Android 平台提供了一个拼写检查框架框架, 在您的应用中实施和访问拼写检查功能。该框架是 文本服务 API。
要在应用中使用该框架,您需要创建一个 Android 服务, 生成一个拼写检查工具 session 对象。根据您提供的文字, 会话对象会返回相应拼写 检查工具。
拼写检查工具生命周期
下图显示了拼写检查工具服务的生命周期:
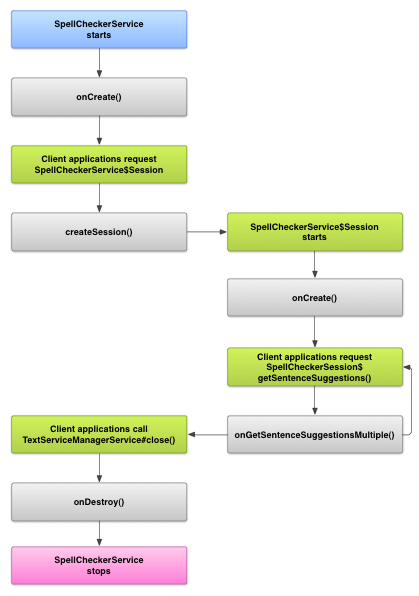
如需启动拼写检查,您的应用会开始实现拼写检查 Checker 服务。应用中的客户端,例如 activity 或单个界面 向该服务请求拼写检查工具会话,然后使用该会话 获取文字建议。当客户端终止其操作时,它会关闭 拼写检查工具会话。如有必要,您的应用可以关闭 Checker 服务。
实现拼写检查工具服务
如需在应用中使用拼写检查工具框架,请添加拼写检查工具服务 组件。您还可以添加 可选 activity。添加 XML 元数据文件 ,并将相应的元素添加到 您的清单文件
拼写检查工具类
使用以下类定义服务和会话对象:
-
- 以下类的子类
SpellCheckerServiceSpellCheckerService实现了Service类和拼写检查工具框架接口。在您的子类中, 实现以下方法: <ph type="x-smartling-placeholder">- </ph>
createSession()- 一个工厂方法,用于返回
SpellCheckerService.Session对象 需要检查拼写。
- 以下类的子类
-
- 通过
SpellCheckerService.Session- 拼写检查服务提供给客户端,以便 它们会将文本传递给拼写检查工具并获得建议。在此 类,请实现以下方法: <ph type="x-smartling-placeholder">
- </ph>
onCreate()- 系统为响应
createSession()。在此方法中,您可以初始化SpellCheckerService.Session对象 当前语言区域和其他详细信息。 onGetSentenceSuggestionsMultiple()- 执行实际的拼写检查。此方法会返回
SentenceSuggestionsInfo包含对传递给它的句子的建议。
您还可以选择实现
onCancel(), 用于处理取消拼写检查的请求;onGetSuggestions(), 用于处理字词建议请求;或onGetSuggestionsMultiple(), 用于处理批量字词建议请求。 。
- 通过
拼写检查工具清单和元数据
除代码之外,还应提供相应的清单文件和元数据 文件。
