A capacidade de definir as formas a serem desenhadas no contexto de uma visualização do OpenGL ES é o primeiro passo para criar gráficos sofisticados para seu aplicativo. Desenhar com o OpenGL ES pode ser um pouco complicado sem saber algumas coisas básicas sobre como o OpenGL ES espera que você defina objetos gráficos.
Esta lição explica o sistema de coordenadas do OpenGL ES em relação a uma tela de dispositivo Android, a classe fundamentos da definição de uma forma, formas de faces, bem como definição de triângulos e quadrados.
Definir um triângulo
O OpenGL ES permite que você defina objetos desenhados usando coordenadas no espaço tridimensional. Então,
antes de desenhar um triângulo, é preciso definir as coordenadas dele. No OpenGL, a maneira comum de fazer
o objetivo é definir uma matriz de vértices de números de ponto flutuante para as coordenadas. Para o máximo
eficiência, grave essas coordenadas em um ByteBuffer, que é transmitido à
Pipeline de gráficos do OpenGL ES para processamento.
Kotlin
// number of coordinates per vertex in this array const val COORDS_PER_VERTEX = 3 var triangleCoords = floatArrayOf( // in counterclockwise order: 0.0f, 0.622008459f, 0.0f, // top -0.5f, -0.311004243f, 0.0f, // bottom left 0.5f, -0.311004243f, 0.0f // bottom right ) class Triangle { // Set color with red, green, blue and alpha (opacity) values val color = floatArrayOf(0.63671875f, 0.76953125f, 0.22265625f, 1.0f) private var vertexBuffer: FloatBuffer = // (number of coordinate values * 4 bytes per float) ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(triangleCoords.size * 4).run { // use the device hardware's native byte order order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()) // create a floating point buffer from the ByteBuffer asFloatBuffer().apply { // add the coordinates to the FloatBuffer put(triangleCoords) // set the buffer to read the first coordinate position(0) } } }
Java
public class Triangle { private FloatBuffer vertexBuffer; // number of coordinates per vertex in this array static final int COORDS_PER_VERTEX = 3; static float triangleCoords[] = { // in counterclockwise order: 0.0f, 0.622008459f, 0.0f, // top -0.5f, -0.311004243f, 0.0f, // bottom left 0.5f, -0.311004243f, 0.0f // bottom right }; // Set color with red, green, blue and alpha (opacity) values float color[] = { 0.63671875f, 0.76953125f, 0.22265625f, 1.0f }; public Triangle() { // initialize vertex byte buffer for shape coordinates ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect( // (number of coordinate values * 4 bytes per float) triangleCoords.length * 4); // use the device hardware's native byte order bb.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()); // create a floating point buffer from the ByteBuffer vertexBuffer = bb.asFloatBuffer(); // add the coordinates to the FloatBuffer vertexBuffer.put(triangleCoords); // set the buffer to read the first coordinate vertexBuffer.position(0); } }
Por padrão, o OpenGL ES pressupõe um sistema de coordenadas em que [0,0,0] (X,Y,Z) especifica o centro do
o frame GLSurfaceView,
[1,1,0] é o canto superior direito do frame e
[-1,-1,0] é o canto inferior esquerdo do frame. Para ver uma ilustração desse sistema de coordenadas, consulte a
Desenvolvedor do OpenGL ES
guia.
As coordenadas dessa forma são definidas em sentido anti-horário. O desenho A ordem é importante porque define qual lado é a face frontal da forma, que você normalmente quer desenhar, e a face traseira, que você pode optar por não desenhar usando a seleção do OpenGL ES característica do rosto. Para mais informações sobre rostos e seleções, consulte Guia do desenvolvedor do OpenGL ES.
Definir um quadrado
Definir triângulos é muito fácil no OpenGL, mas e se você quiser um pouco mais complexo? Por exemplo, um quadrado? Há várias maneiras de fazer isso, mas um caminho comum para desenhar um forma no OpenGL ES é usar dois triângulos desenhados juntos:
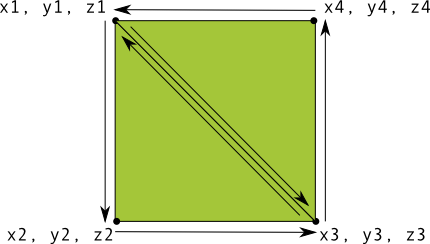
Figura 1. Desenhar um quadrado usando dois triângulos.
Novamente, você deve definir os vértices em sentido anti-horário para os dois triângulos que
representam essa forma e colocam os valores em uma ByteBuffer. Para evitar
definindo as duas coordenadas compartilhadas por cada triângulo duas vezes, use uma lista de desenhos para informar ao
pipeline de gráficos do OpenGL ES sobre como desenhar esses vértices. Veja o código dessa forma:
Kotlin
// number of coordinates per vertex in this array const val COORDS_PER_VERTEX = 3 var squareCoords = floatArrayOf( -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, // top left -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // bottom left 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // bottom right 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f // top right ) class Square2 { private val drawOrder = shortArrayOf(0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 3) // order to draw vertices // initialize vertex byte buffer for shape coordinates private val vertexBuffer: FloatBuffer = // (# of coordinate values * 4 bytes per float) ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(squareCoords.size * 4).run { order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()) asFloatBuffer().apply { put(squareCoords) position(0) } } // initialize byte buffer for the draw list private val drawListBuffer: ShortBuffer = // (# of coordinate values * 2 bytes per short) ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(drawOrder.size * 2).run { order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()) asShortBuffer().apply { put(drawOrder) position(0) } } }
Java
public class Square { private FloatBuffer vertexBuffer; private ShortBuffer drawListBuffer; // number of coordinates per vertex in this array static final int COORDS_PER_VERTEX = 3; static float squareCoords[] = { -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, // top left -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // bottom left 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // bottom right 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f }; // top right private short drawOrder[] = { 0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 3 }; // order to draw vertices public Square() { // initialize vertex byte buffer for shape coordinates ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect( // (# of coordinate values * 4 bytes per float) squareCoords.length * 4); bb.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()); vertexBuffer = bb.asFloatBuffer(); vertexBuffer.put(squareCoords); vertexBuffer.position(0); // initialize byte buffer for the draw list ByteBuffer dlb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect( // (# of coordinate values * 2 bytes per short) drawOrder.length * 2); dlb.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()); drawListBuffer = dlb.asShortBuffer(); drawListBuffer.put(drawOrder); drawListBuffer.position(0); } }
Esse exemplo mostra o que é preciso para criar formas mais complexas com o OpenGL. Em em geral, você usa coleções de triângulos para desenhar objetos. Na próxima aula, você vai aprender a desenhar essas formas na tela.
