每个文本字段都需要特定类型的文本输入,例如电子邮件地址、电话号码或纯文本。您必须为应用中的每个文本字段指定输入类型,以便系统能够显示相应的软键盘输入法(例如屏幕键盘)。
除了输入法提供的按钮类型之外,您还可以指定相关行为,例如输入法是否提供拼写建议、是否将新句子的首字母大写,以及是否使用完成或下一步等操作按钮替换回车按钮。本页介绍了如何指定这些特征。
指定键盘类型
请始终通过向 <EditText> 元素添加 android:inputType 属性来声明文本字段的输入法。
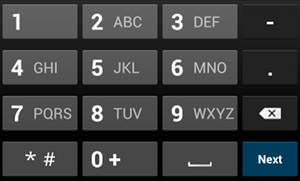
phone 输入类型。例如,如果您需要使用输入电话号码的输入法,请使用 "phone" 值:
<EditText android:id="@+id/phone" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="@string/phone_hint" android:inputType="phone" />
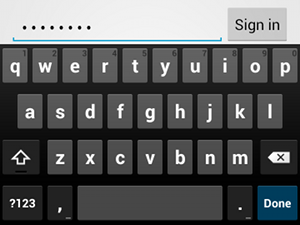
textPassword 输入类型。如果文本字段是用于输入密码,请使用 "textPassword" 值,以便让文本字段隐藏用户输入:
<EditText android:id="@+id/password" android:hint="@string/password_hint" android:inputType="textPassword" ... />
参考文档列出了 android:inputType 属性的多个值,您可以将其中一些值组合使用以指定输入法的外观和其他行为。
启用拼写建议和其他行为
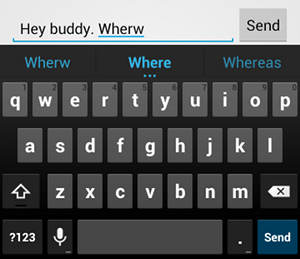
textAutoCorrect 可以自动更正拼写错误。借助 android:inputType 属性,您可以为输入法指定各种行为。最重要的是,如果文本字段是用于输入基本文本(例如短信),请使用 "textAutoCorrect" 值启用自动拼写更正。
您可以将不同的行为和输入法样式与 android:inputType 属性结合使用。例如,以下代码展示了如何创建既能够将句子的首字母大写,又能够自动更正拼写错误的文本字段:
<EditText android:id="@+id/message" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:inputType= "textCapSentences|textAutoCorrect" ... />
指定输入法操作
大多数软键盘输入法都会在左下角提供一个适合当前文本字段的用户操作按钮。默认情况下,系统会使用此按钮执行下一步或完成操作,除非文本字段支持多行文本(例如使用 android:inputType="textMultiLine"),在这种情况下,此操作按钮即为回车符。不过,您也可以指定可能更适合您的文本字段的其他操作,例如发送或转到。
如需指定键盘操作按钮,请使用操作值为 "actionSend" 或 "actionSearch" 等的 android:imeOptions 属性。例如:

android:imeOptions="actionSend",系统会显示发送按钮。<EditText android:id="@+id/search" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="@string/search_hint" android:inputType="text" android:imeOptions="actionSend" />
然后,您可以通过为 EditText 元素定义 TextView.OnEditorActionListener 来监听操作按钮按下操作。在监听器中,响应 EditorInfo 类中定义的相应 IME 操作 ID,例如 IME_ACTION_SEND,如以下示例所示:
Kotlin
findViewById<EditText>(R.id.search).setOnEditorActionListener { v, actionId, event -> return@setOnEditorActionListener when (actionId) { EditorInfo.IME_ACTION_SEND -> { sendMessage() true } else -> false } }
Java
EditText editText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.search); editText.setOnEditorActionListener(new OnEditorActionListener() { @Override public boolean onEditorAction(TextView v, int actionId, KeyEvent event) { boolean handled = false; if (actionId == EditorInfo.IME_ACTION_SEND) { sendMessage(); handled = true; } return handled; } });
提供自动填充建议
如果您想要在用户输入时提供建议,可以使用 EditText 的一个名为 AutoCompleteTextView 的子类。如需实现自动补全功能,您必须指定提供文本建议的 Adapter。有多种适配器可供选择,具体取决于数据的来源,例如数据库或数组。
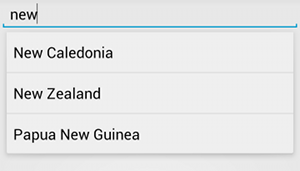
AutoCompleteTextView 示例。以下步骤介绍了如何使用 ArrayAdapter 来设置用于从数组提供建议的 AutoCompleteTextView:
- 将
AutoCompleteTextView添加到布局中。以下是一个仅包含文本字段的布局:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <AutoCompleteTextView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:id="@+id/autocomplete_country" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
- 定义包含所有文本建议的数组。例如,以下是国家/地区名称数组:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <string-array name="countries_array"> <item>Afghanistan</item> <item>Albania</item> <item>Algeria</item> <item>American Samoa</item> <item>Andorra</item> <item>Angola</item> <item>Anguilla</item> <item>Antarctica</item> ... </string-array> </resources>
- 在
Activity或Fragment中,使用以下代码指定用于提供建议的适配器:Kotlin
// Get a reference to the AutoCompleteTextView in the layout. val textView = findViewById(R.id.autocomplete_country) as AutoCompleteTextView // Get the string array. val countries: Array<out String> = resources.getStringArray(R.array.countries_array) // Create the adapter and set it to the AutoCompleteTextView. ArrayAdapter<String>(this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, countries).also { adapter -> textView.setAdapter(adapter) }
Java
// Get a reference to the AutoCompleteTextView in the layout. AutoCompleteTextView textView = (AutoCompleteTextView) findViewById(R.id.autocomplete_country); // Get the string array. String[] countries = getResources().getStringArray(R.array.countries_array); // Create the adapter and set it to the AutoCompleteTextView. ArrayAdapter<String> adapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>(this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, countries); textView.setAdapter(adapter);
在前面的示例中,会初始化新的
ArrayAdapter,以将countries_array字符串数组中的每个项目绑定到simple_list_item_1布局中的一个TextView。这是 Android 提供的布局,可为列表中的文本提供标准外观。 -
通过调用
setAdapter()将适配器分配给AutoCompleteTextView。

