AppSearch는 로컬에 저장된 구조화된 데이터를 관리하기 위한 고성능 기기 내 검색 솔루션입니다. 전체 텍스트 검색을 사용하여 데이터 색인을 생성하고 데이터를 검색하는 API가 포함되어 있습니다. 애플리케이션은 AppSearch를 사용하여 맞춤 인앱 검색 기능을 제공할 수 있으므로 사용자가 오프라인 상태에서도 콘텐츠를 검색할 수 있습니다.
AppSearch는 다음과 같은 기능을 제공합니다.
- I/O 사용량이 적은 빠른 모바일 중심 스토리지 구현
- 대규모 데이터 세트의 매우 효율적인 색인 생성 및 쿼리
- 다국어 지원(예: 영어, 스페인어)
- 관련성 순위 지정 및 사용 점수
I/O 사용량이 적기 때문에 AppSearch는 SQLite에 비해 대규모 데이터 세트의 색인 생성 및 검색에 짧은 지연 시간을 제공합니다. AppSearch는 단일 쿼리를 지원하여 교차 유형 쿼리를 간소화하는 반면 SQLite는 여러 테이블의 결과를 병합합니다.
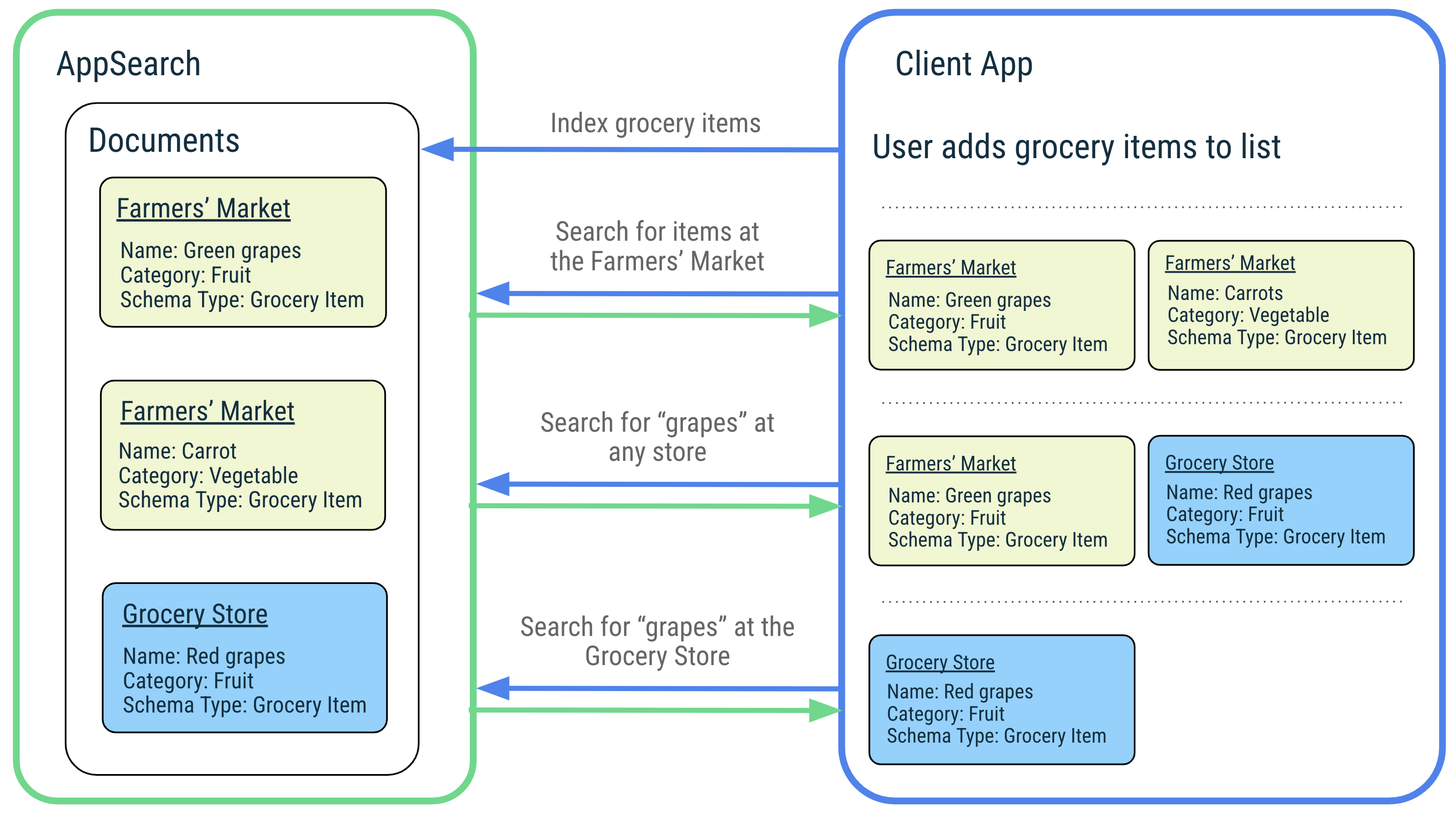
AppSearch의 기능을 설명하기 위해 사용자의 좋아하는 노래를 관리하고 사용자가 쉽게 검색할 수 있는 음악 애플리케이션을 예로 들어 보겠습니다. 사용자는 전 세계의 음악을 다양한 언어로 된 노래 제목으로 즐길 수 있으며, AppSearch는 색인 생성 및 쿼리 작업을 기본적으로 지원합니다. 사용자가 제목이나 아티스트 이름으로 노래를 검색하면 애플리케이션은 AppSearch에 요청을 전달하여 일치하는 노래를 빠르고 효율적으로 검색합니다. 애플리케이션은 결과를 표시하여 사용자가 좋아하는 노래를 빠르게 재생할 수 있도록 합니다.
설정
애플리케이션에서 AppSearch를 사용하려면 애플리케이션의 build.gradle 파일에 다음 종속 항목을 추가합니다.
Groovy
dependencies { def appsearch_version = "1.1.0" implementation "androidx.appsearch:appsearch:$appsearch_version" // Use kapt instead of annotationProcessor if writing Kotlin classes annotationProcessor "androidx.appsearch:appsearch-compiler:$appsearch_version" implementation "androidx.appsearch:appsearch-local-storage:$appsearch_version" // PlatformStorage is compatible with Android 12+ devices, and offers additional features // to LocalStorage. implementation "androidx.appsearch:appsearch-platform-storage:$appsearch_version" // PlayServicesStorage is compatible with all devices that support Google Play Services on // all API levels. It offers the same features as PlatformStorage and is the recommended // solution for lower API levels on which PlatformStorage is not supported. implementation "androidx.appsearch:appsearch-play-services-storage:$appsearch_version" }
Kotlin
dependencies { val appsearch_version = "1.1.0" implementation("androidx.appsearch:appsearch:$appsearch_version") // Use annotationProcessor instead of kapt if writing Java classes kapt("androidx.appsearch:appsearch-compiler:$appsearch_version") implementation("androidx.appsearch:appsearch-local-storage:$appsearch_version") // PlatformStorage is compatible with Android 12+ devices, and offers additional features // to LocalStorage. implementation("androidx.appsearch:appsearch-platform-storage:$appsearch_version") // PlayServicesStorage is compatible with all devices that support Google Play Services on // all API levels. It offers the same features as PlatformStorage and is the recommended // solution for lower API levels on which PlatformStorage is not supported. implementation("androidx.appsearch:appsearch-play-services-storage:$appsearch_version") }
AppSearch 개념
다음 다이어그램은 AppSearch 개념과 상호작용을 보여줍니다.
