在 Wear OS 设备上,用户可通过列表轻松地从一组选项中选择一个项目。
穿戴式设备界面库包含 WearableRecyclerView 类,它是 RecyclerView 的实现,用于创建针对穿戴式设备进行了优化的列表。您可以通过创建一个新的 WearableRecyclerView 容器,在穿戴式应用中使用此界面。
对于简单项目的长列表(例如应用启动器或联系人列表),请使用 WearableRecyclerView。每个项目可能具有一个简短的字符串和一个关联的图标。或者,每个项目也可能只有一个字符串或一个图标。
注意:请避免使用复杂的布局。用户应该只需要扫一眼项目就能知道它是什么,尤其是在穿戴式设备屏幕尺寸有限的情况下。
通过扩展现有 RecyclerView 类,默认情况下,WearableRecyclerView API 会在直列表中显示一系列可垂直滚动的项目。在您的穿戴式应用中,您可以使用 WearableRecyclerView API 选择启用曲线布局和环形滚动手势。
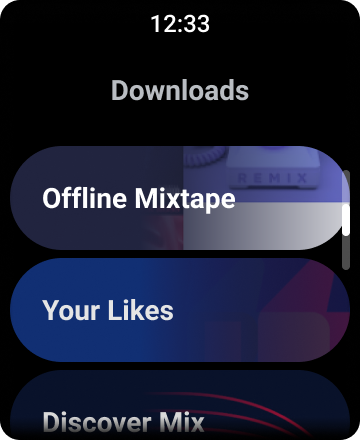
图 1. Wear OS 上的默认列表视图。
本指南将向您介绍如何使用 WearableRecyclerView 类在 Wear OS 应用中创建列表、如何为可滚动项目选择启用曲线布局,以及如何自定义滚动时的子视图外观。
使用 XML 将 WearableRecyclerView 添加到 activity
以下布局会将 WearableRecyclerView 添加到 activity:
<androidx.wear.widget.WearableRecyclerView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/recycler_launcher_view" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:scrollbars="vertical" />
以下示例展示了应用于 activity 的 WearableRecyclerView:
Kotlin
class MainActivity : Activity() { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) } ... }
Java
public class MainActivity extends Activity { @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); } ... }
创建曲线布局
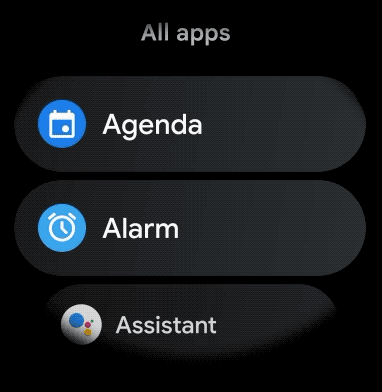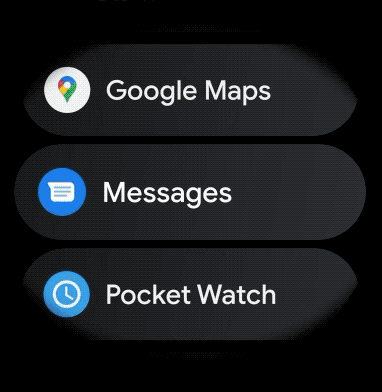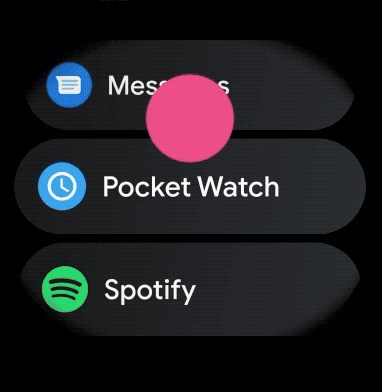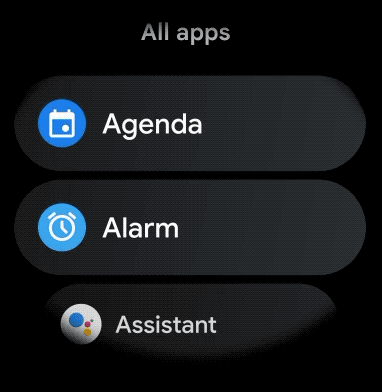
如需为穿戴式应用中的可滚动项目创建曲线布局,请执行以下操作:
-
在相关的 XML 布局中,将
WearableRecyclerView用作主容器。 -
将
setEdgeItemsCenteringEnabled(boolean)方法设置为true。这会使列表中的第一个项目和最后一个项目在屏幕中垂直居中。 -
使用
WearableRecyclerView.setLayoutManager()方法设置项目在屏幕上的布局。
Kotlin
wearableRecyclerView.apply { // To align the edge children (first and last) with the center of the screen. isEdgeItemsCenteringEnabled = true ... layoutManager = WearableLinearLayoutManager(this@MainActivity) }
Java
// To align the edge children (first and last) with the center of the screen. wearableRecyclerView.setEdgeItemsCenteringEnabled(true); ... wearableRecyclerView.setLayoutManager( new WearableLinearLayoutManager(this));
如果您的应用在自定义滚动时的子视图外观方面有特定要求(例如,在项目从中心向外滚动时缩放图标和文本),请扩展
WearableLinearLayoutManager.LayoutCallback 类并替换
onLayoutFinished 方法。
以下代码段举例说明了如何通过扩展 WearableLinearLayoutManager.LayoutCallback 类来自定义随着项目向离中心越来越远的位置滚动而进行缩放:
Kotlin
/** How much icons should scale, at most. */ private const val MAX_ICON_PROGRESS = 0.65f class CustomScrollingLayoutCallback : WearableLinearLayoutManager.LayoutCallback() { private var progressToCenter: Float = 0f override fun onLayoutFinished(child: View, parent: RecyclerView) { child.apply { // Figure out % progress from top to bottom. val centerOffset = height.toFloat() / 2.0f / parent.height.toFloat() val yRelativeToCenterOffset = y / parent.height + centerOffset // Normalize for center. progressToCenter = Math.abs(0.5f - yRelativeToCenterOffset) // Adjust to the maximum scale. progressToCenter = Math.min(progressToCenter, MAX_ICON_PROGRESS) scaleX = 1 - progressToCenter scaleY = 1 - progressToCenter } } }
Java
public class CustomScrollingLayoutCallback extends WearableLinearLayoutManager.LayoutCallback { /** How much icons should scale, at most. */ private static final float MAX_ICON_PROGRESS = 0.65f; private float progressToCenter; @Override public void onLayoutFinished(View child, RecyclerView parent) { // Figure out % progress from top to bottom. float centerOffset = ((float) child.getHeight() / 2.0f) / (float) parent.getHeight(); float yRelativeToCenterOffset = (child.getY() / parent.getHeight()) + centerOffset; // Normalize for center. progressToCenter = Math.abs(0.5f - yRelativeToCenterOffset); // Adjust to the maximum scale. progressToCenter = Math.min(progressToCenter, MAX_ICON_PROGRESS); child.setScaleX(1 - progressToCenter); child.setScaleY(1 - progressToCenter); } }
Kotlin
wearableRecyclerView.layoutManager = WearableLinearLayoutManager(this, CustomScrollingLayoutCallback())
Java
CustomScrollingLayoutCallback customScrollingLayoutCallback = new CustomScrollingLayoutCallback(); wearableRecyclerView.setLayoutManager( new WearableLinearLayoutManager(this, customScrollingLayoutCallback));

