כדי לעשות שימוש חוזר במקטעים, צריך לבנות אותם כרכיבים עצמאיים לחלוטין שמגדירים את הפריסה וההתנהגות שלהם. אחרי שתגדירו את המטרות האלה של מקטעים לשימוש חוזר, אפשר לשייך אותם לפעילות ולהתחבר אותם באמצעות לוגיקת האפליקציה, שיממשו את ממשק המשתמש המורכב הכולל.
לרוב, כדי להגיב בצורה נכונה לאירועי משתמשים ולשתף מידע על המצב, צריכים להיות להם ערוצי תקשורת בין הפעילות מקטעים או בין שני מקטעים או יותר. כדי לשמור על מקטעים עצמאים, אין בהם מקטעים שיתקשרו ישירות עם מקטעים אחרים, בפעילות המארח שלהם.
בספרייה Fragment יש שתי אפשרויות לתקשר:
ViewModel והמקטע
result API. האפשרות המומלצת תלויה בתרחיש לדוגמה. לשיתוף
נתונים קבועים עם ממשקי API מותאמים אישית, צריך להשתמש ב-ViewModel. עבור
תוצאה חד-פעמית עם נתונים שניתן למקם
Bundle, השתמשו במקטע
result API.
בקטעים הבאים מתואר כיצד להשתמש ב-ViewModel ובמקטע
ממשק ה-API של התוצאה לתקשורת בין המקטעים והפעילויות שלך.
שיתוף נתונים באמצעות ViewModel
ViewModel הוא בחירה אידיאלית כאשר
צריך לשתף נתונים בין
מקטעים מרובים או בין מקטעים והפעילות המארחת שלהם.
ViewModel אובייקטים מאחסנים וגם
ניהול נתוני ממשק המשתמש. מידע נוסף על ViewModel זמין במאמר
סקירה כללית של המודל.
שיתוף נתונים עם הפעילות של המארח
במקרים מסוימים, ייתכן שתצטרכו לשתף נתונים בין מקטעים את פעילות המארח שלהם. לדוגמה, אם אתם רוצים להחליף מצב של ממשק משתמש גלובלי שמבוסס על אינטראקציה בתוך מקטע.
כדאי להביא בחשבון את ItemViewModel הבאים:
Kotlin
class ItemViewModel : ViewModel() { private val mutableSelectedItem = MutableLiveData<Item>() val selectedItem: LiveData<Item> get() = mutableSelectedItem fun selectItem(item: Item) { mutableSelectedItem.value = item } }
Java
public class ItemViewModel extends ViewModel { private final MutableLiveData<Item> selectedItem = new MutableLiveData<Item>(); public void selectItem(Item item) { selectedItem.setValue(item); } public LiveData<Item> getSelectedItem() { return selectedItem; } }
בדוגמה הזו, הנתונים המאוחסנים ארוזים
MutableLiveData.
LiveData תואם למחזור החיים
ניראות של מחזיקי נתונים. MutableLiveData מאפשר לערך שלו להיות
השתנה. מידע נוסף על LiveData זמין במאמר
סקירה כללית של LiveData.
גם המקטע וגם הפעילות המארחת שלו יכולים לאחזר מופע משותף.
של ViewModel עם היקף פעילות על ידי העברת הפעילות אל
ViewModelProvider
constructor. ViewModelProvider מטפל ביצירת ViewModel
או לאחזר אותו, אם הוא כבר קיים. שני הרכיבים יכולים להבחין
תשנה את הנתונים האלה.
