การสามารถกำหนดรูปร่างที่จะวาดในบริบทของมุมมอง OpenGL ES เป็นขั้นตอนแรก การสร้างกราฟิกระดับไฮเอนด์สำหรับแอปของคุณ การวาดด้วย OpenGL ES อาจยุ่งยากเล็กน้อยโดยไม่มี การที่คุณรู้ข้อมูลเบื้องต้นเกี่ยวกับวิธีที่ OpenGL ES คาดหวังว่าคุณจะกำหนดวัตถุกราฟิก
บทเรียนนี้อธิบายถึงระบบพิกัด OpenGL ES ที่เกี่ยวข้องกับหน้าจออุปกรณ์ Android พื้นฐานในการกำหนดรูปร่าง กำหนดรูปร่างหน้าตา รวมถึงการกำหนดรูปสามเหลี่ยมและสี่เหลี่ยมจัตุรัส
หาความหมายสามเหลี่ยม
OpenGL ES ให้คุณกำหนดวัตถุที่วาดโดยใช้พิกัดในพื้นที่ทรง 3 มิติ ดังนั้น
ก่อนที่จะวาดรูปสามเหลี่ยมได้ คุณต้องกำหนดพิกัดของรูปสามเหลี่ยมดังกล่าวด้วย ใน OpenGL วิธีทดสอบโดยทั่วไป
สิ่งนี้ใช้กำหนดอาร์เรย์เวอร์เท็กซ์ของจำนวนจุดลอยตัวสำหรับพิกัด สำหรับค่าสูงสุด
ให้เขียนพิกัดเหล่านี้ลงใน ByteBuffer ซึ่งส่งผ่านค่า
ไปป์ไลน์กราฟิก OpenGL ES สำหรับการประมวลผล
Kotlin
// number of coordinates per vertex in this array const val COORDS_PER_VERTEX = 3 var triangleCoords = floatArrayOf( // in counterclockwise order: 0.0f, 0.622008459f, 0.0f, // top -0.5f, -0.311004243f, 0.0f, // bottom left 0.5f, -0.311004243f, 0.0f // bottom right ) class Triangle { // Set color with red, green, blue and alpha (opacity) values val color = floatArrayOf(0.63671875f, 0.76953125f, 0.22265625f, 1.0f) private var vertexBuffer: FloatBuffer = // (number of coordinate values * 4 bytes per float) ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(triangleCoords.size * 4).run { // use the device hardware's native byte order order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()) // create a floating point buffer from the ByteBuffer asFloatBuffer().apply { // add the coordinates to the FloatBuffer put(triangleCoords) // set the buffer to read the first coordinate position(0) } } }
Java
public class Triangle { private FloatBuffer vertexBuffer; // number of coordinates per vertex in this array static final int COORDS_PER_VERTEX = 3; static float triangleCoords[] = { // in counterclockwise order: 0.0f, 0.622008459f, 0.0f, // top -0.5f, -0.311004243f, 0.0f, // bottom left 0.5f, -0.311004243f, 0.0f // bottom right }; // Set color with red, green, blue and alpha (opacity) values float color[] = { 0.63671875f, 0.76953125f, 0.22265625f, 1.0f }; public Triangle() { // initialize vertex byte buffer for shape coordinates ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect( // (number of coordinate values * 4 bytes per float) triangleCoords.length * 4); // use the device hardware's native byte order bb.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()); // create a floating point buffer from the ByteBuffer vertexBuffer = bb.asFloatBuffer(); // add the coordinates to the FloatBuffer vertexBuffer.put(triangleCoords); // set the buffer to read the first coordinate vertexBuffer.position(0); } }
โดยค่าเริ่มต้น OpenGL ES จะถือว่าระบบพิกัดที่ [0,0,0] (X,Y,Z) ระบุจุดศูนย์กลางของ
เฟรม GLSurfaceView
[1,1,0] คือมุมขวาบนของเฟรม และ
[-1,-1,0] คือมุมซ้ายล่างของเฟรม สำหรับภาพประกอบของระบบพิกัดนี้ โปรดดู
นักพัฒนาแอป OpenGL ES
โปรดทราบว่าพิกัดของรูปร่างนี้จะกำหนดตามลำดับทวนเข็มนาฬิกา ภาพวาด ลำดับนั้นสำคัญ เนื่องจากจะกำหนดว่าด้านใดเป็นด้านหน้าของรูปร่าง ซึ่งคุณมัก ต้องการให้วาดและหน้าด้านหลัง ซึ่งคุณสามารถเลือกที่จะไม่วาดโดยใช้คำสั่ง OpenGL ES ของใบหน้า ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับใบหน้าและการเลือกได้ที่ คู่มือนักพัฒนาซอฟต์แวร์ OpenGL ES
นิยามกำลังสอง
