Lorsque vous devez afficher des images statiques dans votre application, vous pouvez utiliser la classe Drawable et ses sous-classes pour dessiner des formes et
images. Une Drawable est une abstraction générale
quelque chose qui peut être dessiné. Les différentes sous-classes aident à définir une image
et vous pouvez les étendre
pour définir vos propres objets drawables
qui se comportent de manière unique.
Il existe deux façons de définir et d'instancier un Drawable, en plus d'utiliser les constructeurs de classe:
- Gonfler une ressource d'image (fichier bitmap) enregistrée dans votre projet
- Gonfler une ressource XML qui définit les propriétés du drawable
Remarque: Vous pouvez préférer utiliser un drawable vectoriel, qui définit une image avec un ensemble de des points, des lignes et des courbes, ainsi que les informations de couleur associées. Cela permet d'utiliser des drawables vectoriels s'adaptent à différentes tailles sans perte de qualité. Pour en savoir plus, consultez la section Données vectorielles Présentation des drawables
Créer des drawables à partir d'images de ressources
Vous pouvez ajouter des éléments graphiques à votre application en référençant un fichier image à partir de votre les ressources du projet. Les types de fichiers acceptés sont les suivants : PNG (recommandé), JPG (acceptable), et GIF (déconseillé). Icônes, logos et autres éléments graphiques de l'application, tels que ceux utilisés sont adaptés à cette technique.
Pour utiliser une ressource image, ajoutez votre fichier à res/drawable/
de votre projet. Une fois dans votre projet, vous pouvez référencer l'image
de votre code ou de votre mise en page XML. Dans tous les cas, on parle d'utilisation
l'ID de ressource, qui correspond au nom du fichier sans l'extension du type de fichier. Pour
exemple, faites référence à my_image.png en tant que my_image.
Remarque:Les ressources d'image placées dans le
Le répertoire res/drawable/ peut être automatiquement optimisé avec
compression d'image sans perte par l'outil aapt pendant la compilation
processus. Par exemple, un fichier PNG en couleurs réelles qui ne nécessite pas plus de 256 couleurs
peut être converti en fichier PNG 8 bits avec une palette de couleurs. Il en résulte une image
de qualité égale, mais qui nécessite moins de mémoire. Par conséquent, les binaires d'image
placé dans ce répertoire peut
changer au moment de la compilation. Si vous prévoyez de lire un
l'image sous forme de flux de bits afin de la convertir en bitmap, placez vos images dans la
le dossier res/raw/, où l'outil aapt ne
les modifier.
L'extrait de code suivant montre comment créer un ImageView qui utilise
une image créée à partir d'une ressource drawable et l'ajoute à la mise en page:
Kotlin
private lateinit var constraintLayout: ConstraintLayout override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Instantiate an ImageView and define its properties val i = ImageView(this).apply { setImageResource(R.drawable.my_image) contentDescription = resources.getString(R.string.my_image_desc) // set the ImageView bounds to match the Drawable's dimensions adjustViewBounds = true layoutParams = ViewGroup.LayoutParams( ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) } // Create a ConstraintLayout in which to add the ImageView constraintLayout = ConstraintLayout(this).apply { // Add the ImageView to the layout. addView(i) } // Set the layout as the content view. setContentView(constraintLayout) }
Java
ConstraintLayout constraintLayout; protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Create a ConstraintLayout in which to add the ImageView constraintLayout = new ConstraintLayout(this); // Instantiate an ImageView and define its properties ImageView i = new ImageView(this); i.setImageResource(R.drawable.my_image); i.setContentDescription(getResources().getString(R.string.my_image_desc)); // set the ImageView bounds to match the Drawable's dimensions i.setAdjustViewBounds(true); i.setLayoutParams(new ViewGroup.LayoutParams( ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT)); // Add the ImageView to the layout and set the layout as the content view. constraintLayout.addView(i); setContentView(constraintLayout); }
Dans d'autres cas, vous pouvez gérer votre ressource image en tant qu'objet Drawable, comme illustré ci-dessous.
