对话框是提示用户做出决定或输入更多信息的小窗口。对话框不会填满屏幕,通常用于需要用户采取行动才能继续执行的模态事件。
Dialog 类是对话框的基类,但请勿直接实例化 Dialog,而是应使用下列子类之一:
AlertDialog- 此对话框可显示标题、最多三个按钮、可选项列表或自定义布局。
DatePickerDialog或TimePickerDialog- 此对话框带有允许用户选择日期或时间的预定义界面。
这些类可定义对话框的样式和结构。您还需要一个 DialogFragment 作为对话框的容器。DialogFragment 类提供了创建对话框和管理其外观所需的所有控件,而不是对 Dialog 对象调用方法。
使用 DialogFragment 来管理对话框可确保对话框能正确处理各种生命周期事件,如用户点按“返回”按钮或旋转屏幕时。此外,DialogFragment 类还允许您以可嵌入组件的形式在较大界面中重复使用对话框界面,类似于传统的 Fragment(例如当您想让对话框界面在大屏幕和小屏幕上具有不同外观时)。
本文档的后续部分将介绍如何将 DialogFragment 与 AlertDialog 对象结合使用。如果您想创建日期或时间选择器,请阅读向应用添加选择器。
创建对话框 fragment
通过扩展 DialogFragment 并在 onCreateDialog() 回调方法中创建 AlertDialog,您可以完成各种对话框设计,包括自定义布局以及 Material Design 对话框中描述的布局。
例如,以下是在 DialogFragment 内管理的基础 AlertDialog:
Kotlin
class StartGameDialogFragment : DialogFragment() { override fun onCreateDialog(savedInstanceState: Bundle?): Dialog { return activity?.let { // Use the Builder class for convenient dialog construction. val builder = AlertDialog.Builder(it) builder.setMessage("Start game") .setPositiveButton("Start") { dialog, id -> // START THE GAME! } .setNegativeButton("Cancel") { dialog, id -> // User cancelled the dialog. } // Create the AlertDialog object and return it. builder.create() } ?: throw IllegalStateException("Activity cannot be null") } } class OldXmlActivity : AppCompatActivity() { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_old_xml) StartGameDialogFragment().show(supportFragmentManager, "GAME_DIALOG") } }
Java
public class StartGameDialogFragment extends DialogFragment { @Override public Dialog onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState) { // Use the Builder class for convenient dialog construction. AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity()); builder.setMessage(R.string.dialog_start_game) .setPositiveButton(R.string.start, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { // START THE GAME! } }) .setNegativeButton(R.string.cancel, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { // User cancels the dialog. } }); // Create the AlertDialog object and return it. return builder.create(); } } // ... StartGameDialogFragment().show(supportFragmentManager, "GAME_DIALOG");
当您创建此类的实例并针对该对象调用 show() 时,对话框将如下图所示。
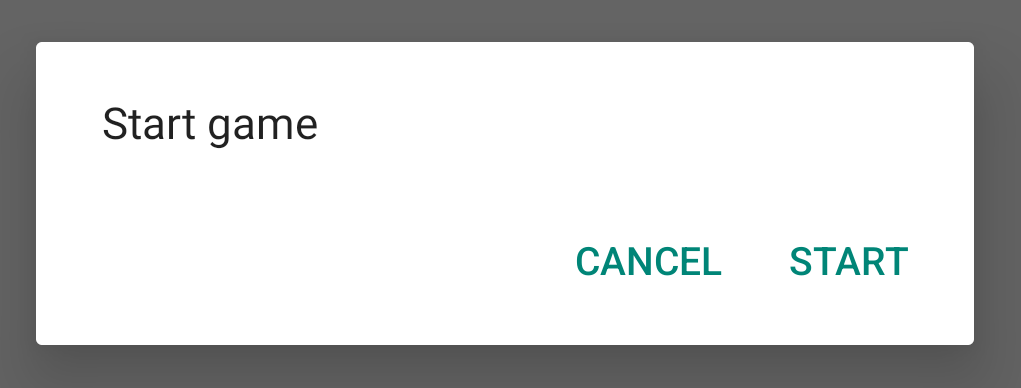
下一部分将详细介绍如何使用 AlertDialog.Builder API 创建对话框。
根据对话框的复杂程度,您可以在 DialogFragment 中实现各种其他回调方法,包括所有基本的 Fragment 生命周期方法。
构建提醒对话框
您可以使用 AlertDialog 类来构建各种对话框设计。通常情况下,该类是您完成构建所需的唯一对话框类。如下图所示,提醒对话框包含三个区域:
- 标题:此为可选项,仅当内容区域被详细消息、列表或自定义布局占据时才应使用标题。如果需要陈述的是一条简单消息或问题,则不需要标题。
- 内容区域:可显示消息、列表或其他自定义布局。
- 操作按钮:对话框中最多可以有三个操作按钮。
您可以使用 AlertDialog.Builder 类提供的 API 来创建含有这几种内容(包括自定义布局)的 AlertDialog。
如需构建 AlertDialog,请执行以下操作:
Kotlin
val builder: AlertDialog.Builder = AlertDialog.Builder(context) builder .setMessage("I am the message") .setTitle("I am the title") val dialog: AlertDialog = builder.create() dialog.show()
Java
// 1. Instantiate an AlertDialog.Builder with its constructor. AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity()); // 2. Chain together various setter methods to set the dialog characteristics. builder.setMessage(R.string.dialog_message) .setTitle(R.string.dialog_title); // 3. Get the AlertDialog. AlertDialog dialog = builder.create();
上述代码段会生成以下对话框:
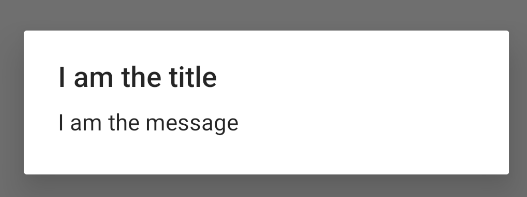
添加按钮