Kotlin
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() { // Using the viewModels() Kotlin property delegate from the activity-ktx // artifact to retrieve the ViewModel in the activity scope. private val viewModel: ItemViewModel by viewModels() override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) viewModel.selectedItem.observe(this, Observer { item -> // Perform an action with the latest item data. }) } } class ListFragment : Fragment() { // Using the activityViewModels() Kotlin property delegate from the // fragment-ktx artifact to retrieve the ViewModel in the activity scope. private val viewModel: ItemViewModel by activityViewModels() // Called when the item is clicked. fun onItemClicked(item: Item) { // Set a new item. viewModel.selectItem(item) } }
Java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private ItemViewModel viewModel; @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); viewModel = new ViewModelProvider(this).get(ItemViewModel.class); viewModel.getSelectedItem().observe(this, item -> { // Perform an action with the latest item data. }); } } public class ListFragment extends Fragment { private ItemViewModel viewModel; @Override public void onViewCreated(@NonNull View view, Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState); viewModel = new ViewModelProvider(requireActivity()).get(ItemViewModel.class); ... items.setOnClickListener(item -> { // Set a new item. viewModel.select(item); }); } }
שיתוף נתונים בין מקטעים
לעיתים קרובות, שני מקטעים או יותר באותה פעילות צריכים לתקשר עם שתי רשתות נוירונים זו מול זו. לדוגמה, נניח שמקטע אחד מציג רשימה נוסף שמאפשר למשתמש להחיל מסננים שונים על הרשימה. הטמעת הפנייה הזו אינה טריוויאלית ללא המקטעים. בתקשורת ישירה, אבל הם כבר לא עצמאי. בנוסף, שני המקטעים חייבים לטפל בתרחיש שבו הקטע השני עדיין לא נוצר או גלוי.
המקטעים האלה יכולים לשתף ViewModel באמצעות היקף הפעילות שלהם.
כדי לטפל בתקשורת הזו. על ידי שיתוף של ViewModel באופן הזה,
הקטעים לא צריכים לדעת זה על זה, ואת הפעילות
לא נדרשת לעשות דבר כדי להקל על התקשורת.
הדוגמה הבאה ממחישה איך שני מקטעים יכולים להשתמש
ViewModel כדי לתקשר:
Kotlin
class ListViewModel : ViewModel() { val filters = MutableLiveData<Set<Filter>>() private val originalList: LiveData<List<Item>>() = ... val filteredList: LiveData<List<Item>> = ... fun addFilter(filter: Filter) { ... } fun removeFilter(filter: Filter) { ... } } class ListFragment : Fragment() { // Using the activityViewModels() Kotlin property delegate from the // fragment-ktx artifact to retrieve the ViewModel in the activity scope. private val viewModel: ListViewModel by activityViewModels() override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { viewModel.filteredList.observe(viewLifecycleOwner, Observer { list -> // Update the list UI. } } } class FilterFragment : Fragment() { private val viewModel: ListViewModel by activityViewModels() override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { viewModel.filters.observe(viewLifecycleOwner, Observer { set -> // Update the selected filters UI. } } fun onFilterSelected(filter: Filter) = viewModel.addFilter(filter) fun onFilterDeselected(filter: Filter) = viewModel.removeFilter(filter) }
Java
public class ListViewModel extends ViewModel { private final MutableLiveData<Set<Filter>> filters = new MutableLiveData<>(); private final LiveData<List<Item>> originalList = ...; private final LiveData<List<Item>> filteredList = ...; public LiveData<List<Item>> getFilteredList() { return filteredList; } public LiveData<Set<Filter>> getFilters() { return filters; } public void addFilter(Filter filter) { ... } public void removeFilter(Filter filter) { ... } } public class ListFragment extends Fragment { private ListViewModel viewModel; @Override public void onViewCreated(@NonNull View view, Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState); viewModel = new ViewModelProvider(requireActivity()).get(ListViewModel.class); viewModel.getFilteredList().observe(getViewLifecycleOwner(), list -> { // Update the list UI. }); } } public class FilterFragment extends Fragment { private ListViewModel viewModel; @Override public void onViewCreated(@NonNull View view, Bundle savedInstanceState) { viewModel = new ViewModelProvider(requireActivity()).get(ListViewModel.class); viewModel.getFilters().observe(getViewLifecycleOwner(), set -> { // Update the selected filters UI. }); } public void onFilterSelected(Filter filter) { viewModel.addFilter(filter); } public void onFilterDeselected(Filter filter) { viewModel.removeFilter(filter); } }
שני הקטעים משתמשים בפעילות המארח שלהם כהיקף של
ViewModelProvider מאחר שהמקטעים משתמשים באותו היקף, הם מקבלים
את אותו מופע של ViewModel, שמאפשר להם לתקשר
הלוך ושוב.