Exemple:
Kotlin
val myImage: Drawable = ResourcesCompat.getDrawable(context.resources, R.drawable.my_image, null)
Java
Resources res = context.getResources(); Drawable myImage = ResourcesCompat.getDrawable(res, R.drawable.my_image, null);
Avertissement:Chaque ressource unique de votre projet
vous ne pouvez conserver qu'un seul état, quel que soit le nombre d'objets différents
instancier pour lui. Par exemple, si vous instanciez deux objets Drawable à partir de la même ressource image et
modifier une propriété (par exemple, la valeur alpha) d'un objet, cela affecte également
l'autre. Lorsqu'il s'agit de plusieurs instances d'une ressource image,
de transformation directe de l'objet Drawable, vous devez effectuer une
préadolescent
Animation.
L'extrait de code XML ci-dessous montre comment ajouter une ressource drawable à un élément ImageView dans la mise en page XML:
<ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:src="@drawable/my_image" android:contentDescription="@string/my_image_desc" />
Pour en savoir plus sur l'utilisation des ressources d'un projet, consultez Ressources et composants.
Remarque:Lorsque vous utilisez des ressources image comme source de vos drawables, vérifiez que la taille des images est adaptée à différentes densités de pixels. Si le Les images ne sont pas correctes. Elles seront ajustées pour s'adapter, ce qui peut entraîner des artefacts dans vos drawables. Pour en savoir plus, consultez l'article Compatibilité avec différents en pixels.
Créer des drawables à partir de ressources XML
Si une Drawable
que vous souhaitez créer, qui ne dépend pas initialement de variables définies par vos
du code ou une interaction de l'utilisateur, définir Drawable en XML est une bonne option. Régulière
si vous vous attendez à ce que les propriétés de votre Drawable changent lors de l'interaction de l'utilisateur
avec votre application, vous devez envisager de définir l'objet en XML, car vous pouvez modifier les propriétés après
l'objet a été instancié.
Après avoir défini votre Drawable en XML, enregistrez le fichier dans le
res/drawable/ de votre projet. L'exemple suivant montre le fichier XML
définit une
TransitionDrawable
ressource, qui hérite de Drawable:
<!-- res/drawable/expand_collapse.xml --> <transition xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <item android:drawable="@drawable/image_expand"/> <item android:drawable="@drawable/image_collapse"/> </transition>
Ensuite, récupérez et instanciez l'objet en appelant
Resources#getDrawable()
et en transmettant l'ID de ressource de votre fichier XML. N'importe quelle valeur
Sous-classe Drawable
compatible avec la méthode inflate() peuvent être définis en XML et instanciés
par votre application.
Chaque classe drawable compatible avec le gonflement XML utilise des attributs XML spécifiques
permettant de définir les propriétés des objets. Le code suivant instancie
TransitionDrawable
et le définit comme le contenu
Objet ImageView:
Kotlin
val transition= ResourcesCompat.getDrawable( context.resources, R.drawable.expand_collapse, null ) as TransitionDrawable val image: ImageView = findViewById(R.id.toggle_image) image.setImageDrawable(transition) // Description of the initial state that the drawable represents. image.contentDescription = resources.getString(R.string.collapsed) // Then you can call the TransitionDrawable object's methods. transition.startTransition(1000) // After the transition is complete, change the image's content description // to reflect the new state.
Java
Resources res = context.getResources(); TransitionDrawable transition = (TransitionDrawable) ResourcesCompat.getDrawable(res, R.drawable.expand_collapse, null); ImageView image = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.toggle_image); image.setImageDrawable(transition); // Description of the initial state that the drawable represents. image.setContentDescription(getResources().getString(R.string.collapsed)); // Then you can call the TransitionDrawable object's methods. transition.startTransition(1000); // After the transition is complete, change the image's content description // to reflect the new state.
Pour en savoir plus sur les attributs XML acceptés, reportez-vous aux classes comme indiqué ci-dessus.