如需添加如图 2 所示的操作按钮,请调用 setPositiveButton() 和 setNegativeButton() 方法:
Kotlin
val builder: AlertDialog.Builder = AlertDialog.Builder(context) builder .setMessage("I am the message") .setTitle("I am the title") .setPositiveButton("Positive") { dialog, which -> // Do something. } .setNegativeButton("Negative") { dialog, which -> // Do something else. } val dialog: AlertDialog = builder.create() dialog.show()
Java
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity()); // Add the buttons. builder.setPositiveButton(R.string.ok, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { // User taps OK button. } }); builder.setNegativeButton(R.string.cancel, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { // User cancels the dialog. } }); // Set other dialog properties. ... // Create the AlertDialog. AlertDialog dialog = builder.create();
set...Button() 方法需要一个按钮标题(由字符串资源提供)以及一个 DialogInterface.OnClickListener(用于定义用户点按该按钮时执行的操作)。
您可以添加三个操作按钮:
- 肯定:使用此选项可接受并继续执行操作(“确定”操作)。
- 否定:用于取消操作。
- 中立:此按钮应用于用户可能不想继续执行操作,但也未必想要取消操作的情况。它出现在肯定按钮和否定按钮之间。例如,实际操作可能是“稍后提醒我”。
对于每种按钮类型,您只能为 AlertDialog 添加一个该类型的按钮。例如,您不能添加多个“肯定”按钮。
前面的代码段会显示如下所示的提醒对话框:
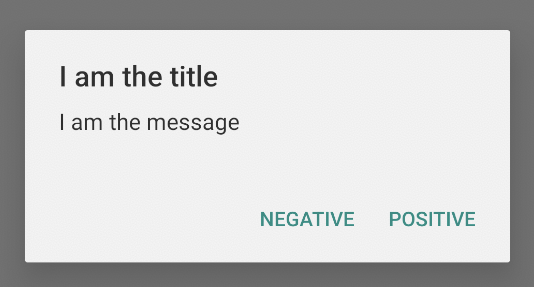
添加列表
可通过 AlertDialog API 提供三种列表:
- 传统的单选列表。
- 永久性单选列表(单选按钮)。
- 永久性多选列表(复选框)。
如需创建如图 5 所示的单选列表,请使用 setItems() 方法:
Kotlin
val builder: AlertDialog.Builder = AlertDialog.Builder(context) builder .setTitle("I am the title") .setPositiveButton("Positive") { dialog, which -> // Do something. } .setNegativeButton("Negative") { dialog, which -> // Do something else. } .setItems(arrayOf("Item One", "Item Two", "Item Three")) { dialog, which -> // Do something on item tapped. } val dialog: AlertDialog = builder.create() dialog.show()
Java
@Override public Dialog onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState) { AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity()); builder.setTitle(R.string.pick_color) .setItems(R.array.colors_array, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) { // The 'which' argument contains the index position of the selected item. } }); return builder.create(); }
此代码段会生成如下所示的对话框:
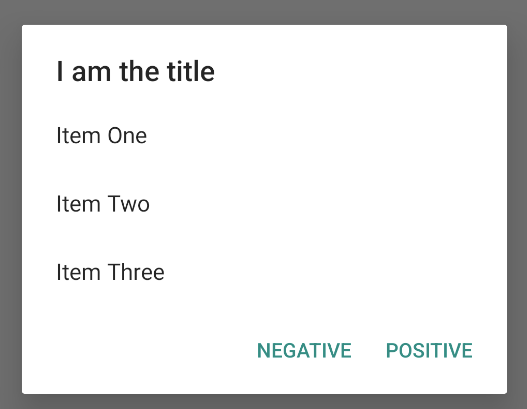
由于列表出现在对话框的内容区域,因此对话框无法同时显示消息和列表。使用 setTitle() 为对话框设置标题。如需为列表指定项目,请调用 setItems(),并传递数组。或者,您也可以使用 setAdapter() 指定列表。这样一来,您便可借助 ListAdapter 使用动态数据(如来自数据库的数据)来支持列表。
如果您使用 ListAdapter 来支持列表,请务必使用 Loader,这样内容便可以异步方式进行加载。使用适配器构建布局和加载器中对此有进一步的说明。
添加永久性多选列表或单选列表
如需添加多选(复选框)或单选(单选按钮)列表,请分别使用 setMultiChoiceItems() 或 setSingleChoiceItems() 方法。
例如,以下示例展示了如何创建如图 6 所示的多选列表,该多选列表将选定项保存在 ArrayList 中:
Kotlin
val builder: AlertDialog.Builder = AlertDialog.Builder(context) builder .setTitle("I am the title") .setPositiveButton("Positive") { dialog, which -> // Do something. } .setNegativeButton("Negative") { dialog, which -> // Do something else. } .setMultiChoiceItems( arrayOf("Item One", "Item Two", "Item Three"), null) { dialog, which, isChecked -> // Do something. } val dialog: AlertDialog = builder.create() dialog.show()
Java
