คอมโพเนนต์การนำทางประกอบด้วยคลาส NavigationUI
คลาสนี้มีเมธอดแบบคงที่ซึ่งจัดการการนําทางด้วยแถบแอปด้านบน ลิ้นชักการนําทาง และการนําทางด้านล่าง
แถบแอปด้านบน
แถบแอปด้านบนเป็นตำแหน่งที่แสดงข้อมูลและการดําเนินการจากหน้าจอปัจจุบันอย่างสอดคล้องกันตลอดทั้งแอป
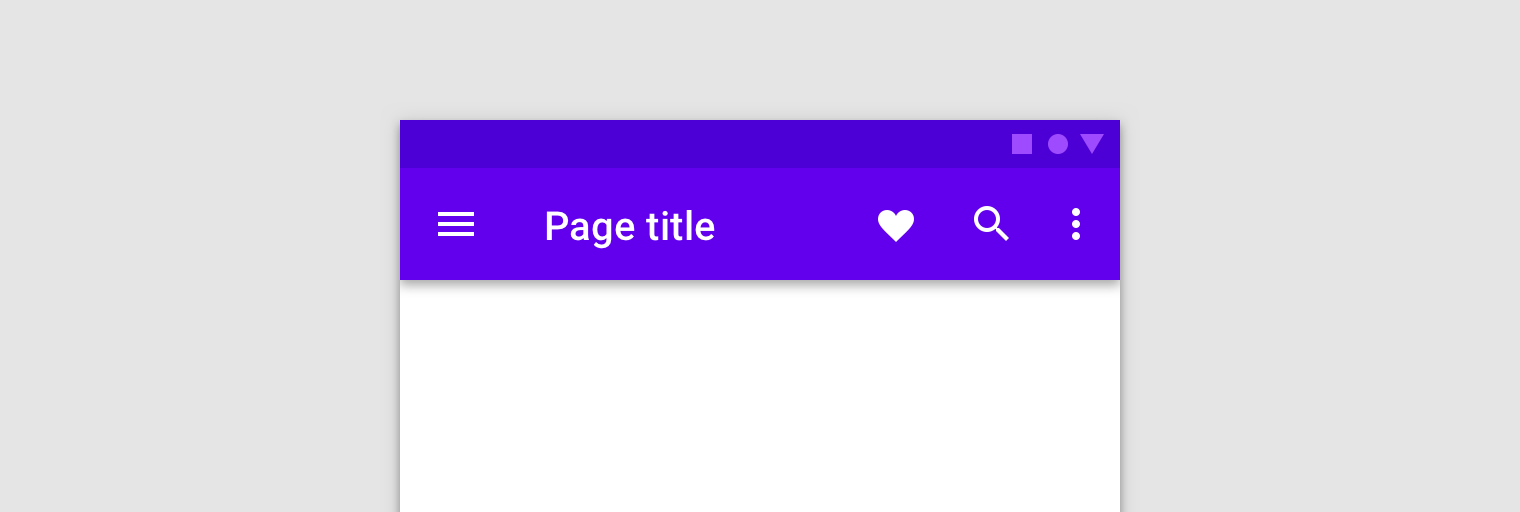
NavigationUI มีเมธอดที่จะอัปเดตเนื้อหาในแถบแอปด้านบนโดยอัตโนมัติเมื่อผู้ใช้ไปยังส่วนต่างๆ ของแอป เช่น NavigationUI ใช้ป้ายกํากับปลายทางจากกราฟการนําทางเพื่ออัปเดตชื่อแถบแอปด้านบนให้เป็นปัจจุบันอยู่เสมอ
<navigation> <fragment ... android:label="Page title"> ... </fragment> </navigation>
เมื่อใช้ NavigationUI กับการติดตั้งใช้งานแถบแอปด้านบนที่อธิบายไว้ด้านล่าง ระบบจะป้อนข้อมูลป้ายกำกับที่คุณแนบกับปลายทางโดยอัตโนมัติจากอาร์กิวเมนต์ที่ระบุให้กับปลายทางโดยใช้รูปแบบ {argName} ในป้ายกำกับ
NavigationUI รองรับแถบแอปด้านบนประเภทต่อไปนี้
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับแถบแอปได้ที่ตั้งค่าแถบแอป
AppBarConfiguration
NavigationUI ใช้ออบเจ็กต์ AppBarConfiguration เพื่อจัดการลักษณะการทำงานของปุ่มการนำทางที่มุมซ้ายบนของพื้นที่แสดงผลของแอป ลักษณะการทํางานของปุ่มนําทางจะเปลี่ยนไปโดยขึ้นอยู่กับว่าผู้ใช้อยู่ที่ปลายทางระดับบนสุดหรือไม่
ปลายทางระดับบนสุดคือปลายทางระดับรูทหรือระดับสูงสุดในชุดปลายทางที่เกี่ยวข้องตามลําดับชั้น ปลายทางระดับบนสุดจะไม่แสดงปุ่ม "ขึ้น" ในแถบแอปด้านบนเนื่องจากไม่มีปลายทางในระดับที่สูงขึ้น โดยค่าเริ่มต้น ปลายทางเริ่มต้นของแอปจะเป็นปลายทางระดับบนสุดเพียงแห่งเดียว
เมื่อผู้ใช้อยู่ที่ปลายทางระดับบนสุด ปุ่มการนำทางจะเปลี่ยนเป็น
ไอคอนลิ้นชัก
![]() หากปลายทางใช้
หากปลายทางใช้ DrawerLayout หากปลายทางไม่ได้ใช้ DrawerLayout ระบบจะซ่อนปุ่มการนำทาง เมื่อผู้ใช้อยู่ที่ปลายทางอื่น ปุ่มการนําทางจะปรากฏเป็นปุ่มขึ้น
 หากต้องการกำหนดค่าปุ่มการนำทางโดยใช้เฉพาะปลายทางเริ่มต้นเป็นปลายทางระดับบนสุด ให้สร้างออบเจ็กต์
หากต้องการกำหนดค่าปุ่มการนำทางโดยใช้เฉพาะปลายทางเริ่มต้นเป็นปลายทางระดับบนสุด ให้สร้างออบเจ็กต์ AppBarConfiguration และส่งกราฟการนำทางที่เกี่ยวข้อง ดังที่แสดงด้านล่าง
Kotlin
val appBarConfiguration = AppBarConfiguration(navController.graph)
Java
AppBarConfiguration appBarConfiguration = new AppBarConfiguration.Builder(navController.getGraph()).build();
ในบางกรณี คุณอาจต้องกําหนดปลายทางระดับบนสุดหลายรายการแทนการใช้ปลายทางเริ่มต้น การใช้ BottomNavigationView เป็นกรณีการใช้งานที่พบบ่อยสำหรับกรณีนี้ ซึ่งคุณอาจมีหน้าจอพี่น้องที่ไม่ได้เชื่อมโยงกันตามลําดับชั้น และแต่ละหน้าจออาจมีปลายทางที่เกี่ยวข้องเป็นของตนเอง ในกรณีเช่นนี้ คุณสามารถส่งชุดรหัสปลายทางไปยังคอนสตรคเตอร์แทนได้ ดังที่แสดงด้านล่าง
