) par rapport aux limites de
application. Si l'application n'occupe pas tout l'écran, l'API applique la
coin arrondi basé sur le point central de l'angle arrondi de la fenêtre
les limites de l'application.
L'extrait de code suivant montre comment une application peut éviter que son interface utilisateur soit tronquée en
en définissant une marge de vue en fonction des informations de RoundedCorner. Dans ce
il s'agit de l'angle supérieur droit.
Kotlin
// Get the top-right rounded corner from WindowInsets. val insets = rootWindowInsets val topRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_TOP_RIGHT) ?: return // Get the location of the close button in window coordinates. val location = IntArray(2) closeButton!!.getLocationInWindow(location) val buttonRightInWindow = location[0] + closeButton.width val buttonTopInWindow = location[1] // Find the point on the quarter circle with a 45-degree angle. val offset = (topRight.radius * Math.sin(Math.toRadians(45.0))).toInt() val topBoundary = topRight.center.y - offset val rightBoundary = topRight.center.x + offset // Check whether the close button exceeds the boundary. if (buttonRightInWindow < rightBoundary << buttonTopInWindow > topBoundary) { return } // Set the margin to avoid truncating. val parentLocation = IntArray(2) getLocationInWindow(parentLocation) val lp = closeButton.layoutParams as FrameLayout.LayoutParams lp.rightMargin = Math.max(buttonRightInWindow - rightBoundary, 0) lp.topMargin = Math.max(topBoundary - buttonTopInWindow, 0) closeButton.layoutParams = lp
Java
// Get the top-right rounded corner from WindowInsets. final WindowInsets insets = getRootWindowInsets(); final RoundedCorner topRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(POSITION_TOP_RIGHT); if (topRight == null) { return; } // Get the location of the close button in window coordinates. int [] location = new int[2]; closeButton.getLocationInWindow(location); final int buttonRightInWindow = location[0] + closeButton.getWidth(); final int buttonTopInWindow = location[1]; // Find the point on the quarter circle with a 45-degree angle. final int offset = (int) (topRight.getRadius() * Math.sin(Math.toRadians(45))); final int topBoundary = topRight.getCenter().y - offset; final int rightBoundary = topRight.getCenter().x + offset; // Check whether the close button exceeds the boundary. if (buttonRightInWindow < rightBoundary << buttonTopInWindow > topBoundary) { return; } // Set the margin to avoid truncating. int [] parentLocation = new int[2]; getLocationInWindow(parentLocation); FrameLayout.LayoutParams lp = (FrameLayout.LayoutParams) closeButton.getLayoutParams(); lp.rightMargin = Math.max(buttonRightInWindow - rightBoundary, 0); lp.topMargin = Math.max(topBoundary - buttonTopInWindow, 0); closeButton.setLayoutParams(lp);
Faites attention au découpage
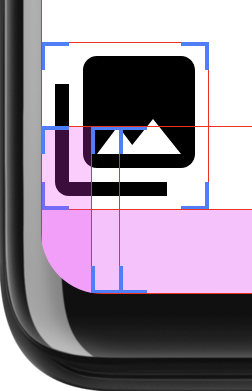
Si l'interface utilisateur occupe tout l'écran, les angles arrondis peuvent entraîner des problèmes de contenu le rognage. Par exemple, la figure 2 montre une icône dans le coin de l'écran avec la mise en page dessinée derrière les barres système:

Vous pouvez éviter cela en vérifiant les angles arrondis et en appliquant une marge intérieure pour que le contenu de votre application hors des coins de l'appareil, comme illustré Exemple:
Kotlin
class InsetsLayout(context: Context, attrs: AttributeSet) : FrameLayout(context, attrs) { override fun onLayout(changed: Boolean, left: Int, top: Int, right: Int, bottom: Int) { val insets = rootWindowInsets if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.S && insets != null) { applyRoundedCornerPadding(insets) } super.onLayout(changed, left, top, right, bottom) } @RequiresApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.S) private fun applyRoundedCornerPadding(insets: WindowInsets) { val topLeft = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_TOP_LEFT) val topRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_TOP_RIGHT) val bottomLeft = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_BOTTOM_LEFT) val bottomRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_BOTTOM_RIGHT) val leftRadius = max(topLeft?.radius ?: 0, bottomLeft?.radius ?: 0) val topRadius = max(topLeft?.radius ?: 0, topRight?.radius ?: 0) val rightRadius = max(topRight?.radius ?: 0, bottomRight?.radius ?: 0) val bottomRadius = max(bottomLeft?.radius ?: 0, bottomRight?.radius ?: 0) val windowManager = context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE) as WindowManager val windowBounds = windowManager.currentWindowMetrics.bounds val safeArea = Rect( windowBounds.left + leftRadius, windowBounds.top + topRadius, windowBounds.right - rightRadius, windowBounds.bottom - bottomRadius ) val location = intArrayOf(0, 0) getLocationInWindow(location) val leftMargin = location[0] - windowBounds.left val topMargin = location[1] - windowBounds.top val rightMargin = windowBounds.right - right - location[0] val bottomMargin = windowBounds.bottom - bottom - location[1] val layoutBounds = Rect( location[0] + paddingLeft, location[1] + paddingTop, location[0] + width - paddingRight, location[1] + height - paddingBottom ) if (layoutBounds != safeArea && layoutBounds.contains(safeArea)) { setPadding( calculatePadding(leftRadius, leftMargin, paddingLeft), calculatePadding(topRadius, topMargin, paddingTop), calculatePadding(rightRadius, rightMargin, paddingRight), calculatePadding(bottomRadius, bottomMargin, paddingBottom) ) } } private fun calculatePadding(radius1: Int?, radius2: Int?, margin: Int, padding: Int): Int = (max(radius1 ?: 0, radius2 ?: 0) - margin - padding).coerceAtLeast(0) }