@Override public Dialog onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState) { selectedItems = new ArrayList(); // Where we track the selected items AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity()); // Set the dialog title. builder.setTitle(R.string.pick_toppings) // Specify the list array, the items to be selected by default (null for // none), and the listener through which to receive callbacks when items // are selected. .setMultiChoiceItems(R.array.toppings, null, new DialogInterface.OnMultiChoiceClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which, boolean isChecked) { if (isChecked) { // If the user checks the item, add it to the selected // items. selectedItems.add(which); } else if (selectedItems.contains(which)) { // If the item is already in the array, remove it. selectedItems.remove(which); } } }) // Set the action buttons .setPositiveButton(R.string.ok, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { // User taps OK, so save the selectedItems results // somewhere or return them to the component that opens the // dialog. ... } }) .setNegativeButton(R.string.cancel, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { ... } }); return builder.create(); }
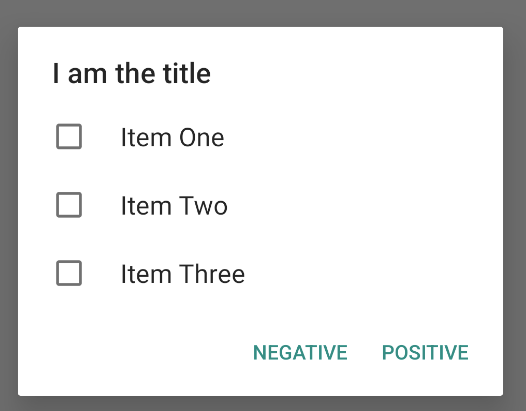
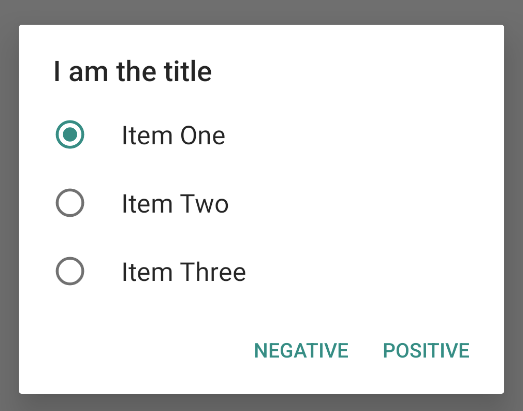
单选题提醒对话框的获取方式如下所示:
Kotlin
val builder: AlertDialog.Builder = AlertDialog.Builder(context) builder .setTitle("I am the title") .setPositiveButton("Positive") { dialog, which -> // Do something. } .setNegativeButton("Negative") { dialog, which -> // Do something else. } .setSingleChoiceItems( arrayOf("Item One", "Item Two", "Item Three"), 0 ) { dialog, which -> // Do something. } val dialog: AlertDialog = builder.create() dialog.show()
Java
String[] choices = {"Item One", "Item Two", "Item Three"}; AlertDialog.Builder builder = AlertDialog.Builder(context); builder .setTitle("I am the title") .setPositiveButton("Positive", (dialog, which) -> { }) .setNegativeButton("Negative", (dialog, which) -> { }) .setSingleChoiceItems(choices, 0, (dialog, which) -> { }); AlertDialog dialog = builder.create(); dialog.show();
这会产生以下示例:
创建自定义布局
如果您想在对话框中使用自定义布局,请创建一个布局,然后通过对 AlertDialog.Builder 对象调用 setView(),将该布局添加至 AlertDialog。
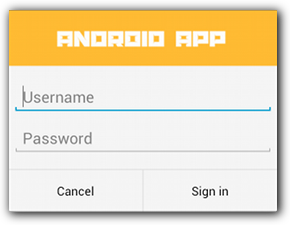
默认情况下,自定义布局会填充对话框窗口,但您仍可使用 AlertDialog.Builder 方法来添加按钮和标题。
例如,以下是前面自定义对话框布局的布局文件:
res/layout/dialog_signin.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <ImageView android:src="@drawable/header_logo" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="64dp" android:scaleType="center" android:background="#FFFFBB33" android:contentDescription="@string/app_name" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/username" android:inputType="textEmailAddress" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="16dp" android:layout_marginLeft="4dp" android:layout_marginRight="4dp" android:layout_marginBottom="4dp" android:hint="@string/username" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/password" android:inputType="textPassword" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="4dp" android:layout_marginLeft="4dp" android:layout_marginRight="4dp" android:layout_marginBottom="16dp" android:fontFamily="sans-serif" android:hint="@string/password"/> </LinearLayout>
如需在 DialogFragment 中膨胀布局,请使用 getLayoutInflater() 获取 LayoutInflater 并调用 inflate()。第一个参数是布局资源 ID,第二个参数是布局的父视图。然后,您可以调用 setView(),将布局放入对话框中。详见下例。
Kotlin
