窗口大小类别是一组主观的视口划分点,有助于您设计、开发和测试响应式/自适应布局。这些划分点可平衡布局简单性与灵活性,以便针对独特情形优化您的应用。
窗口大小类别将应用中可用的显示区域分类为:紧凑、中等、展开、大或超大。可用宽度和高度是单独分类的,因此在任何时间点,应用都有两个窗口大小类别:宽度窗口大小类别和高度窗口大小类别。但由于垂直滚动的普遍存在,可用宽度通常比可用高度更重要;因此,宽度窗口大小类别很可能与应用的界面更相关。
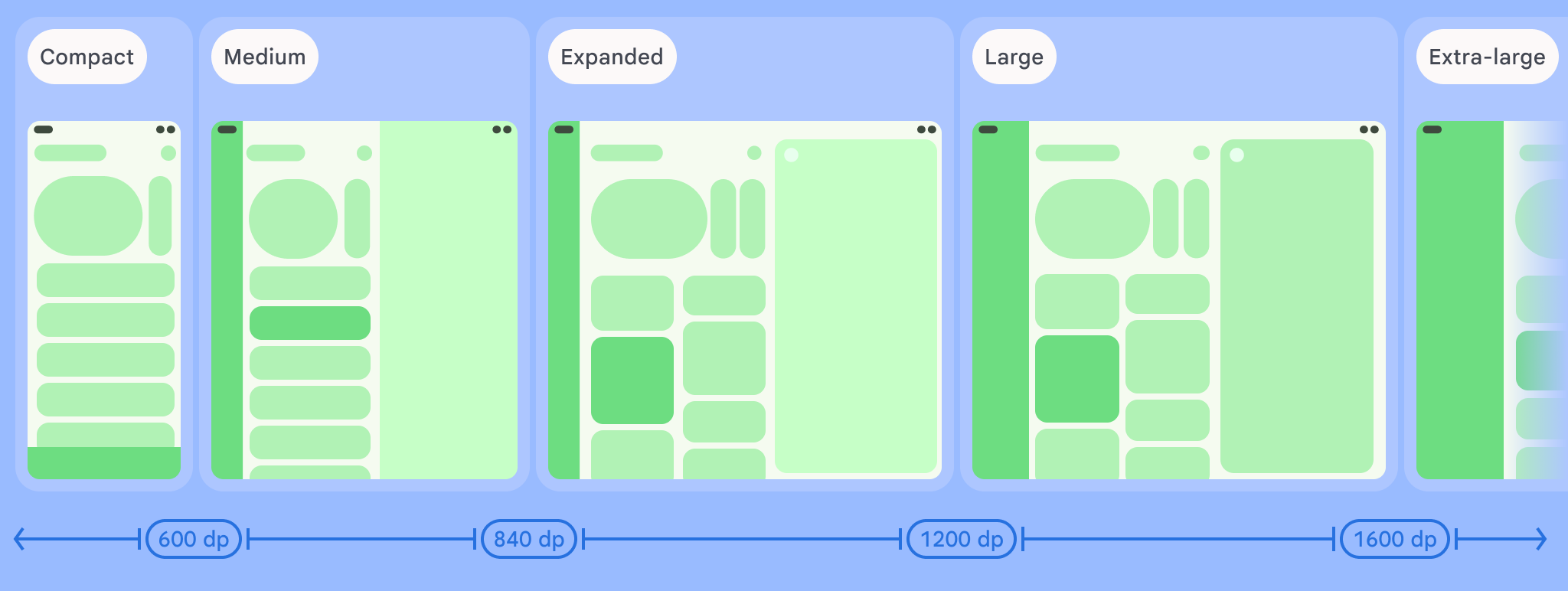
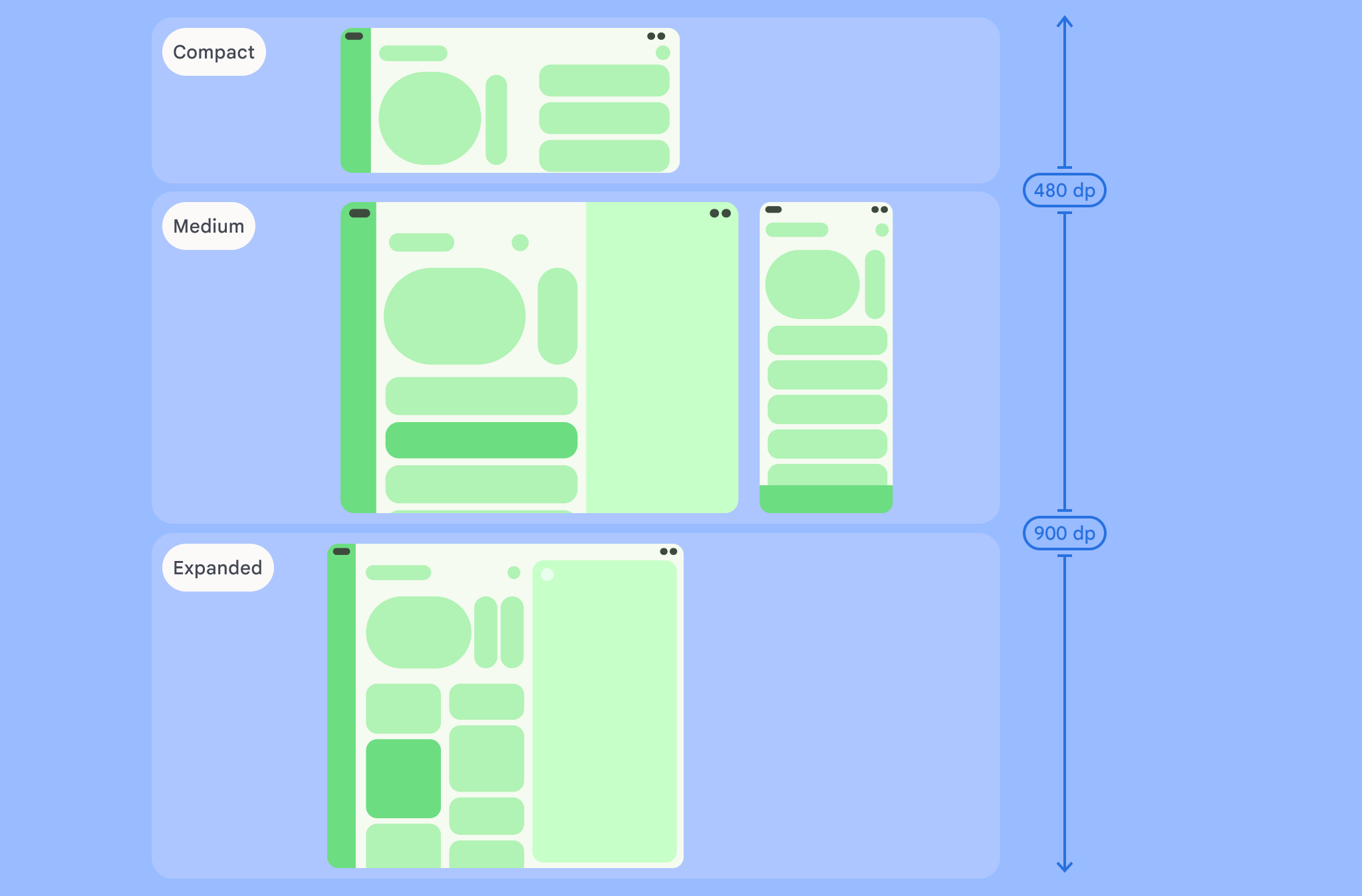
如图所示,这些划分点让您可以继续从设备和配置的角度考虑布局。每个大小类别划分点代表了典型设备场景的大多数情况,当您考虑基于划分点的布局设计时,这可能是一个有用的参考框架。
| 大小类别 | 划分点 | 设备表示 |
|---|---|---|
| 较小的宽度 | 宽度 < 600dp | 99.96% 的手机处于竖屏模式 |
| 中等宽度 | 600dp ≤ 宽度 < 840dp | 93.73% 的平板电脑处于竖屏模式,
大多数展开的大型内部显示屏处于竖屏模式 |
| 较大宽度 | 840dp ≤ 宽度 < 1200dp | 97.22% 的平板电脑处于横屏模式,
大多数展开的大型内部显示屏处于横屏模式时,至少具有展开的宽度 |
| 较宽宽度 | 1200dp ≤ 宽度 < 1600dp | 大型平板电脑显示屏 |
| 超大宽度 | 宽度 ≥ 1600dp | 桌面展示广告 |
| 较小的高度 | 高度 < 480dp | 99.78% 的手机处于横屏模式 |
| 中等高度 | 480dp ≤ 高度 < 900dp | 96.56% 的平板电脑处于横屏模式,
97.59% 的手机处于竖屏模式 |
| 展开高度 | 高度 ≥ 900dp | 94.25% 的平板电脑处于竖屏模式 |
虽然使用实体设备直观地查看大小类别很有用,但窗口大小类别不是由设备屏幕的尺寸明确决定的。窗口大小类别不适用于 isTablet‑type 逻辑,而是由应用可用的窗口大小决定(无论运行应用的设备是什么类型);这有两个重大影响:
实体设备不能保证特定的窗口大小类别。应用可用的屏幕空间可能会与设备的屏幕尺寸不同,这有很多原因。在移动设备上,分屏模式可以在两个应用之间分割屏幕。在 ChromeOS 中,Android 应用可以呈现在可任意调整大小的桌面型窗口中。可折叠设备可以有两个大小不同的屏幕,分别可通过折叠或展开设备使用。
窗口大小类别在应用的整个生命周期内可能会发生变化。当应用处于运行状态时,设备更改屏幕方向、进行多任务处理和折叠/展开可能会改变可用的屏幕空间量。因此,窗口大小类别是动态的,应用的界面应相应地调整。
窗口大小类别与 Material Design 布局指南中的紧凑型、中等和扩展型划分点一一对应。此外,还添加了大型和超大型断点,以便更好地定位桌面设备和外接显示屏。
使用窗口大小类别来做出高级应用布局决策,如决定是否使用特定的规范布局以利用额外的屏幕空间。
您可以计算当前的
WindowSizeClass
使用
WindowSizeClass#compute()
Jetpack 提供的函数,
WindowManager 库。以下示例
显示了如何计算窗口大小类别,并在
窗口大小类别变更:
Kotlin