Drawables géométriques
Un objet ShapeDrawable peut être une bonne option
pour dessiner de façon dynamique
un graphique en deux dimensions. Vous pouvez
dessiner des formes primitives par programmation sur un objet ShapeDrawable ;
et appliquer les styles
dont votre application a besoin.
ShapeDrawable est une sous-classe de Drawable. Pour cette raison, vous pouvez utiliser un
ShapeDrawable partout où un Drawable est attendu. Pour
Par exemple, vous pouvez utiliser un objet ShapeDrawable pour définir l'arrière-plan
d'une vue en la transmettant à la méthode setBackgroundDrawable() de la vue. Vous pouvez également dessiner votre forme
votre propre vue personnalisée et de l'ajouter à une mise en page de votre application.
Comme ShapeDrawable possède sa propre méthode draw(), vous pouvez créer un
sous-classe de View qui dessine ShapeDrawable
lors de l'événement onDraw(), comme illustré dans
l'exemple de code suivant:
Kotlin
class CustomDrawableView(context: Context) : View(context) { private val drawable: ShapeDrawable = run { val x = 10 val y = 10 val width = 300 val height = 50 contentDescription = context.resources.getString(R.string.my_view_desc) ShapeDrawable(OvalShape()).apply { // If the color isn't set, the shape uses black as the default. paint.color = 0xff74AC23.toInt() // If the bounds aren't set, the shape can't be drawn. setBounds(x, y, x + width, y + height) } } override fun onDraw(canvas: Canvas) { drawable.draw(canvas) } }
Java
public class CustomDrawableView extends View { private ShapeDrawable drawable; public CustomDrawableView(Context context) { super(context); int x = 10; int y = 10; int width = 300; int height = 50; setContentDescription(context.getResources().getString( R.string.my_view_desc)); drawable = new ShapeDrawable(new OvalShape()); // If the color isn't set, the shape uses black as the default. drawable.getPaint().setColor(0xff74AC23); // If the bounds aren't set, the shape can't be drawn. drawable.setBounds(x, y, x + width, y + height); } protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { drawable.draw(canvas); } }
Vous pouvez utiliser la classe CustomDrawableView dans l'exemple de code
ci-dessus comme vous le feriez
pour n'importe quelle autre vue personnalisée. Par exemple, vous pouvez
l'ajouter par programmation à une activité dans votre application, comme indiqué ci-dessous
Exemple:
Kotlin
private lateinit var customDrawableView: CustomDrawableView override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) customDrawableView = CustomDrawableView(this) setContentView(customDrawableView) }
Java
CustomDrawableView customDrawableView; protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); customDrawableView = new CustomDrawableView(this); setContentView(customDrawableView); }
Si vous préférez utiliser la vue personnalisée dans la mise en page XML,
La classe CustomDrawableView doit remplacer le constructeur View(Context, AttributeSet), qui est appelé lorsque la classe est
gonflée à partir du XML. L'exemple suivant montre comment déclarer
CustomDrawableView dans la mise en page XML:
<com.example.shapedrawable.CustomDrawableView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
La classe ShapeDrawable, comme beaucoup d'autres
types drawable dans le package android.graphics.drawable, vous permet de
définir les différentes propriétés de l'objet en utilisant des méthodes publiques. Quelques exemples
les propriétés que vous souhaitez ajuster incluent
la transparence alpha, le filtre de couleur,
le tramage, l'opacité et la couleur.
Vous pouvez également définir des formes drawables primitives à l'aide de ressources XML. Pour plus plus d'informations, voir Drawable géométrique dans Types de ressources drawables.
Drawables NinePatch
Un élément graphique NinePatchDrawable correspond à
Image bitmap extensible qui peut servir d'arrière-plan à une vue. Android
redimensionne automatiquement l'image pour l'adapter au contenu de l'affichage. Une
exemple d'utilisation d'une image NinePatch pour l'arrière-plan utilisé par les applications Android standards
Boutons : les boutons doivent être étirés pour accueillir des chaînes de différentes longueurs. A
Le graphique NinePatch est une image PNG standard comportant une bordure supplémentaire d'un pixel.
Il doit être enregistré avec l'extension 9.png dans
res/drawable/ de votre projet.