override fun onCreateDialog(savedInstanceState: Bundle?): Dialog { return activity?.let { val builder = AlertDialog.Builder(it) // Get the layout inflater. val inflater = requireActivity().layoutInflater; // Inflate and set the layout for the dialog. // Pass null as the parent view because it's going in the dialog // layout. builder.setView(inflater.inflate(R.layout.dialog_signin, null)) // Add action buttons. .setPositiveButton(R.string.signin, DialogInterface.OnClickListener { dialog, id -> // Sign in the user. }) .setNegativeButton(R.string.cancel, DialogInterface.OnClickListener { dialog, id -> getDialog().cancel() }) builder.create() } ?: throw IllegalStateException("Activity cannot be null") }
Java
@Override public Dialog onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState) { AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity()); // Get the layout inflater. LayoutInflater inflater = requireActivity().getLayoutInflater(); // Inflate and set the layout for the dialog. // Pass null as the parent view because it's going in the dialog layout. builder.setView(inflater.inflate(R.layout.dialog_signin, null)) // Add action buttons .setPositiveButton(R.string.signin, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { // Sign in the user. } }) .setNegativeButton(R.string.cancel, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { LoginDialogFragment.this.getDialog().cancel(); } }); return builder.create(); }
如果您想要自定义对话框,可以改为将 Activity 显示为对话框,而不是使用 Dialog API。创建一个 activity,并在 <activity> 清单元素中将其主题设置为 Theme.Holo.Dialog:
<activity android:theme="@android:style/Theme.Holo.Dialog" >
Activity 现在会显示在一个对话框窗口中,而非全屏显示。
将事件传回对话框的宿主
当用户点按对话框的某个操作按钮或从列表中选择某一项时,您的 DialogFragment 可能会自行执行必要的操作,但通常情况下,您会希望将事件传递给打开对话框的 activity 或 fragment。为此,请为每种点击事件定义带有方法的接口。然后,在从该对话框接收操作事件的宿主组件中实现该接口。
例如,以下 DialogFragment 定义了一个接口,通过该接口将事件传回给宿主 activity:
Kotlin
class NoticeDialogFragment : DialogFragment() { // Use this instance of the interface to deliver action events. internal lateinit var listener: NoticeDialogListener // The activity that creates an instance of this dialog fragment must // implement this interface to receive event callbacks. Each method passes // the DialogFragment in case the host needs to query it. interface NoticeDialogListener { fun onDialogPositiveClick(dialog: DialogFragment) fun onDialogNegativeClick(dialog: DialogFragment) } // Override the Fragment.onAttach() method to instantiate the // NoticeDialogListener. override fun onAttach(context: Context) { super.onAttach(context) // Verify that the host activity implements the callback interface. try { // Instantiate the NoticeDialogListener so you can send events to // the host. listener = context as NoticeDialogListener } catch (e: ClassCastException) { // The activity doesn't implement the interface. Throw exception. throw ClassCastException((context.toString() + " must implement NoticeDialogListener")) } } }
Java
public class NoticeDialogFragment extends DialogFragment { // The activity that creates an instance of this dialog fragment must // implement this interface to receive event callbacks. Each method passes // the DialogFragment in case the host needs to query it. public interface NoticeDialogListener { public void onDialogPositiveClick(DialogFragment dialog); public void onDialogNegativeClick(DialogFragment dialog); } // Use this instance of the interface to deliver action events. NoticeDialogListener listener; // Override