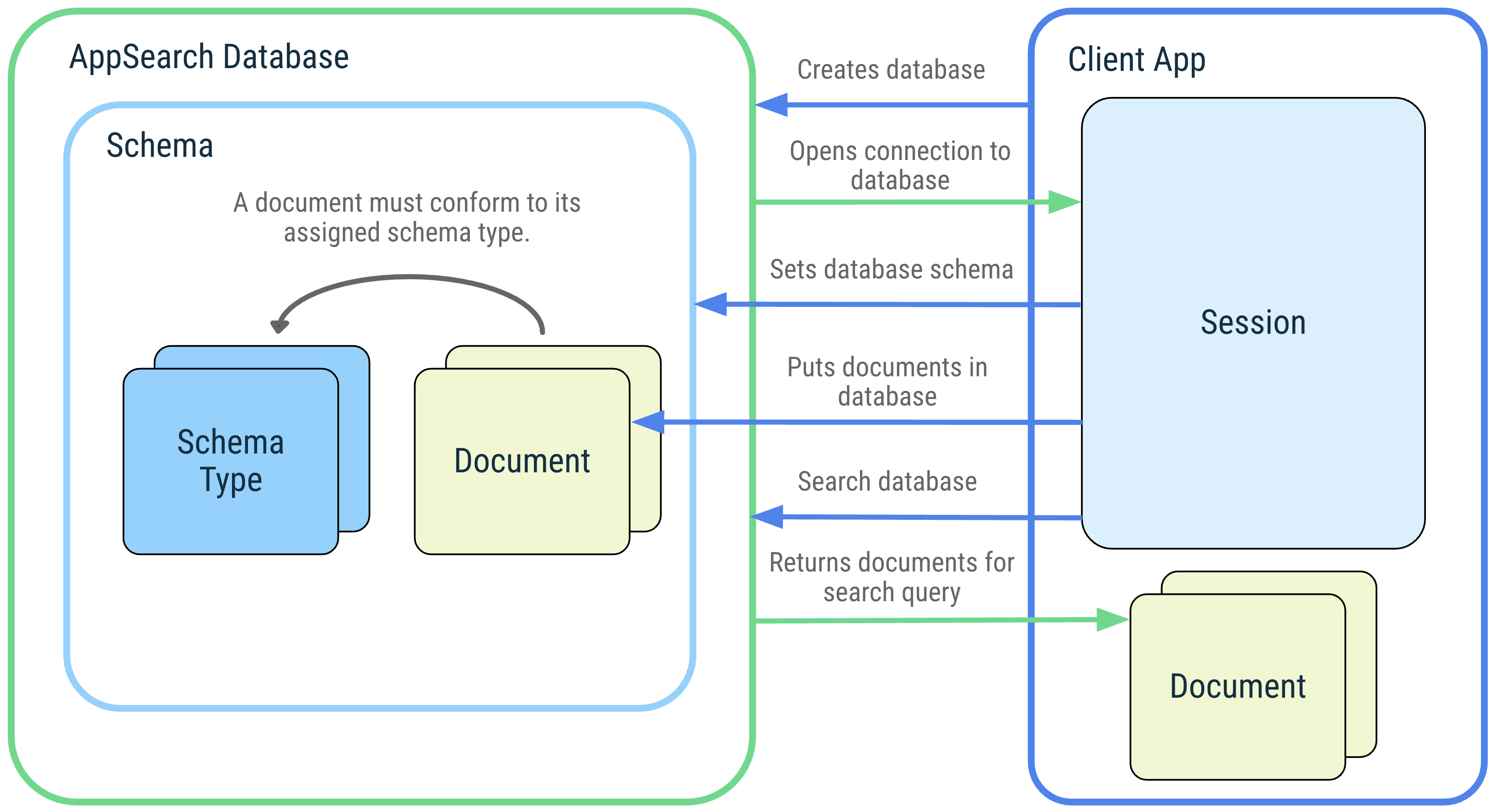 그림 1. AppSearch 개념 다이어그램: AppSearch 데이터베이스, 스키마, 스키마 유형, 문서, 세션, 검색
그림 1. AppSearch 개념 다이어그램: AppSearch 데이터베이스, 스키마, 스키마 유형, 문서, 세션, 검색
데이터베이스 및 세션
AppSearch 데이터베이스는 데이터베이스 스키마를 준수하는 문서 모음입니다. 클라이언트 애플리케이션은 애플리케이션 컨텍스트와 데이터베이스 이름을 제공하여 데이터베이스를 만듭니다. 데이터베이스는 데이터베이스를 만든 애플리케이션에서만 열 수 있습니다. 데이터베이스가 열리면 데이터베이스와 상호작용하는 세션이 반환됩니다. 세션은 AppSearch API를 호출하기 위한 진입점이며 클라이언트 애플리케이션에서 닫을 때까지 열려 있습니다.