清单文件定义了 控制设置,如以下示例所示:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.android.samplespellcheckerservice" > <application android:label="@string/app_name" > <service android:label="@string/app_name" android:name=".SampleSpellCheckerService" android:permission="android.permission.BIND_TEXT_SERVICE" > <intent-filter > <action android:name="android.service.textservice.SpellCheckerService" /> </intent-filter> <meta-data android:name="android.view.textservice.scs" android:resource="@xml/spellchecker" /> </service> <activity android:label="@string/sample_settings" android:name="SpellCheckerSettingsActivity" > <intent-filter > <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest>
想要使用此服务的组件必须请求相应权限
BIND_TEXT_SERVICE
以确保只有系统绑定到该服务服务的定义
还指定了 spellchecker.xml 元数据文件,即
具体说明。
元数据文件 spellchecker.xml 包含以下内容
XML:
<spell-checker xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:label="@string/spellchecker_name" android:settingsActivity="com.example.SpellCheckerSettingsActivity"> <subtype android:label="@string/subtype_generic" android:subtypeLocale="en” /> <subtype android:label="@string/subtype_generic" android:subtypeLocale="fr” /> </spell-checker>
元数据指定了拼写检查工具用于控制的 activity 设置。还定义了拼写检查工具的子类型。在这种情况下, 子类型定义了拼写检查工具可以处理的语言区域。
从客户端访问拼写检查工具服务
使用
TextView和
EditText
视图会自动从拼写检查中受益,因为 TextView
系统会自动使用拼写检查工具:
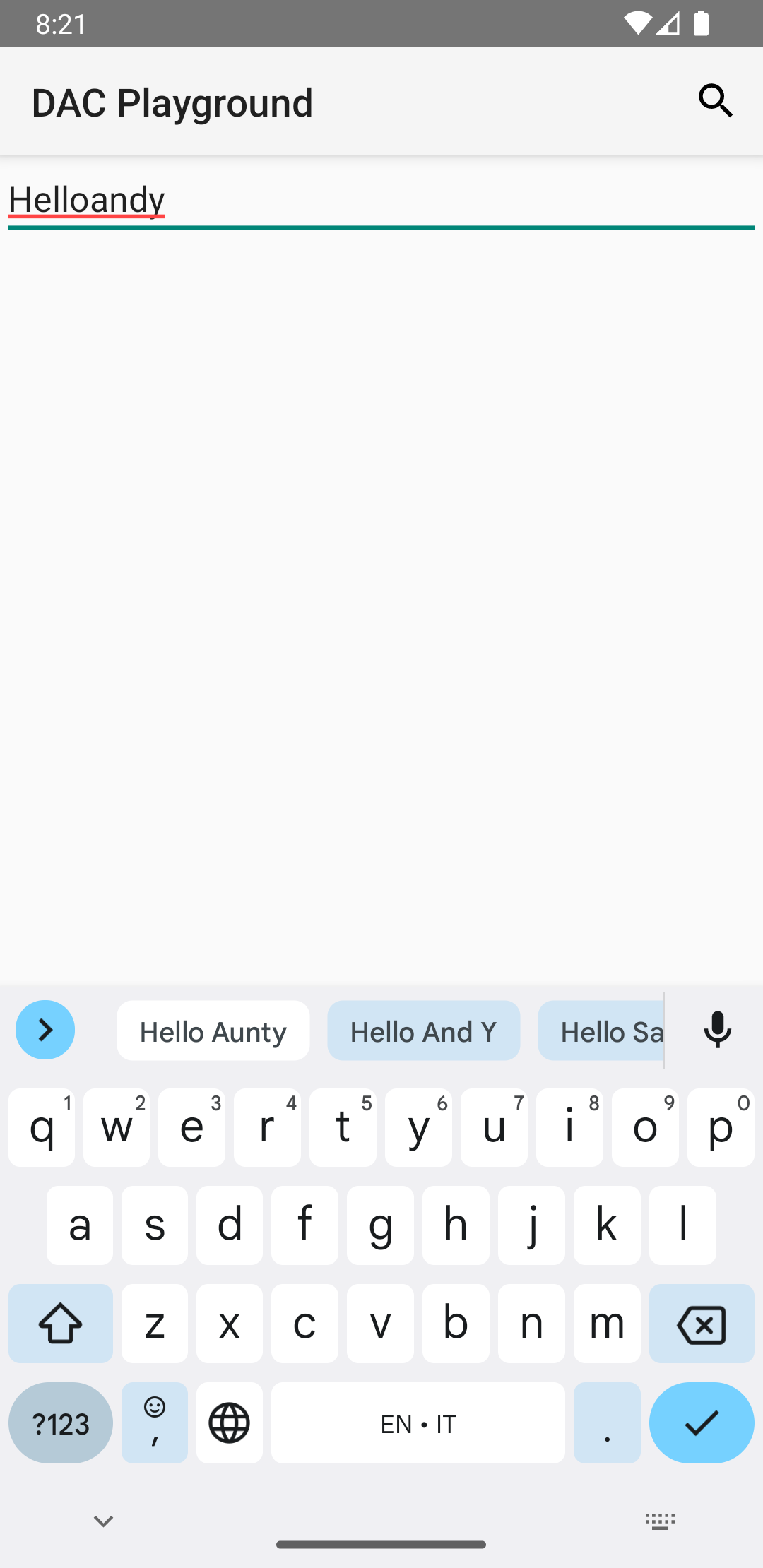
EditText。
不过,您可能需要在以下位置直接与拼写检查工具服务交互: 。下图显示了用于交互的控制流 使用拼写检查工具服务:
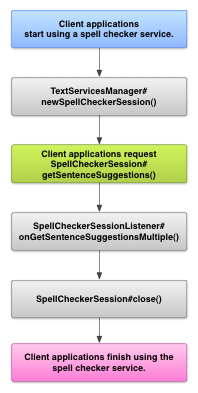
通过 拉丁语 Android 开源项目中的输入法编辑器包含一个示例 拼写检查。