the Fragment.onAttach() method to instantiate the // NoticeDialogListener. @Override public void onAttach(Context context) { super.onAttach(context); // Verify that the host activity implements the callback interface. try { // Instantiate the NoticeDialogListener so you can send events to // the host. listener = (NoticeDialogListener) context; } catch (ClassCastException e) { // The activity doesn't implement the interface. Throw exception. throw new ClassCastException(activity.toString() + " must implement NoticeDialogListener"); } } ... }
对话框的宿主 activity 会使用对话框 fragment 的构造函数创建对话框实例,并通过 NoticeDialogListener 接口的实现接收对话框的事件:
Kotlin
class MainActivity : FragmentActivity(), NoticeDialogFragment.NoticeDialogListener { fun showNoticeDialog() { // Create an instance of the dialog fragment and show it. val dialog = NoticeDialogFragment() dialog.show(supportFragmentManager, "NoticeDialogFragment") } // The dialog fragment receives a reference to this Activity through the // Fragment.onAttach() callback, which it uses to call the following // methods defined by the NoticeDialogFragment.NoticeDialogListener // interface. override fun onDialogPositiveClick(dialog: DialogFragment) { // User taps the dialog's positive button. } override fun onDialogNegativeClick(dialog: DialogFragment) { // User taps the dialog's negative button. } }
Java
public class MainActivity extends FragmentActivity implements NoticeDialogFragment.NoticeDialogListener{ ... public void showNoticeDialog() { // Create an instance of the dialog fragment and show it. DialogFragment dialog = new NoticeDialogFragment(); dialog.show(getSupportFragmentManager(), "NoticeDialogFragment"); } // The dialog fragment receives a reference to this Activity through the // Fragment.onAttach() callback, which it uses to call the following // methods defined by the NoticeDialogFragment.NoticeDialogListener // interface. @Override public void onDialogPositiveClick(DialogFragment dialog) { // User taps the dialog's positive button. ... } @Override public void onDialogNegativeClick(DialogFragment dialog) { // User taps the dialog's negative button. ... } }
由于宿主 activity 会实现 NoticeDialogListener(由上例中显示的 onAttach() 回调方法强制执行),因此对话框 fragment 可使用接口回调方法向 activity 传递点击事件:
Kotlin
override fun onCreateDialog(savedInstanceState: Bundle): Dialog { return activity?.let { // Build the dialog and set up the button click handlers. val builder = AlertDialog.Builder(it) builder.setMessage(R.string.dialog_start_game) .setPositiveButton(R.string.start, DialogInterface.OnClickListener { dialog, id -> // Send the positive button event back to the // host activity. listener.onDialogPositiveClick(this) }) .setNegativeButton(R.string.cancel, DialogInterface.OnClickListener { dialog, id -> // Send the negative button event back to the // host activity. listener.onDialogNegativeClick(this) }) builder.create() } ?: throw IllegalStateException("Activity cannot be null") }
Java