스키마 및 스키마 유형
스키마는 AppSearch 데이터베이스 내 데이터의 조직 구조를 나타냅니다.
스키마는 고유한 데이터 유형을 나타내는 스키마 유형으로 구성됩니다. 스키마 유형은 이름, 데이터 유형, 카디널리티가 포함된 속성으로 구성됩니다. 스키마 유형이 데이터베이스 스키마에 추가되면 해당 스키마 유형의 문서를 만들어 데이터베이스에 추가할 수 있습니다.
문서
AppSearch에서 데이터 단위는 문서로 표시됩니다. AppSearch 데이터베이스의 각 문서는 네임스페이스와 ID로 고유하게 식별됩니다. 네임스페이스는 사용자 계정과 같이 하나의 소스만 쿼리해야 하는 경우 여러 소스에서 데이터를 분리하는 데 사용됩니다.
문서에는 생성 타임스탬프, 수명 (TTL), 검색 중에 순위에 사용할 수 있는 점수가 포함됩니다. 문서에는 문서에 있어야 하는 추가 데이터 속성을 설명하는 스키마 유형도 할당됩니다.
문서 클래스는 문서의 추상화입니다. 문서의 콘텐츠를 나타내는 주석이 달린 필드가 포함되어 있습니다. 기본적으로 문서 클래스의 이름은 스키마 유형의 이름을 설정합니다.
검색
문서에 색인이 생성되며 쿼리를 제공하여 검색할 수 있습니다. 문서에 검색어의 용어가 포함되어 있거나 다른 검색 사양과 일치하는 경우 문서가 검색 결과와 일치하여 검색 결과에 포함됩니다. 결과는 점수 및 순위 전략에 따라 정렬됩니다. 검색 결과는 순차적으로 검색할 수 있는 페이지로 표시됩니다.
AppSearch는 필터, 페이지 크기 구성, 스니펫 생성 등 검색을 위한 맞춤설정을 제공합니다.
플랫폼 저장소, 로컬 저장소 또는 Play 서비스 저장소
AppSearch는 LocalStorage, PlatformStorage, PlayServicesStorage의 세 가지 저장소 솔루션을 제공합니다. LocalStorage를 사용하면 애플리케이션이 애플리케이션 데이터 디렉터리에 있는 앱별 색인을 관리합니다. PlatformStorage 및 PlayServicesStorage를 모두 사용하면 애플리케이션이 시스템 전체 중앙 색인에 기여합니다. PlatformStorage의 색인은 시스템 서버에 호스팅되고 PlayServicesStorage의 색인은 Google Play 서비스의 저장소에 호스팅됩니다. 이러한 중앙 색인 내의 데이터 액세스는 애플리케이션이 제공한 데이터와 다른 애플리케이션에서 명시적으로 공유한 데이터로 제한됩니다. 이러한 모든 저장소 옵션은 동일한 API를 공유하며 기기 버전에 따라 서로 바꿀 수 있습니다.