ใน OpenGL การกำหนดรูปสามเหลี่ยมนั้นค่อนข้างง่ายมาก แต่ถ้าอยากได้เพิ่มอีกเล็กน้อย ที่ซับซ้อนหรือไม่ สมมติว่าเป็นรูปสี่เหลี่ยม คุณสามารถทำได้หลายวิธี แต่เส้นทางโดยทั่วไปในการวาดภาพ รูปร่างใน OpenGL ES คือใช้สามเหลี่ยม 2 รูปวาดด้วยกัน ดังนี้
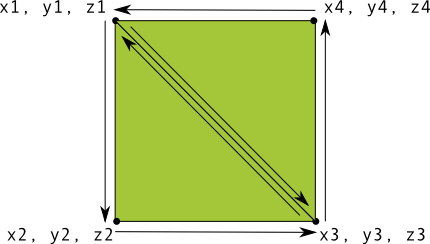
รูปที่ 1 วาดสี่เหลี่ยมจัตุรัสโดยใช้สามเหลี่ยม 2 รูป
คุณควรกำหนดจุดยอดมุมในลำดับทวนเข็มนาฬิกาสำหรับสามเหลี่ยมทั้งสองที่
แทนรูปร่างนี้ และใส่ค่าในรูปแบบ ByteBuffer เพื่อหลีกเลี่ยง
กำหนดพิกัด 2 พิกัดที่แต่ละสามเหลี่ยมใช้ร่วมกัน 2 ครั้ง ให้ใช้รายการวาดเพื่อบอก
วิธีวาดจุดยอดเหล่านี้ของกราฟิกไปป์ไลน์ของ OpenGL ES นี่คือโค้ดสำหรับรูปร่างนี้
Kotlin
// number of coordinates per vertex in this array const val COORDS_PER_VERTEX = 3 var squareCoords = floatArrayOf( -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, // top left -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // bottom left 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // bottom right 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f // top right ) class Square2 { private val drawOrder = shortArrayOf(0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 3) // order to draw vertices // initialize vertex byte buffer for shape coordinates private val vertexBuffer: FloatBuffer = // (# of coordinate values * 4 bytes per float) ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(squareCoords.size * 4).run { order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()) asFloatBuffer().apply { put(squareCoords) position(0) } } // initialize byte buffer for the draw list private val drawListBuffer: ShortBuffer = // (# of coordinate values * 2 bytes per short) ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(drawOrder.size * 2).run { order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()) asShortBuffer().apply { put(drawOrder) position(0) } } }
Java
public class Square { private FloatBuffer vertexBuffer; private ShortBuffer drawListBuffer; // number of coordinates per vertex in this array static final int COORDS_PER_VERTEX = 3; static float squareCoords[] = { -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, // top left -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // bottom left 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // bottom right 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f }; // top right private short drawOrder[] = { 0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 3 }; // order to draw vertices public Square() { // initialize vertex byte buffer for shape coordinates ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect( // (# of coordinate values * 4 bytes per float) squareCoords.length * 4); bb.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()); vertexBuffer = bb.asFloatBuffer(); vertexBuffer.put(squareCoords); vertexBuffer.position(0); // initialize byte buffer for the draw list ByteBuffer dlb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect( // (# of coordinate values * 2 bytes per short) drawOrder.length * 2); dlb.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()); drawListBuffer = dlb.asShortBuffer(); drawListBuffer.put(drawOrder); drawListBuffer.position(0); } }
ตัวอย่างนี้ช่วยให้คุณเห็นถึงสิ่งที่ต้องใช้ในการสร้างรูปร่างที่ซับซ้อนมากขึ้นด้วย OpenGL ใน โดยใช้คอลเล็กชันสามเหลี่ยมเพื่อวาดวัตถุ ในบทเรียนถัดไป คุณจะได้เรียนรู้วิธีวาด รูปทรงเหล่านี้บนหน้าจอ