Kotlin
val appBarConfiguration = AppBarConfiguration(setOf(R.id.main, R.id.profile))
Java
AppBarConfiguration appBarConfiguration = new AppBarConfiguration.Builder(R.id.main, R.id.profile).build();
สร้างแถบเครื่องมือ
หากต้องการสร้างแถบเครื่องมือด้วย NavigationUI ก่อนอื่นให้กำหนดแถบในกิจกรรมหลัก ดังที่แสดง
<LinearLayout> <androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar android:id="@+id/toolbar" /> <androidx.fragment.app.FragmentContainerView android:id="@+id/nav_host_fragment" ... /> ... </LinearLayout>
จากนั้นเรียกใช้ setupWithNavController() จากเมธอด onCreate() ของกิจกรรมหลัก ดังที่แสดงในตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้
Kotlin
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) ... val navController = findNavController(R.id.nav_host_fragment) val appBarConfiguration = AppBarConfiguration(navController.graph) findViewById<Toolbar>(R.id.toolbar) .setupWithNavController(navController, appBarConfiguration) }
Java
@Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); ... NavController navController = Navigation.findNavController(this, R.id.nav_host_fragment); AppBarConfiguration appBarConfiguration = new AppBarConfiguration.Builder(navController.getGraph()).build(); Toolbar toolbar = findViewById(R.id.toolbar); NavigationUI.setupWithNavController( toolbar, navController, appBarConfiguration); }
หากต้องการกำหนดค่าปุ่มการนําทางให้ปรากฏเป็นปุ่มขึ้นสําหรับปลายทางทั้งหมด ให้ส่งชุดรหัสปลายทางที่ว่างเปล่าสําหรับปลายทางระดับบนสุดเมื่อสร้าง AppBarConfiguration ซึ่งอาจมีประโยชน์ในกรณีที่คุณมีกิจกรรมที่ 2 ที่ควรแสดงปุ่มขึ้นใน Toolbar ของปลายทางทั้งหมด ซึ่งจะช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ไปยังกิจกรรมหลักได้เมื่อไม่มีปลายทางอื่นในกองซ้อนด้านหลัง คุณสามารถใช้ setFallbackOnNavigateUpListener() เพื่อควบคุมลักษณะการทํางานของเงื่อนไขที่ทำงานในกรณีที่ navigateUp() ไม่ทําการใดๆ ดังที่แสดงในตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้
Kotlin
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { ... val navHostFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.nav_host_fragment) as NavHostFragment val navController = navHostFragment.navController val appBarConfiguration = AppBarConfiguration( topLevelDestinationIds = setOf(), fallbackOnNavigateUpListener = ::onSupportNavigateUp ) findViewById<Toolbar>(R.id.toolbar) .setupWithNavController(navController, appBarConfiguration) }
Java
@Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { ... NavHostFragment navHostFragment = (NavHostFragment) supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.nav_host_fragment); NavController navController = navHostFragment.getNavController(); AppBarConfiguration appBarConfiguration = new AppBarConfiguration.Builder() .setFallbackOnNavigateUpListener(::onSupportNavigateUp) .build(); Toolbar toolbar = findViewById(R.id.toolbar); NavigationUI.setupWithNavController( toolbar, navController, appBarConfiguration); }
รวม CollapsingToolbarLayout
หากต้องการใส่ CollapsingToolbarLayout ไว้ในแถบเครื่องมือ ให้กําหนดแถบเครื่องมือและเลย์เอาต์โดยรอบในกิจกรรมก่อน ดังที่แสดงด้านล่าง
<LinearLayout> <com.google.android.material.appbar.AppBarLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="@dimen/tall_toolbar_height"> <com.google.android.material.appbar.CollapsingToolbarLayout android:id="@+id/collapsing_toolbar_layout" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" app:contentScrim="?attr/colorPrimary" app:expandedTitleGravity="top" app:layout_scrollFlags="scroll|exitUntilCollapsed|snap"> <androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar android:id="@+id/toolbar" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="?attr/actionBarSize" app:layout_collapseMode="pin"/> </com.google.android.material.appbar.CollapsingToolbarLayout> </com.google.android.material.appbar.AppBarLayout> <androidx.fragment.app.FragmentContainerView android:id="@+id/nav_host_fragment" ... /> ... </LinearLayout>
ถัดไป ให้เรียกใช้ setupWithNavController()
จากเมธอด onCreate ของกิจกรรมหลัก ดังที่แสดงด้านล่าง
Kotlin
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) ... val layout = findViewById<CollapsingToolbarLayout>(R.id.collapsing_toolbar_layout) val toolbar = findViewById<Toolbar>(R.id.toolbar) val navHostFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.nav_host_fragment) as NavHostFragment val navController = navHostFragment.navController val appBarConfiguration = AppBarConfiguration(navController.graph) layout.setupWithNavController(toolbar, navController, appBarConfiguration) }
Java
@Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); ... CollapsingToolbarLayout layout = findViewById(R.id.collapsing_toolbar_layout); Toolbar toolbar = findViewById(R.id.toolbar); NavHostFragment navHostFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.nav_host_fragment); NavController navController = navHostFragment.getNavController(); AppBarConfiguration appBarConfiguration = new AppBarConfiguration.Builder(navController.getGraph()).build(); NavigationUI.setupWithNavController(layout, toolbar, navController, appBarConfiguration); }