Kotlin
if (BuildCompat.isAtLeastS()) { appSearchSessionFuture.setFuture( PlatformStorage.createSearchSession( PlatformStorage.SearchContext.Builder(mContext, DATABASE_NAME) .build() ) ) } else { if (usePlayServicesStorageBelowS) { appSearchSessionFuture.setFuture( PlayServicesStorage.createSearchSession( PlayServicesStorage.SearchContext.Builder(mContext, DATABASE_NAME) .build() ) ) } else { appSearchSessionFuture.setFuture( LocalStorage.createSearchSession( LocalStorage.SearchContext.Builder(mContext, DATABASE_NAME) .build() ) ) } }
자바
if (BuildCompat.isAtLeastS()) { mAppSearchSessionFuture.setFuture(PlatformStorage.createSearchSession( new PlatformStorage.SearchContext.Builder(mContext, DATABASE_NAME) .build())); } else { if (usePlayServicesStorageBelowS) { mAppSearchSessionFuture.setFuture(PlayServicesStorage.createSearchSession( new PlayServicesStorage.SearchContext.Builder(mContext, DATABASE_NAME) .build())); } else { mAppSearchSessionFuture.setFuture(LocalStorage.createSearchSession( new LocalStorage.SearchContext.Builder(mContext, DATABASE_NAME) .build())); } }
PlatformStorage 및 PlayServicesStorage를 사용하면 애플리케이션이 데이터를 다른 애플리케이션과 안전하게 공유하여 다른 애플리케이션에서도 앱의 데이터를 검색할 수 있습니다. 읽기 전용 애플리케이션 데이터 공유는 인증서 핸드셰이크를 사용하여 다른 애플리케이션에 데이터를 읽을 권한이 있는지 확인하여 부여됩니다. setSchemaTypeVisibilityForPackage() 문서에서 이 API에 관해 자세히 알아보세요.
또한 PlatformStorage를 사용하면 색인이 생성된 데이터를 시스템 UI 노출 영역에 표시할 수 있습니다. 애플리케이션은 시스템 UI 노출 영역에 데이터의 일부 또는 전부가 표시되지 않도록 선택할 수 있습니다. setSchemaTypeDisplayedBySystem() 문서에서 이 API에 관해 자세히 알아보세요.
| 기능 | LocalStorage (Android 5.0 이상과 호환됨) |
PlatformStorage (Android 12 이상과 호환됨) |
PlayServicesStorage (Android 5.0 이상과 호환됨) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 효율적인 전체 텍스트 검색 | |||
| 다국어 지원 | |||
| 바이너리 크기가 줄었습니다. | |||
| 애플리케이션 간 데이터 공유 | |||
| 시스템 UI 노출 영역에 데이터를 표시하는 기능 | |||
| 무제한의 문서 크기와 개수를 색인 생성할 수 있습니다. | |||
| 추가 바인더 지연 시간 없이 더 빠른 작업 |
LocalStorage와 PlatformStorage 중에서 선택할 때 고려해야 할 추가적인 장단점이 있습니다. PlatformStorage는 AppSearch 시스템 서비스 위에 Jetpack API를 래핑하므로 LocalStorage를 사용하는 것에 비해 APK 크기에 미치는 영향은 미미합니다. 그러나 이는 AppSearch 작업이 AppSearch 시스템 서비스를 호출할 때 추가 바인더 지연 시간이 발생한다는 것을 의미합니다. PlatformStorage를 사용하면 AppSearch는 애플리케이션이 색인화할 수 있는 문서 수와 문서 크기를 제한하여 효율적인 중앙 색인을 보장합니다. PlayServicesStorage도 PlatformStorage와 동일한 제한사항이 적용되며 Google Play 서비스가 있는 기기에서만 지원됩니다.
AppSearch 시작하기
이 섹션의 예에서는 AppSearch API를 사용하여 가상의 메모 작성 애플리케이션과 통합하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
문서 클래스 작성
AppSearch와 통합하는 첫 번째 단계는 데이터베이스에 삽입할 데이터를 설명하는 문서 클래스를 작성하는 것입니다. @Document 주석을 사용하여 클래스를 문서 클래스로 표시합니다.문서 클래스의 인스턴스를 사용하여 데이터베이스에 문서를 저장하고 데이터베이스에서 문서를 검색할 수 있습니다.