public class NoticeDialogFragment extends DialogFragment { ... @Override public Dialog onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState) { // Build the dialog and set up the button click handlers. AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity()); builder.setMessage(R.string.dialog_start_game) .setPositiveButton(R.string.start, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { // Send the positive button event back to the host activity. listener.onDialogPositiveClick(NoticeDialogFragment.this); } }) .setNegativeButton(R.string.cancel, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { // Send the negative button event back to the host activity. listener.onDialogNegativeClick(NoticeDialogFragment.this); } }); return builder.create(); } }
显示对话框
如果您想显示对话框,请创建一个 DialogFragment 实例并调用 show(),以传递对话框 fragment 的 FragmentManager 和标记名称。
您可以从 FragmentActivity 调用 getSupportFragmentManager() 或从 Fragment 调用 getParentFragmentManager(),从而获取 FragmentManager。请参阅以下示例:
Kotlin
fun confirmStartGame() { val newFragment = StartGameDialogFragment() newFragment.show(supportFragmentManager, "game") }
Java
public void confirmStartGame() { DialogFragment newFragment = new StartGameDialogFragment(); newFragment.show(getSupportFragmentManager(), "game"); }
第二个参数 "game" 是系统用于保存 fragment 状态并在必要时进行恢复的唯一标记名称。该标记还允许您通过调用 findFragmentByTag() 来获取 fragment 的句柄。
全屏显示对话框或将其显示为嵌入式 fragment
您可能希望界面设计的某个部分在某些情况下显示为对话框,在其他情况下全屏显示或显示为嵌入式 fragment。您可能还希望根据设备的屏幕尺寸,使其以不同的方式显示。DialogFragment 类可让您灵活地完成此操作,因为它可以充当可嵌入的 Fragment。
不过,在这种情况下,您无法使用 AlertDialog.Builder 或其他 Dialog 对象来构建对话框。如果您想让 DialogFragment 拥有嵌入能力,请在布局中定义对话框的界面,然后在 onCreateView() 回调中加载布局。
以下示例 DialogFragment 可显示为对话框或可嵌入 fragment,使用名为 purchase_items.xml 的布局:
Kotlin
class CustomDialogFragment : DialogFragment() { // The system calls this to get the DialogFragment's layout, regardless of // whether it's being displayed as a dialog or an embedded fragment. override fun onCreateView( inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?, savedInstanceState: Bundle? ): View { // Inflate the layout to use as a dialog or embedded fragment. return inflater.inflate(R.layout.purchase_items, container, false) } // The system calls this only when creating the layout in a dialog. override fun onCreateDialog(savedInstanceState: Bundle): Dialog { // The only reason you might override this method when using // onCreateView() is to modify the dialog characteristics. For example, // the dialog includes a title by default, but your custom layout might // not need it. Here, you can remove the dialog title, but you must // call the superclass to get the Dialog. val dialog = super.onCreateDialog(savedInstanceState) dialog.requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE) return dialog } }
Java
public class CustomDialogFragment extends DialogFragment { // The system calls this to get the DialogFragment's layout, regardless of // whether it's being displayed as a dialog or an embedded fragment. @Override public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) { // Inflate the layout to use as a dialog or embedded fragment. return inflater.inflate(R.layout.purchase_items, container, false); } // The system calls this only when creating the layout in a dialog. @Override public Dialog onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState) { // The only reason you might override this method when using // onCreateView() is to modify the dialog characteristics. For example, // the dialog includes a title by default, but your custom layout might // not need it. Here, you can remove the dialog title, but you must // call the superclass to get the Dialog. Dialog dialog = super.onCreateDialog(savedInstanceState); dialog.requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE); return dialog; } }