แถบการดำเนินการ
หากต้องการเพิ่มการรองรับการนําทางไปยังแถบการดำเนินการเริ่มต้น ให้เรียกใช้ setupActionBarWithNavController() จากเมธอด onCreate() ของกิจกรรมหลัก ดังที่แสดงด้านล่าง โปรดทราบว่าคุณต้องประกาศ AppBarConfiguration ไว้นอก onCreate() เนื่องจากคุณต้องใช้ AppBarConfiguration เมื่อลบล้าง onSupportNavigateUp() ด้วย
Kotlin
private lateinit var appBarConfiguration: AppBarConfiguration ... override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { ... val navHostFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.nav_host_fragment) as NavHostFragment val navController = navHostFragment.navController appBarConfiguration = AppBarConfiguration(navController.graph) setupActionBarWithNavController(navController, appBarConfiguration) }
Java
AppBarConfiguration appBarConfiguration; ... @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { ... NavHostFragment navHostFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.nav_host_fragment); NavController navController = navHostFragment.getNavController(); appBarConfiguration = new AppBarConfiguration.Builder(navController.getGraph()).build(); NavigationUI.setupActionBarWithNavController(this, navController, appBarConfiguration); }
ถัดไป ให้ลบล้าง onSupportNavigateUp() เพื่อจัดการการไปยังด้านบน
Kotlin
override fun onSupportNavigateUp(): Boolean { val navController = findNavController(R.id.nav_host_fragment) return navController.navigateUp(appBarConfiguration) || super.onSupportNavigateUp() }
Java
@Override public boolean onSupportNavigateUp() { NavController navController = Navigation.findNavController(this, R.id.nav_host_fragment); return NavigationUI.navigateUp(navController, appBarConfiguration) || super.onSupportNavigateUp(); }
รองรับแถบแอปรูปแบบต่างๆ
การเพิ่มแถบแอปด้านบนลงในกิจกรรมจะทํางานได้ดีเมื่อเลย์เอาต์ของแถบแอปคล้ายกันสําหรับปลายทางแต่ละแห่งในแอป อย่างไรก็ตาม หากแถบแอปด้านบนมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงอย่างมากในปลายทางต่างๆ ให้พิจารณานําแถบแอปด้านบนออกจากกิจกรรมและกำหนดไว้ในแต่ละกลุ่มย่อยปลายทางแทน
ตัวอย่างเช่น ปลายทางหนึ่งอาจใช้ Toolbar มาตรฐาน ขณะที่ปลายทางอื่นใช้ AppBarLayout เพื่อสร้างแถบแอปที่ซับซ้อนมากขึ้นพร้อมแท็บ ดังที่แสดงในรูปที่ 2
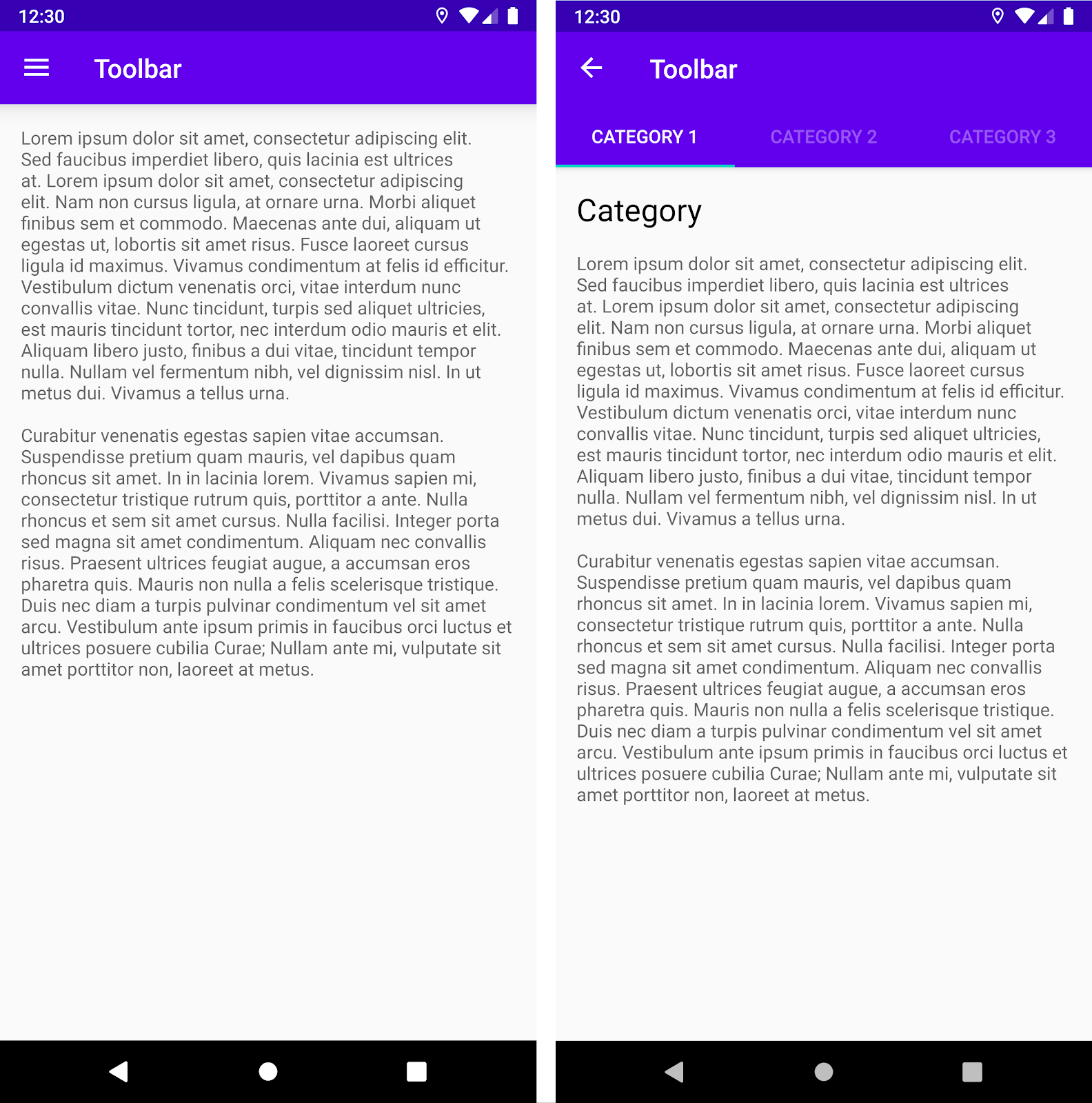