다음 코드는 메모 객체의 텍스트 색인을 생성하기 위한 @Document.StringProperty 주석이 달린 필드가 있는 메모 문서 클래스를 정의합니다.
Kotlin
@Document public data class Note( // Required field for a document class. All documents MUST have a namespace. @Document.Namespace val namespace: String, // Required field for a document class. All documents MUST have an Id. @Document.Id val id: String, // Optional field for a document class, used to set the score of the // document. If this is not included in a document class, the score is set // to a default of 0. @Document.Score val score: Int, // Optional field for a document class, used to index a note's text for this // document class. @Document.StringProperty(indexingType = AppSearchSchema.StringPropertyConfig.INDEXING_TYPE_PREFIXES) val text: String )
자바
@Document public class Note { // Required field for a document class. All documents MUST have a namespace. @Document.Namespace private final String namespace; // Required field for a document class. All documents MUST have an Id. @Document.Id private final String id; // Optional field for a document class, used to set the score of the // document. If this is not included in a document class, the score is set // to a default of 0. @Document.Score private final int score; // Optional field for a document class, used to index a note's text for this // document class. @Document.StringProperty(indexingType = StringPropertyConfig.INDEXING_TYPE_PREFIXES) private final String text; Note(@NonNull String id, @NonNull String namespace, int score, @NonNull String text) { this.id = Objects.requireNonNull(id); this.namespace = Objects.requireNonNull(namespace); this.score = score; this.text = Objects.requireNonNull(text); } @NonNull public String getNamespace() { return namespace; } @NonNull public String getId() { return id; } public int getScore() { return score; } @NonNull public String getText() { return text; } }
데이터베이스 열기
문서를 사용하려면 먼저 데이터베이스를 만들어야 합니다. 다음 코드는 notes_app라는 새 데이터베이스를 만들고 데이터베이스 연결을 나타내고 데이터베이스 작업을 위한 API를 제공하는 AppSearchSession의 ListenableFuture를 가져옵니다.
Kotlin
val context: Context = getApplicationContext() val sessionFuture = LocalStorage.createSearchSession( LocalStorage.SearchContext.Builder(context, /*databaseName=*/"notes_app") .build() )
자바
Context context = getApplicationContext(); ListenableFuture<AppSearchSession> sessionFuture = LocalStorage.createSearchSession( new LocalStorage.SearchContext.Builder(context, /*databaseName=*/ "notes_app") .build() );
스키마 설정
데이터베이스에 문서를 저장하고 데이터베이스에서 문서를 검색하려면 먼저 스키마를 설정해야 합니다. 데이터베이스 스키마는 '스키마 유형'이라고 하는 다양한 유형의 구조화된 데이터로 구성됩니다. 다음 코드는 문서 클래스를 스키마 유형으로 제공하여 스키마를 설정합니다.
Kotlin
val setSchemaRequest = SetSchemaRequest.Builder().addDocumentClasses(Note::class.java) .build() val setSchemaFuture = Futures.transformAsync( sessionFuture, { session -> session?.setSchema(setSchemaRequest) }, mExecutor )
자바
SetSchemaRequest setSchemaRequest = new SetSchemaRequest.Builder().addDocumentClasses(Note.class) .build(); ListenableFuture<SetSchemaResponse> setSchemaFuture = Futures.transformAsync(sessionFuture, session -> session.setSchema(setSchemaRequest), mExecutor);
데이터베이스에 문서 삽입
스키마 유형을 추가하면 해당 유형의 문서를 데이터베이스에 추가할 수 있습니다.
다음 코드는 Note 문서 클래스 빌더를 사용하여 스키마 유형 Note의 문서를 빌드합니다. 이 샘플의 임의 사용자를 나타내도록 문서 네임스페이스 user1를 설정합니다. 그러면 문서가 데이터베이스에 삽입되고 리스너가 연결되어 put 작업의 결과를 처리합니다.
Kotlin
val note = Note( namespace="user1", id="noteId", score=10, text="Buy fresh fruit" ) val putRequest = PutDocumentsRequest.Builder().addDocuments(note).build() val putFuture = Futures.transformAsync( sessionFuture, { session -> session?.put(putRequest) }, mExecutor ) Futures.addCallback( putFuture, object : FutureCallback<AppSearchBatchResult<String, Void>?> { override fun onSuccess(result: AppSearchBatchResult<String, Void>?) { // Gets map of successful results from Id to Void val successfulResults = result?.successes // Gets map of failed results from Id to AppSearchResult val failedResults = result?.failures } override fun onFailure(t: Throwable) { Log.e(TAG, "Failed to put documents.", t) } }, mExecutor )
자바
Note note = new Note(/*namespace=*/"user1", /*id=*/ "noteId", /*score=*/ 10, /*text=*/ "Buy fresh fruit!"); PutDocumentsRequest putRequest = new PutDocumentsRequest.Builder().addDocuments(note) .build(); ListenableFuture<AppSearchBatchResult<String, Void>> putFuture = Futures.transformAsync(sessionFuture, session -> session.put(putRequest), mExecutor); Futures.addCallback(putFuture, new FutureCallback<AppSearchBatchResult<String, Void>>() { @Override public void onSuccess(@Nullable AppSearchBatchResult<String, Void> result) { // Gets map of successful results from Id to Void Map<String, Void> successfulResults = result.getSuccesses(); // Gets map of failed results from Id to AppSearchResult Map<String, AppSearchResult<Void>> failedResults = result.getFailures(); } @Override public void onFailure(@NonNull Throwable t) { Log.e(TAG, "Failed to put documents.", t); } }, mExecutor);
검색
이 섹션에 설명된 검색 작업을 사용하여 색인이 생성된 문서를 검색할 수 있습니다. 다음 코드는 user1 네임스페이스에 속한 문서의 데이터베이스에서 'fruit'이라는 용어에 대한 쿼리를 실행합니다.
Kotlin
val searchSpec = SearchSpec.Builder() .addFilterNamespaces("user1") .build(); val searchFuture = Futures.transform( sessionFuture, { session -> session?.search("fruit", searchSpec) }, mExecutor ) Futures.addCallback( searchFuture, object : FutureCallback<SearchResults> { override fun onSuccess(searchResults: SearchResults?) { iterateSearchResults(searchResults) } override fun onFailure(t: Throwable?) { Log.e("TAG", "Failed to search notes in AppSearch.", t) } }, mExecutor )
자바
SearchSpec searchSpec = new SearchSpec.Builder() .addFilterNamespaces("user1") .build(); ListenableFuture<SearchResults> searchFuture = Futures.transform(sessionFuture, session -> session.search("fruit", searchSpec), mExecutor); Futures.addCallback(searchFuture, new FutureCallback<SearchResults>() { @Override public void onSuccess(@Nullable SearchResults searchResults) { iterateSearchResults(searchResults); } @Override public void onFailure(@NonNull Throwable t) { Log.e(TAG, "Failed to search notes in AppSearch.", t); } }, mExecutor);
SearchResults 반복
검색은 SearchResult 객체의 페이지에 액세스할 수 있는 SearchResults 인스턴스를 반환합니다. 각 SearchResult는 일치하는 GenericDocument를 보유합니다. GenericDocument는 모든 문서가 변환되는 문서의 일반적인 형식입니다. 다음 코드는 검색 결과의 첫 페이지를 가져와 결과를 다시 Note 문서로 변환합니다.