שיתוף נתונים בין מקטע הורה למקטע צאצא
בעבודה עם מקטעים צאצאים, המקטע ההורה והצאצא שלו
יכול להיות שתצטרכו לשתף נתונים בין מקטעים. כדי לשתף נתונים בין
את המקטעים האלה, צריך להשתמש במקטע ההורה כהיקף ViewModel, כפי שמוצג
בדוגמה הבאה:
Kotlin
class ListFragment: Fragment() { // Using the viewModels() Kotlin property delegate from the fragment-ktx // artifact to retrieve the ViewModel. private val viewModel: ListViewModel by viewModels() override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { viewModel.filteredList.observe(viewLifecycleOwner, Observer { list -> // Update the list UI. } } } class ChildFragment: Fragment() { // Using the viewModels() Kotlin property delegate from the fragment-ktx // artifact to retrieve the ViewModel using the parent fragment's scope private val viewModel: ListViewModel by viewModels({requireParentFragment()}) ... }
Java
public class ListFragment extends Fragment { private ListViewModel viewModel; @Override public void onViewCreated(@NonNull View view, Bundle savedInstanceState) { viewModel = new ViewModelProvider(this).get(ListViewModel.class); viewModel.getFilteredList().observe(getViewLifecycleOwner(), list -> { // Update the list UI. } } } public class ChildFragment extends Fragment { private ListViewModel viewModel; @Override public void onViewCreated(@NonNull View view, Bundle savedInstanceState) { viewModel = new ViewModelProvider(requireParentFragment()).get(ListViewModel.class); ... } }
הגבלה של ViewModel לתרשים הניווט
אם משתמשים בספריית הניווט, אפשר גם
היקף ViewModel למחזור החיים של יעד
NavBackStackEntry עבור
לדוגמה, ViewModel יכול להיות בהיקף של NavBackStackEntry
של ListFragment:
Kotlin
class ListFragment: Fragment() { // Using the navGraphViewModels() Kotlin property delegate from the fragment-ktx // artifact to retrieve the ViewModel using the NavBackStackEntry scope. // R.id.list_fragment == the destination id of the ListFragment destination private val viewModel: ListViewModel by navGraphViewModels(R.id.list_fragment) override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { viewModel.filteredList.observe(viewLifecycleOwner, Observer { item -> // Update the list UI. } } }
Java
public class ListFragment extends Fragment { private ListViewModel viewModel; @Override public void onViewCreated(@NonNull View view, Bundle savedInstanceState) { NavController navController = NavHostFragment.findNavController(this); NavBackStackEntry backStackEntry = navController.getBackStackEntry(R.id.list_fragment) viewModel = new ViewModelProvider(backStackEntry).get(ListViewModel.class); viewModel.getFilteredList().observe(getViewLifecycleOwner(), list -> { // Update the list UI. } } }
למידע נוסף על קביעת היקף ל-ViewModel ל-NavBackStackEntry, אפשר לעיין במאמר
אינטראקציה פרוגרמטית עם רכיב הניווט.
קבלת תוצאות באמצעות Fragment result API
במקרים מסוימים, יכול להיות שתרצו להעביר ערך חד-פעמי בין שני מקטעים או בין מקטע לבין פעילות המארח שלו. לדוגמה, ייתכן שיש לך מקטע שקורא קודי QR, ומעביר את הנתונים חזרה למקטע קודם.