Utilisez la bordure pour définir les zones étirables et statiques de l'image. Pour indiquer une section étirable, vous devez tracer au moins une largeur d'un pixel d'un pixel. des lignes noires sur la partie gauche et supérieure de la bordure (les autres pixels de bordure doivent être entièrement transparentes ou blanches). Vous pouvez avoir autant de sections étirables comme vous le souhaitez. La taille relative des sections étirables reste la même, donc la section la plus grande reste toujours la plus grande.
Vous pouvez également définir une section drawable facultative de l'image (par exemple,
les lignes de marge intérieure) en traçant une ligne à droite et une ligne en bas. Si un
L'objet View définit l'élément graphique NinePatch comme arrière-plan.
puis spécifie le texte de la vue, il s'étire de sorte que tout le texte
n'occupe que la zone désignée par les lignes de droite et du bas (le cas échéant).
Si les lignes de marge intérieure ne sont pas incluses, Android utilise les lignes de gauche et du haut pour
pour définir cette zone de drawable.
Pour clarifier la différence entre les lignes, les lignes de gauche et du haut définissent quels pixels de l'image peuvent être répliqués afin d'étirer l'image. Les lignes du bas et de droite définissent la zone relative au sein de l'image qui le contenu de la vue peut occuper.
La figure 1 montre un exemple de graphique NinePatch utilisé pour définir un bouton:
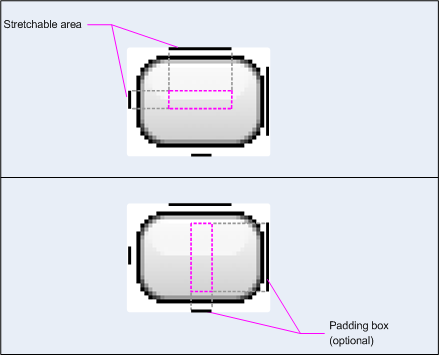
Figure 1:exemple d'image NinePatch qui définit un bouton
Ce graphique NinePatch définit une zone étirable avec les parties gauche et supérieure et la zone drawable avec les lignes du bas et de droite. Dans l'image du haut, les lignes grises en pointillé identifient les zones de l'image répliquées pour étirer l'image. Le rectangle rose dans l'image du bas identifie la région dans laquelle le contenu de l'affichage est autorisé. Si le contenu n’est pas s'adaptent à cette zone, l'image est étirée pour s'adapter à cette zone.
L'outil Draw 9-patch très pratique de créer vos images NinePatch, à l'aide d'un graphique WYSIWYG éditeur. Il génère même des avertissements si la zone que vous avez définie pour le format étirable risque de produire des artefacts de dessin en raison de l'affichage la réplication.
L'exemple de code XML de mise en page suivant montre comment ajouter un graphique NinePatch
à quelques boutons. L'image NinePatch est enregistrée dans
res/drawable/my_button_background.9.png
<Button android:id="@+id/tiny" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentTop="true" android:layout_centerInParent="true" android:text="Tiny" android:textSize="8sp" android:background="@drawable/my_button_background"/> <Button android:id="@+id/big" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentBottom="true" android:layout_centerInParent="true" android:text="Biiiiiiig text!" android:textSize="30sp" android:background="@drawable/my_button_background"/>
Notez que layout_width et layout_height
sont définis sur wrap_content pour que le bouton s'adapte parfaitement.
autour du texte.
La figure 2 montre les deux boutons affichés à partir des images XML et NinePatch. comme indiqué ci-dessus. Notez que la largeur et la hauteur du bouton varient avec le texte, et l'image de fond s'étire pour s'adapter à cet élément.

Figure 2:Boutons affichés au format XML ressource et un graphique NinePatch
Drawables personnalisés
Pour créer des dessins personnalisés, vous pouvez étendre la classe Drawable (ou l'une de ses sous-classes).
La méthode la plus importante à implémenter est draw(Canvas)
car cela fournit l'objet Canvas que vous devez utiliser pour fournir
vos instructions de dessin.