Kotlin
Futures.transform( searchResults?.nextPage, { page: List<SearchResult>? -> // Gets GenericDocument from SearchResult. val genericDocument: GenericDocument = page!![0].genericDocument val schemaType = genericDocument.schemaType val note: Note? = try { if (schemaType == "Note") { // Converts GenericDocument object to Note object. genericDocument.toDocumentClass(Note::class.java) } else null } catch (e: AppSearchException) { Log.e( TAG, "Failed to convert GenericDocument to Note", e ) null } note }, mExecutor )
자바
Futures.transform(searchResults.getNextPage(), page -> { // Gets GenericDocument from SearchResult. GenericDocument genericDocument = page.get(0).getGenericDocument(); String schemaType = genericDocument.getSchemaType(); Note note = null; if (schemaType.equals("Note")) { try { // Converts GenericDocument object to Note object. note = genericDocument.toDocumentClass(Note.class); } catch (AppSearchException e) { Log.e(TAG, "Failed to convert GenericDocument to Note", e); } } return note; }, mExecutor);
문서 삭제
사용자가 메모를 삭제하면 애플리케이션은 데이터베이스에서 상응하는 Note 문서를 삭제합니다. 이렇게 하면 메모가 더 이상 쿼리에서 표시되지 않습니다. 다음 코드는 데이터베이스에서 ID별로 Note 문서를 삭제하도록 명시적으로 요청합니다.
Kotlin
val removeRequest = RemoveByDocumentIdRequest.Builder("user1") .addIds("noteId") .build() val removeFuture = Futures.transformAsync( sessionFuture, { session -> session?.remove(removeRequest) }, mExecutor )
자바
RemoveByDocumentIdRequest removeRequest = new RemoveByDocumentIdRequest.Builder("user1") .addIds("noteId") .build(); ListenableFuture<AppSearchBatchResult<String, Void>> removeFuture = Futures.transformAsync(sessionFuture, session -> session.remove(removeRequest), mExecutor);
디스크에 저장
데이터베이스 업데이트는 requestFlush()를 호출하여 주기적으로 디스크에 유지되어야 합니다. 다음 코드는 리스너와 함께 requestFlush()를 호출하여 호출이 성공했는지 확인합니다.
Kotlin
val requestFlushFuture = Futures.transformAsync( sessionFuture, { session -> session?.requestFlush() }, mExecutor ) Futures.addCallback(requestFlushFuture, object : FutureCallback<Void?> { override fun onSuccess(result: Void?) { // Success! Database updates have been persisted to disk. } override fun onFailure(t: Throwable) { Log.e(TAG, "Failed to flush database updates.", t) } }, mExecutor)
자바
ListenableFuture<Void> requestFlushFuture = Futures.transformAsync(sessionFuture, session -> session.requestFlush(), mExecutor); Futures.addCallback(requestFlushFuture, new FutureCallback<Void>() { @Override public void onSuccess(@Nullable Void result) { // Success! Database updates have been persisted to disk. } @Override public void onFailure(@NonNull Throwable t) { Log.e(TAG, "Failed to flush database updates.", t); } }, mExecutor);
세션 닫기
애플리케이션에서 더 이상 데이터베이스 작업을 호출하지 않을 때 AppSearchSession를 닫아야 합니다. 다음 코드는 이전에 열었던 AppSearch 세션을 닫고 모든 업데이트를 디스크에 유지합니다.
Kotlin
val closeFuture = Futures.transform<AppSearchSession, Unit>(sessionFuture, { session -> session?.close() Unit }, mExecutor )
Java
ListenableFuture<Void> closeFuture = Futures.transform(sessionFuture, session -> { session.close(); return null; }, mExecutor);
추가 리소스
AppSearch에 관해 자세히 알아보려면 다음 추가 리소스를 참고하세요.
샘플
- Android AppSearch 샘플 (Kotlin): AppSearch를 사용하여 사용자의 메모에 색인을 생성하고 사용자가 메모를 검색할 수 있는 메모 작성 앱입니다.
의견 보내기
다음 리소스를 통해 의견을 보내고 아이디어를 공유해 주세요.
버그를 수정할 수 있도록 버그를 신고해 주세요.