ב-Fragment מגרסה 1.3.0 ואילך,
בכל FragmentManager
implements
FragmentResultOwner
כלומר FragmentManager יכול לשמש כמאגר מרכזי של מקטעים
תוצאות. השינוי הזה מאפשר לרכיבים לתקשר זה עם זה באמצעות
הגדרה של תוצאות מקטעים והאזנה לתוצאות האלה, בלי שיהיה צורך
ליצור הפניות ישירות בין הרכיבים האלה.
העברת תוצאות בין מקטעים
כדי להעביר נתונים חזרה למקטע A ממקטע B, קודם צריך להגדיר האזנה לתוצאה
בקטע A, המקטע שמקבל את התוצאה. שיחת טלפון
setFragmentResultListener()
בקטע FragmentManager של מקטע A, כמו שאפשר לראות בדוגמה הבאה:
Kotlin
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Use the Kotlin extension in the fragment-ktx artifact. setFragmentResultListener("requestKey") { requestKey, bundle -> // We use a String here, but any type that can be put in a Bundle is supported. val result = bundle.getString("bundleKey") // Do something with the result. } }
Java
@Override public void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); getParentFragmentManager().setFragmentResultListener("requestKey", this, new FragmentResultListener() { @Override public void onFragmentResult(@NonNull String requestKey, @NonNull Bundle bundle) { // We use a String here, but any type that can be put in a Bundle is supported. String result = bundle.getString("bundleKey"); // Do something with the result. } }); }
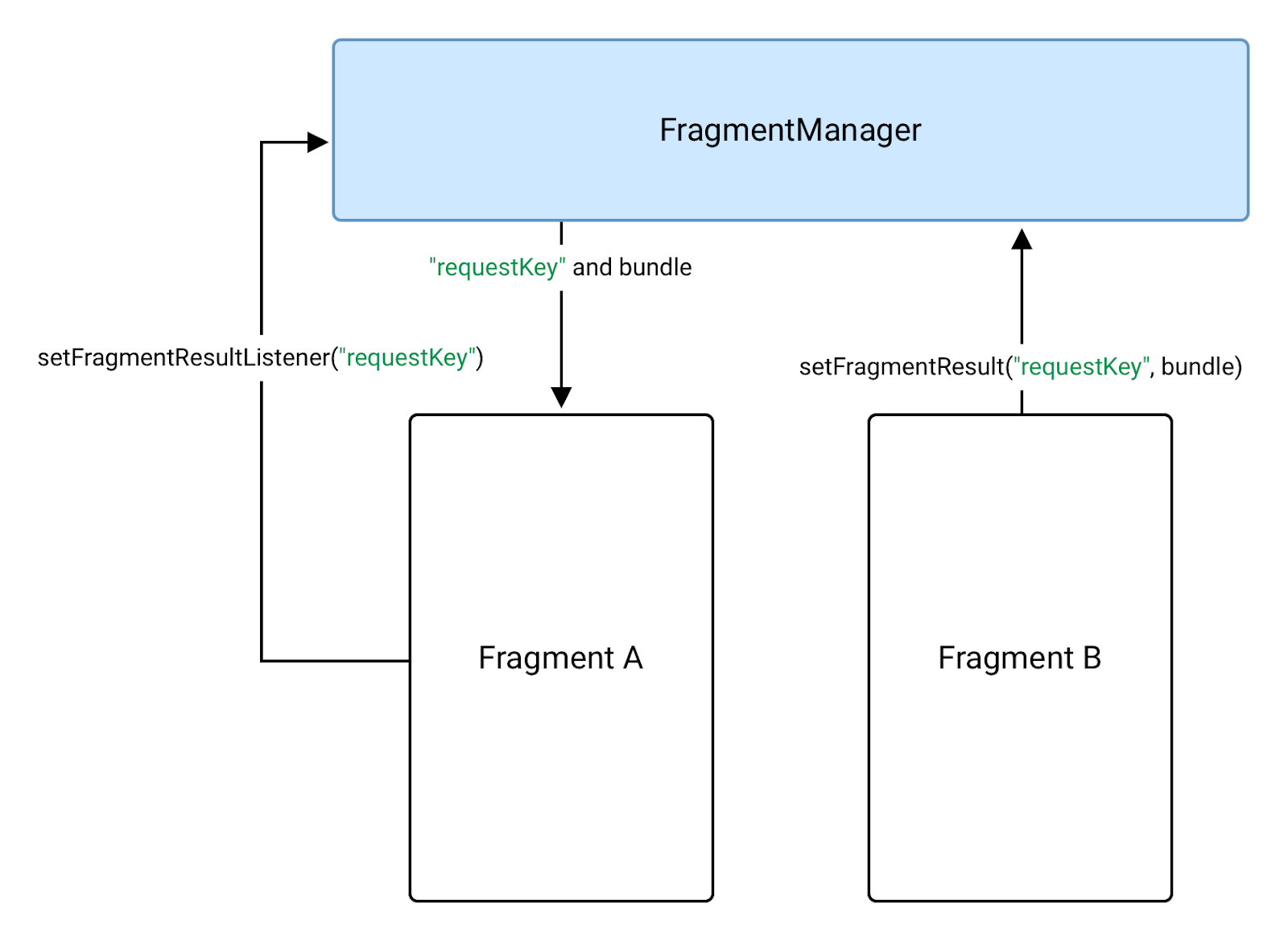
FragmentManager.בקטע B, הקטע שיוצר את התוצאה, קובעים את התוצאה
באותו FragmentManager באמצעות אותו requestKey. אפשר לבצע
אז באמצעות
setFragmentResult()
API:
Kotlin
button.setOnClickListener { val result = "result" // Use the Kotlin extension in the fragment-ktx artifact. setFragmentResult("requestKey", bundleOf("bundleKey" to result)) }
Java
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { Bundle result = new Bundle(); result.putString("bundleKey", "result"); getParentFragmentManager().setFragmentResult("requestKey", result); } });
לאחר מכן, מקטע A מקבל את התוצאה ומבצע את הקריאה החוזרת (callback) של ה-listener
אחרי שהקטע
STARTED
אפשר לשמור רק מאזין אחד ותוצאה למפתח נתון. אם תתקשרו
setFragmentResult() יותר מפעם אחת לאותו מפתח, ואם ה-listener
אינו STARTED, המערכת מחליפה את כל התוצאות הממתינות בתוצאות המעודכנות
תוצאה אחת.
אם מגדירים תוצאה ללא מאזין מתאים שיקבל אותה,
התוצאה תישמר ב-FragmentManager עד שתגדירו אוזן עם
אותו מקש. לאחר שהמאזין מקבל תוצאה ומפעיל את
קריאה חוזרת (callback) של onFragmentResult(), התוצאה נמחקת. להתנהגות הזו
שתי השלכות עיקריות:
- מקטעים במקבץ האחורי לא מקבלים תוצאות עד
מופיעים כ-
STARTED. - אם המקטע להאזנה לתוצאה הוא
STARTEDכשהתוצאה מוגדרת, הקריאה החוזרת של המאזין ואז מופעלת באופן מיידי.
בדיקת תוצאות של מקטעים
כדאי להשתמש
FragmentScenario
כדי לבדוק שיחות אל setFragmentResult() ו-setFragmentResultListener().
כדי ליצור תרחיש למקטע בבדיקה, השתמשו ב-
launchFragmentInContainer
או
launchFragment,
ואז מפעילים ידנית את השיטה שלא נבדקת.
כדי לבדוק את setFragmentResultListener(), צריך ליצור תרחיש עם
מקטע שמבצע את הקריאה ל-setFragmentResultListener(). בשלב הבא,
צריך להתקשר ישירות אל setFragmentResult() ולאמת את התוצאה:
@Test
fun testFragmentResultListener() {
val scenario = launchFragmentInContainer<ResultListenerFragment>()
scenario.onFragment { fragment ->
val expectedResult = "result"
fragment.parentFragmentManager.setFragmentResult("requestKey", bundleOf("bundleKey" to expectedResult))
assertThat(fragment.result).isEqualTo(expectedResult)
}
}
class ResultListenerFragment : Fragment() {
var result : String? = null
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
// Use the Kotlin extension in the fragment-ktx artifact.
setFragmentResultListener("requestKey") { requestKey, bundle ->
result = bundle.getString("bundleKey")
}
}
}
כדי לבדוק את setFragmentResult(), צריך ליצור תרחיש עם המקטע שגורם
קריאה אל setFragmentResult(). בשלב הבא, מתקשרים אל setFragmentResultListener()
ישירות, ומאמתים את התוצאה:
@Test
fun testFragmentResult() {
val scenario = launchFragmentInContainer<ResultFragment>()
lateinit var actualResult: String?
scenario.onFragment { fragment ->
fragment.parentFragmentManager
.setFragmentResultListener("requestKey") { requestKey, bundle ->
actualResult = bundle.getString("bundleKey")
}
}
onView(withId(R.id.result_button)).perform(click())
assertThat(actualResult).isEqualTo("result")
}
class ResultFragment : Fragment(R.layout.fragment_result) {
override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
view.findViewById(R.id.result_button).setOnClickListener {
val result = "result"
// Use the Kotlin extension in the fragment-ktx artifact.
setFragmentResult("requestKey", bundleOf("bundleKey" to result))
}
}
}
העברת התוצאות בין מקטעי הורה ומקטע צאצא
כדי להעביר תוצאה ממקטע צאצא להורה,
יש להשתמש ב-getChildFragmentManager() ממקטע ההורה במקום ב-
getParentFragmentManager() כשמחייגים setFragmentResultListener().
Kotlin
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Set the listener on the child fragmentManager. childFragmentManager.setFragmentResultListener("requestKey") { key, bundle -> val result = bundle.getString("bundleKey") // Do something with the result. } }
Java
@Override public void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Set the listener on the child fragmentManager. getChildFragmentManager() .setFragmentResultListener("requestKey", this, new FragmentResultListener() { @Override public void onFragmentResult(@NonNull String requestKey, @NonNull Bundle bundle) { String result = bundle.getString("bundleKey"); // Do something with the result. } }); }
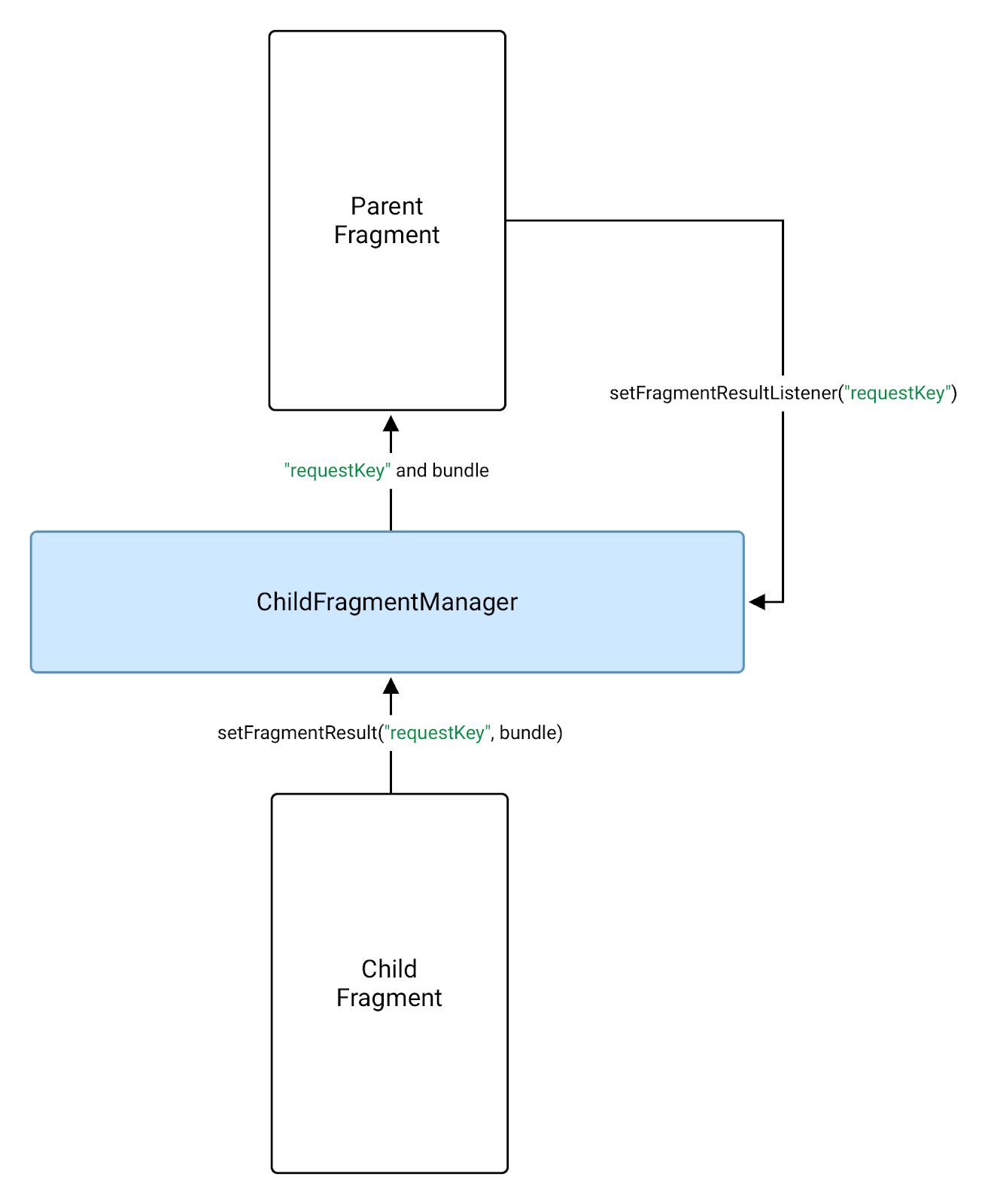
FragmentManager כדי לשלוח תוצאה להורה.מקטע הצאצא מגדיר את התוצאה ב-FragmentManager שלו. ההורה
הפונקציה מקבלת את התוצאה כשהמקטע הוא STARTED:
Kotlin
button.setOnClickListener { val result = "result" // Use the Kotlin extension in the fragment-ktx artifact. setFragmentResult("requestKey", bundleOf("bundleKey" to result)) }
Java
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { Bundle result = new Bundle(); result.putString("bundleKey", "result"); // The child fragment needs to still set the result on its parent fragment manager. getParentFragmentManager().setFragmentResult("requestKey", result); } });
קבלת תוצאות בפעילות המארח
כדי לקבל תוצאת מקטע בפעילות המארח, צריך להגדיר האזנה לתוצאה
במנהל המקטעים באמצעות
getSupportFragmentManager()
Kotlin
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) supportFragmentManager .setFragmentResultListener("requestKey", this) { requestKey, bundle -> // We use a String here, but any type that can be put in a Bundle is supported. val result = bundle.getString("bundleKey") // Do something with the result. } } }
Java
class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { @Override public void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); getSupportFragmentManager().setFragmentResultListener("requestKey", this, new FragmentResultListener() { @Override public void onFragmentResult(@NonNull String requestKey, @NonNull Bundle bundle) { // We use a String here, but any type that can be put in a Bundle is supported. String result = bundle.getString("bundleKey"); // Do something with the result. } }); } }