class MainActivity : Activity() { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // ... // Replace with a known container that you can safely add a // view to where the view won't affect the layout and the view // won't be replaced. val container: ViewGroup = binding.container // Add a utility view to the container to hook into // View.onConfigurationChanged(). This is required for all // activities, even those that don't handle configuration // changes. You can't use Activity.onConfigurationChanged(), // since there are situations where that won't be called when // the configuration changes. View.onConfigurationChanged() is // called in those scenarios. container.addView(object : View(this) { override fun onConfigurationChanged(newConfig: Configuration?) { super.onConfigurationChanged(newConfig) computeWindowSizeClasses() } }) computeWindowSizeClasses() } private fun computeWindowSizeClasses() { val metrics = WindowMetricsCalculator.getOrCreate().computeCurrentWindowMetrics(this) val width = metrics.bounds.width() val height = metrics.bounds.height() val density = resources.displayMetrics.density val windowSizeClass = WindowSizeClass.compute(width/density, height/density) // COMPACT, MEDIUM, or EXPANDED val widthWindowSizeClass = windowSizeClass.windowWidthSizeClass // COMPACT, MEDIUM, or EXPANDED val heightWindowSizeClass = windowSizeClass.windowHeightSizeClass // Use widthWindowSizeClass and heightWindowSizeClass. } }
Java
public class MainActivity extends Activity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // ... // Replace with a known container that you can safely add a // view to where the view won't affect the layout and the view // won't be replaced. ViewGroup container = binding.container; // Add a utility view to the container to hook into // View.onConfigurationChanged(). This is required for all // activities, even those that don't handle configuration // changes. You can't use Activity.onConfigurationChanged(), // since there are situations where that won't be called when // the configuration changes. View.onConfigurationChanged() is // called in those scenarios. container.addView(new View(this) { @Override protected void onConfigurationChanged(Configuration newConfig) { super.onConfigurationChanged(newConfig); computeWindowSizeClasses(); } }); computeWindowSizeClasses(); } private void computeWindowSizeClasses() { WindowMetrics metrics = WindowMetricsCalculator.getOrCreate() .computeCurrentWindowMetrics(this); int width = metrics.getBounds().width(); int height = metrics.getBounds().height(); float density = getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density; WindowSizeClass windowSizeClass = WindowSizeClass.compute(width/density, height/density); // COMPACT, MEDIUM, or EXPANDED WindowWidthSizeClass widthWindowSizeClass = windowSizeClass.getWindowWidthSizeClass(); // COMPACT, MEDIUM, or EXPANDED WindowHeightSizeClass heightWindowSizeClass = windowSizeClass.getWindowHeightSizeClass(); // Use widthWindowSizeClass and heightWindowSizeClass. } }
测试窗口大小类别
当您做出布局更改时,请在各种窗口大小下测试布局行为,尤其是在紧凑型、中等和展开式划分点宽度下。
如果您的某个现有布局适合紧凑型屏幕,请首先针对展开宽度大小类别优化布局,因为这样可以为额外的内容或界面变化提供最大的空间。然后,决定什么布局对中等宽度类别有意义,并考虑添加专用布局。
后续步骤
如需详细了解如何使用窗口大小类别创建响应式/自适应布局,请参阅以下内容:
对于基于 Compose 的布局:支持不同的屏幕尺寸
对于基于视图的布局:使用 View 实现响应式/自适应设计
如需详细了解如何让应用在所有设备上以及所有屏幕尺寸下都表现出色,请参阅:

