検索は Android の主要なユーザー機能です。コンテンツがデバイス上にあるかインターネット上にあるかに関係なく、ユーザーが使用できるデータを検索できる必要があります。一貫性のある検索エクスペリエンスをユーザーに提供するために、Android には、アプリに検索を実装するのに役立つ検索フレームワークが用意されています。
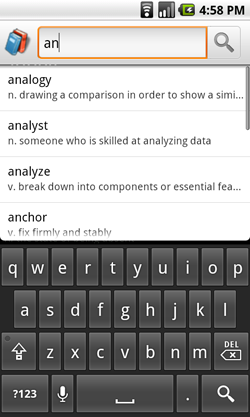
図 1. カスタム検索候補が表示された検索ダイアログ。
検索フレームワークは、画面の一番上に表示される検索ダイアログと、アクティビティ レイアウトに埋め込むことができる検索ウィジェット(SearchView)という 2 つの検索入力モードを提供します。どちらのモードでも、Android システムが、検索を実行する特定のアクティビティに検索クエリを渡すことによって検索の実装をサポートします。また、検索ダイアログまたは検索ウィジェットでは、ユーザーが入力しているときに検索候補を表示させることもできます。図 1 に、オプションの検索候補が表示されている検索ダイアログの例を示します。
検索ダイアログまたは検索ウィジェットをセットアップすると、以下を行えるようになります。
- 音声検索を有効にします。
- 最近のユーザークエリに基づいて検索候補を表示します。
- アプリデータの実際の検索結果と一致するカスタム検索候補を表示する。
- アプリの検索候補をシステム全体のクイック検索ボックスで表示します。
注: 検索フレームワークは、データを検索するための API を提供していません。検索を実行するには、データに適した API を使用する必要があります。たとえば、データが SQLite データベースに保存されている場合は、android.database.sqlite API を使用して検索を実行します。
また、アプリ内で検索インターフェースを呼び出す専用の検索ボタンがデバイスにあるとは限りません。検索ダイアログまたはカスタムのインターフェースを使用する場合は、検索インターフェースを有効化する検索ボタンを UI に用意する必要があります。詳しくは、検索ダイアログを呼び出すをご覧ください。
以下のページで、Android のフレームワークを使用して検索を実装する方法が説明されています。
- 検索インターフェースを作成する
- 検索ダイアログまたは検索ウィジェットを使用するようにアプリを設定する方法が説明されています。
- 最近のクエリに基づく候補を追加する
- 以前に使用したクエリに基づいて候補を表示する方法が説明されています。
- カスタム候補を追加する
- アプリのカスタムデータに基づいて候補を表示する方法と、それらの候補をシステム全体のクイック検索ボックスに表示する方法が説明されています。
- 検索可能性の設定
- 検索可能構成ファイルのリファレンス ドキュメント。特定の動作については、他のドキュメントの設定ファイルの説明もご覧ください。
ユーザーのプライバシーを保護する
アプリに検索を実装する場合、ユーザーのプライバシーを保護するための対策を講じます。多くのユーザーは、スマートフォンでのアクティビティ(検索を含む)を個人情報と考えています。ユーザーのプライバシーを保護するには、以下の原則を遵守する必要があります。
- サーバーに個人情報を送信しない(送信する必要がある場合はログに記録しない)
個人情報とは、名前、メールアドレス、お支払い情報などのユーザー個人を特定可能な情報や、そうした情報に合理的に関連付けることができるその他のデータのことです。サーバーのサポートが必要な検索をアプリで実装する場合、検索クエリとともに個人情報を送信しないでください。たとえば、郵便番号で店舗を検索する場合、ユーザー ID も送信する必要はないため、サーバーには郵便番号のみを送信します。個人情報を送信する必要がある場合は、ログに記録しないでください。ログに記録する必要がある場合は、データを厳重に保護し、できるだけ早く消去してください。
- 検索履歴を消去する方法をユーザーに提供する
検索フレームワークを利用すると、ユーザーが入力しているときにコンテキスト固有の候補をアプリで表示できます。ユーザーが以前のセッションで行った検索やその他のアクションに基づいて候補が表示されることもあります。ユーザーは、以前の検索が他のデバイス ユーザーに表示されないようにしたいと思っているかもしれません。以前の検索アクティビティがわかるような候補をアプリで表示する場合、ユーザーが検索履歴を消去できる方法を実装してください。
SearchRecentSuggestionsを使用している場合は、clearHistory()メソッドを呼び出すことができます。カスタム候補を実装する場合は、ユーザーが実行可能な同様の「履歴消去」メソッドをコンテンツ プロバイダで提供する必要があります。

