כל שדה טקסט מצפה לסוג מסוים של קלט טקסט, כמו כתובת אימייל, מספר טלפון או טקסט פשוט. עליכם לציין את סוג הקלט לכל שדה טקסט באפליקציה כדי שהמערכת תציג את שיטת הקלט הרלוונטית, כמו מקלדת במסך.
בנוסף לסוג הלחצנים שזמינים בשיטת הקלט, אפשר לציין התנהגויות כמו: האם שיטת הקלט מספקת הצעות לאיות, האם היא הופכת משפטים חדשים לאותיות רישיות והאם היא מחליפה את לחצן החזרה למחרוזת הקודמת בלחצן פעולה כמו סיום או הבא. בדף הזה נסביר איך לציין את המאפיינים האלה.
מציינים את סוג המקלדת
תמיד צריך להצהיר על שיטת הקלט של שדות הטקסט על ידי הוספת המאפיין android:inputType לאלמנט <EditText>.
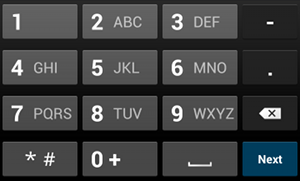
phone.לדוגמה, אם רוצים להשתמש בשיטת קלט להזנת מספר טלפון, משתמשים בערך "phone":
<EditText android:id="@+id/phone" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="@string/phone_hint" android:inputType="phone" />
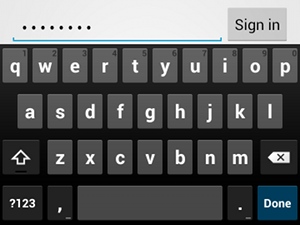
textPassword.אם שדה הטקסט מיועד לסיסמה, משתמשים בערך "textPassword" כדי ששדה הטקסט יכסה את הקלט של המשתמש:
<EditText android:id="@+id/password" android:hint="@string/password_hint" android:inputType="textPassword" ... />
יש כמה ערכים אפשריים שמתועדים במאפיין android:inputType, ואפשר לשלב בין חלק מהערכים כדי לציין את המראה של שיטת הקלט ואת ההתנהגויות הנוספות שלה.
הפעלת הצעות איות והתנהגויות אחרות
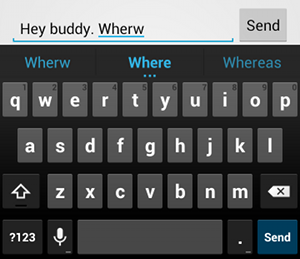
textAutoCorrect מאפשרת תיקון אוטומטי של שגיאות איות.המאפיין android:inputType מאפשר לציין התנהגויות שונות לשיטת הקלט. חשוב במיוחד: אם שדה הטקסט מיועד להזנת טקסט בסיסי, כמו הודעת טקסט, צריך להפעיל תיקון אוטומטי של איות באמצעות הערך "textAutoCorrect".
אפשר לשלב בין סגנונות שונים של שיטות קלט והתנהגויות שונות באמצעות המאפיין android:inputType. לדוגמה, כך יוצרים שדה טקסט שמתחיל את המילה הראשונה במשפט באות רישית, וגם מתקן שגיאות איות באופן אוטומטי:
<EditText android:id="@+id/message" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:inputType= "textCapSentences|textAutoCorrect" ... />
ציון הפעולה של שיטת הקלט
ברוב שיטות הקלט האלקטרוניות מופיע לחצן פעולה של המשתמש בפינה התחתונה, שמתאים לשדה הטקסט הנוכחי. כברירת מחדל, המערכת משתמשת בלחצן הזה לפעולה הבא או סיום, אלא אם שדה הטקסט תומך בטקסט בכמה שורות – כמו ב-android:inputType="textMultiLine". במקרה כזה, לחצן הפעולה הוא מקש החזרה למחרוזת. עם זאת, אפשר לציין פעולות אחרות שעשויות להתאים יותר לשדה הטקסט, כמו שליחה או מעבר.
כדי לציין את לחצן הפעולה במקלדת, משתמשים במאפיין android:imeOptions עם ערך פעולה כמו "actionSend" או "actionSearch". לדוגמה:

android:imeOptions="actionSend".<EditText android:id="@+id/search" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="@string/search_hint" android:inputType="text" android:imeOptions="actionSend" />
לאחר מכן תוכלו להאזין ללחיצות על לחצן הפעולה על ידי הגדרת TextView.OnEditorActionListener לאלמנט EditText. בתגובה לפעולה, צריך להחזיר את מזהה הפעולה המתאים של IME שמוגדר בכיתה EditorInfo, למשל IME_ACTION_SEND, כפי שמתואר בדוגמה הבאה:
Kotlin
findViewById<EditText>(R.id.search).setOnEditorActionListener { v, actionId, event -> return@setOnEditorActionListener when (actionId) { EditorInfo.IME_ACTION_SEND -> { sendMessage() true } else -> false } }
Java
EditText editText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.search); editText.setOnEditorActionListener(new OnEditorActionListener() { @Override public boolean onEditorAction(TextView v, int actionId, KeyEvent event) { boolean handled = false; if (actionId == EditorInfo.IME_ACTION_SEND) { sendMessage(); handled = true; } return handled; } });
שליחת הצעות להשלמה אוטומטית
אם אתם רוצים לספק הצעות למשתמשים בזמן שהם מקלידים, תוכלו להשתמש בתת-סוג של EditText שנקרא AutoCompleteTextView.
כדי להטמיע את המילוי האוטומטי, צריך לציין Adapter שמספק את הצעות הטקסט. יש כמה מתאמים זמינים, בהתאם למקור הנתונים, למשל ממסד נתונים או ממערך.
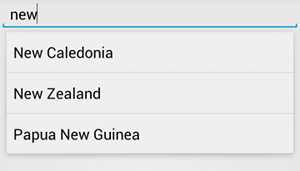
AutoCompleteTextView עם הצעות לטקסט.בתהליך הבא מוסבר איך להגדיר AutoCompleteTextView שמספק הצעות ממערך באמצעות ArrayAdapter:
- מוסיפים את
AutoCompleteTextViewלפריסה. זוהי פריסה עם שדה הטקסט בלבד:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <AutoCompleteTextView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:id="@+id/autocomplete_country" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
- מגדירים את המערך שמכיל את כל הצעות הטקסט. לדוגמה, זוהי מערך של שמות מדינות:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <string-array name="countries_array"> <item>Afghanistan</item> <item>Albania</item> <item>Algeria</item> <item>American Samoa</item> <item>Andorra</item> <item>Angola</item> <item>Anguilla</item> <item>Antarctica</item> ... </string-array> </resources>
- ב-
Activityאו ב-Fragment, משתמשים בקוד הבא כדי לציין את המתאם שמספק את ההצעות:Kotlin
// Get a reference to the AutoCompleteTextView in the layout. val textView = findViewById(R.id.autocomplete_country) as AutoCompleteTextView // Get the string array. val countries: Array<out String> = resources.getStringArray(R.array.countries_array) // Create the adapter and set it to the AutoCompleteTextView. ArrayAdapter<String>(this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, countries).also { adapter -> textView.setAdapter(adapter) }
Java
// Get a reference to the AutoCompleteTextView in the layout. AutoCompleteTextView textView = (AutoCompleteTextView) findViewById(R.id.autocomplete_country); // Get the string array. String[] countries = getResources().getStringArray(R.array.countries_array); // Create the adapter and set it to the AutoCompleteTextView. ArrayAdapter<String> adapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>(this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, countries); textView.setAdapter(adapter);
בדוגמה הקודמת, מתבצעת אתחול של
ArrayAdapterחדש כדי לקשר כל פריט במערך המחרוזותcountries_arrayל-TextViewשקיים בפריסהsimple_list_item_1. זוהי פריסה ש-Android מספקת ומספקת מראה סטנדרטי לטקסט ברשימה. -
מקצים את המתאם ל-
AutoCompleteTextViewבאמצעות קריאה ל-setAdapter().