以下示例会根据屏幕尺寸确定将 fragment 显示为对话框还是全屏界面:
Kotlin
fun showDialog() { val fragmentManager = supportFragmentManager val newFragment = CustomDialogFragment() if (isLargeLayout) { // The device is using a large layout, so show the fragment as a // dialog. newFragment.show(fragmentManager, "dialog") } else { // The device is smaller, so show the fragment fullscreen. val transaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction() // For a polished look, specify a transition animation. transaction.setTransition(FragmentTransaction.TRANSIT_FRAGMENT_OPEN) // To make it fullscreen, use the 'content' root view as the container // for the fragment, which is always the root view for the activity. transaction .add(android.R.id.content, newFragment) .addToBackStack(null) .commit() } }
Java
public void showDialog() { FragmentManager fragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager(); CustomDialogFragment newFragment = new CustomDialogFragment(); if (isLargeLayout) { // The device is using a large layout, so show the fragment as a // dialog. newFragment.show(fragmentManager, "dialog"); } else { // The device is smaller, so show the fragment fullscreen. FragmentTransaction transaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction(); // For a polished look, specify a transition animation. transaction.setTransition(FragmentTransaction.TRANSIT_FRAGMENT_OPEN); // To make it fullscreen, use the 'content' root view as the container // for the fragment, which is always the root view for the activity. transaction.add(android.R.id.content, newFragment) .addToBackStack(null).commit(); } }
如需详细了解如何执行 fragment 事务,请参阅 Fragment。
在本示例中,mIsLargeLayout 布尔值指定当前设备是否必须使用应用的大布局设计,进而将此 fragment 显示为对话框,而非全屏显示。设置这种布尔值的最佳方式是声明一个布尔资源值,其中包含适用于不同屏幕尺寸的备用资源值。例如,以下两个版本的布尔资源适用于不同屏幕尺寸:
res/values/bools.xml
<!-- Default boolean values --> <resources> <bool name="large_layout">false</bool> </resources>
res/values-large/bools.xml
<!-- Large screen boolean values --> <resources> <bool name="large_layout">true</bool> </resources>
然后,您可以在 activity 的 onCreate() 方法执行期间初始化 mIsLargeLayout 值,如以下示例所示:
Kotlin
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) isLargeLayout = resources.getBoolean(R.bool.large_layout) }
Java
boolean isLargeLayout; @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); isLargeLayout = getResources().getBoolean(R.bool.large_layout); }
在大屏幕上将 activity 显示为对话框
相对于在小屏幕上将对话框显示为全屏界面,您可以在大屏幕上将 Activity 显示为对话框,从而达到相同的效果。您选择的方法取决于应用设计,但当应用专为小屏幕而设计,并且您希望通过将短生存期 activity 显示为对话框来提升平板电脑体验时,将 activity 显示为对话框通常很有用。
如需仅在大屏幕上将 activity 显示为对话框,请将 Theme.Holo.DialogWhenLarge 主题应用于 <activity> 清单元素:
<activity android:theme="@android:style/Theme.Holo.DialogWhenLarge" >
如需详细了解如何使用主题设置 activity 的样式,请参阅样式和主题。
关闭对话框
当用户点按使用 AlertDialog.Builder 创建的操作按钮时,系统会为您关闭对话框。
系统还会在用户点按对话框列表中的项时关闭对话框,列表使用单选按钮或复选框的情况除外。否则,您可以通过对 DialogFragment 调用 dismiss() 来手动关闭对话框。
如果您需要在对话框消失时执行特定操作,可以在 DialogFragment 中实现 onDismiss() 方法。
您还可取消对话框。这是一个特殊事件,表示用户离开对话框,且并未完成任务。如果用户点按返回按钮或点按对话框区域外部的屏幕,或者您对 Dialog 显式调用 cancel()(例如,为响应对话框中的“取消”按钮),就会发生这种情况。
如上例所示,您可以通过在 DialogFragment 类中实现 onCancel() 来响应取消事件。