Java
public class InsetsLayout extends FrameLayout { public InsetsLayout(@NonNull Context context) { super(context); } public InsetsLayout(@NonNull Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) { super(context, attrs); } @Override protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) { WindowInsets insets = getRootWindowInsets(); if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.S && insets != null) { applyRoundedCornerPadding(insets); } super.onLayout(changed, left, top, right, bottom); } @RequiresApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.S) private void applyRoundedCornerPadding(WindowInsets insets) { RoundedCorner topLeft = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_TOP_LEFT); RoundedCorner topRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_TOP_RIGHT); RoundedCorner bottomLeft = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_BOTTOM_LEFT); RoundedCorner bottomRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_BOTTOM_RIGHT); int radiusTopLeft = 0; int radiusTopRight = 0; int radiusBottomLeft = 0; int radiusBottomRight = 0; if (topLeft != null) radiusTopLeft = topLeft.getRadius(); if (topRight != null) radiusTopRight = topRight.getRadius(); if (bottomLeft != null) radiusBottomLeft = bottomLeft.getRadius(); if (bottomRight != null) radiusBottomRight = bottomRight.getRadius(); int leftRadius = Math.max(radiusTopLeft, radiusBottomLeft); int topRadius = Math.max(radiusTopLeft, radiusTopRight); int rightRadius = Math.max(radiusTopRight, radiusBottomRight); int bottomRadius = Math.max(radiusBottomLeft, radiusBottomRight); WindowManager windowManager = (WindowManager) getContext().getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE); Rect windowBounds = windowManager.getCurrentWindowMetrics().getBounds(); Rect safeArea = new Rect( windowBounds.left + leftRadius, windowBounds.top + topRadius, windowBounds.right - rightRadius, windowBounds.bottom - bottomRadius ); int[] location = {0, 0}; getLocationInWindow(location); int leftMargin = location[0] - windowBounds.left; int topMargin = location[1] - windowBounds.top; int rightMargin = windowBounds.right - getRight() - location[0]; int bottomMargin = windowBounds.bottom - getBottom() - location[1]; Rect layoutBounds = new Rect( location[0] + getPaddingLeft(), location[1] + getPaddingTop(), location[0] + getWidth() - getPaddingRight(), location[1] + getHeight() - getPaddingBottom() ); if (!layoutBounds.equals(safeArea) && layoutBounds.contains(safeArea)) { setPadding( calculatePadding(radiusTopLeft, radiusBottomLeft, leftMargin, getPaddingLeft()), calculatePadding(radiusTopLeft, radiusTopRight, topMargin, getPaddingTop()), calculatePadding(radiusTopRight, radiusBottomRight, rightMargin, getPaddingRight()), calculatePadding(radiusBottomLeft, radiusBottomRight, bottomMargin, getPaddingBottom()) ); } } private int calculatePadding(int radius1, int radius2, int margin, int padding) { return Math.max(Math.max(radius1, radius2) - margin - padding, 0); } }
Cette mise en page détermine si l'interface utilisateur s'étend jusqu'à la zone des angles arrondis et ajoute une marge intérieure là où c'est le cas. La figure 3 présente l'option "Afficher les limites de la mise en page" développeur pour montrer plus clairement la marge intérieure appliquée:
<ph type="x-smartling-placeholder">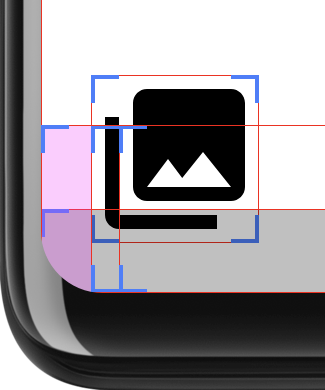
Pour ce faire, cette mise en page calcule deux rectangles: safeArea est
l'aire comprise dans les rayons des angles arrondis, et layoutBounds est la taille
de la mise en page, moins les marges intérieures. Si layoutArea contient entièrement safeArea, alors
les enfants de la mise en page peuvent être rognés. Dans ce cas, la marge intérieure est
ajouté pour s'assurer que la mise en page reste dans safeArea.
En vérifiant si layoutBounds encadre complètement safeArea, vous évitez d'ajouter
une marge intérieure lorsque la mise en page ne s'étend pas jusqu'aux bords de l'écran. Figure 4
affiche la mise en page lorsqu'elle n'est pas dessinée derrière la barre de navigation. Dans ce cas,
la mise en page ne s'étend pas suffisamment vers le bas pour être dans les coins arrondis, car
ils s'inscrivent dans la zone occupée par la barre de navigation. Aucune marge intérieure n'est requise.