Le code suivant montre une sous-classe simple de Drawable.
qui dessine un cercle:
Kotlin
class MyDrawable : Drawable() { private val redPaint: Paint = Paint().apply { setARGB(255, 255, 0, 0) } override fun draw(canvas: Canvas) { // Get the drawable's bounds val width: Int = bounds.width() val height: Int = bounds.height() val radius: Float = Math.min(width, height).toFloat() / 2f // Draw a red circle in the center canvas.drawCircle((width / 2).toFloat(), (height / 2).toFloat(), radius, redPaint) } override fun setAlpha(alpha: Int) { // This method is required } override fun setColorFilter(colorFilter: ColorFilter?) { // This method is required } override fun getOpacity(): Int = // Must be PixelFormat.UNKNOWN, TRANSLUCENT, TRANSPARENT, or OPAQUE PixelFormat.OPAQUE }
Java
public class MyDrawable extends Drawable { private final Paint redPaint; public MyDrawable() { // Set up color and text size redPaint = new Paint(); redPaint.setARGB(255, 255, 0, 0); } @Override public void draw(Canvas canvas) { // Get the drawable's bounds int width = getBounds().width(); int height = getBounds().height(); float radius = Math.min(width, height) / 2; // Draw a red circle in the center canvas.drawCircle(width/2, height/2, radius, redPaint); } @Override public void setAlpha(int alpha) { // This method is required } @Override public void setColorFilter(ColorFilter colorFilter) { // This method is required } @Override public int getOpacity() { // Must be PixelFormat.UNKNOWN, TRANSLUCENT, TRANSPARENT, or OPAQUE return PixelFormat.OPAQUE; } }
Vous pouvez ensuite ajouter votre drawable où vous le souhaitez, par exemple à une
ImageView, comme indiqué ici:
Kotlin
val myDrawing = MyDrawable() val image: ImageView = findViewById(R.id.imageView) image.setImageDrawable(myDrawing) image.contentDescription = resources.getString(R.string.my_image_desc)
Java
MyDrawable mydrawing = new MyDrawable(); ImageView image = findViewById(R.id.imageView); image.setImageDrawable(mydrawing); image.setContentDescription(getResources().getString(R.string.my_image_desc));
Sur Android 7.0 (niveau d'API 24) ou version ultérieure, vous pouvez également définir des instances de votre drawable personnalisé. avec XML comme suit:
- Utilisation du nom de classe complet comme nom de l'élément XML. Pour cette approche,
La classe drawable doit être une classe publique de premier niveau:
<com.myapp.MyDrawable xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:color="#ffff0000" />
- Utiliser
drawablecomme nom de balise XML et spécifier la classe complète nom de l'attribut de classe. Cette approche peut être utilisée à la fois pour les classes publiques de premier niveau et classes internes statiques publiques:<drawable xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" class="com.myapp.MyTopLevelClass$MyDrawable" android:color="#ffff0000" />
Ajouter une teinte aux drawables
Avec Android 5.0 (niveau d'API 21) ou version ultérieure, vous pouvez colorer les bitmaps et neuf correctifs définis comme
les masques alpha. Vous pouvez les colorer avec des ressources de couleur ou des attributs de thème qui correspondent à des couleurs
(par exemple, ?android:attr/colorPrimary). En général, vous créez ces composants
une seule fois et coloriez-les automatiquement
pour les assortir à votre thème.
Vous pouvez appliquer une teinte à BitmapDrawable, NinePatchDrawable ou VectorDrawable
à l'aide de la méthode setTint(). Vous pouvez
définissez également le mode et la couleur de la teinte dans vos mises en page à l'aide des propriétés android:tint et
Attributs android:tintMode.
Extraire les couleurs proéminentes d'une image
La bibliothèque Android Support inclut la classe Palette, qui vous permet d'extraire les couleurs proéminentes d'une image.
Vous pouvez charger vos drawables en tant que Bitmap et le transmettre à Palette pour accéder à ses couleurs.
Pour en savoir plus, consultez la section Sélectionner des couleurs avec
l'API Palette.