Toolbar AppBarLayout ที่มี Toolbar และแท็บหากต้องการใช้ตัวอย่างนี้ภายในข้อมูลโค้ดของปลายทางโดยใช้ NavigationUI ก่อนอื่นให้กําหนดแถบแอปในเลย์เอาต์ข้อมูลโค้ดแต่ละรายการ โดยเริ่มจากข้อมูลโค้ดปลายทางที่ใช้แถบเครื่องมือมาตรฐาน ดังนี้
<LinearLayout>
<androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar
android:id="@+id/toolbar"
... />
...
</LinearLayout>
ถัดไป ให้กําหนดข้อมูลโค้ดปลายทางที่ใช้แถบแอปที่มีแท็บ
<LinearLayout>
<com.google.android.material.appbar.AppBarLayout
... />
<androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar
android:id="@+id/toolbar"
... />
<com.google.android.material.tabs.TabLayout
... />
</com.google.android.material.appbar.AppBarLayout>
...
</LinearLayout>
ตรรกะการกําหนดค่าการนําทางเหมือนกันสําหรับทั้ง 2 รายการนี้ ยกเว้นว่าคุณควรเรียกใช้ setupWithNavController() จากภายในเมธอด onViewCreated() ของแต่ละรายการแทนที่จะเริ่มต้นจากกิจกรรม
Kotlin
override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { val navController = findNavController() val appBarConfiguration = AppBarConfiguration(navController.graph) view.findViewById<Toolbar>(R.id.toolbar) .setupWithNavController(navController, appBarConfiguration) }
Java
@Override public void onViewCreated(@NonNull View view, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { NavController navController = Navigation.findNavController(view); AppBarConfiguration appBarConfiguration = new AppBarConfiguration.Builder(navController.getGraph()).build(); Toolbar toolbar = view.findViewById(R.id.toolbar); NavigationUI.setupWithNavController( toolbar, navController, appBarConfiguration); }
เชื่อมโยงปลายทางกับรายการในเมนู
NavigationUI ยังมีตัวช่วยสำหรับเชื่อมโยงปลายทางกับคอมโพเนนต์ UI ที่ทำงานด้วยเมนูด้วย NavigationUI มีเมธอดตัวช่วย onNavDestinationSelected() ซึ่งใช้ MenuItem พร้อมกับ NavController ที่โฮสต์ปลายทางที่เกี่ยวข้อง หาก id ของ MenuItem ตรงกับ id ของปลายทาง NavController ก็จะไปยังปลายทางนั้นได้
ตัวอย่างเช่น ข้อมูลโค้ด XML ด้านล่างจะกำหนดรายการเมนูและปลายทางด้วย id ทั่วไป details_page_fragment
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <navigation xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" ... > ... <fragment android:id="@+id/details_page_fragment" android:label="@string/details" android:name="com.example.android.myapp.DetailsFragment" /> </navigation>
<menu xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> ... <item android:id="@+id/details_page_fragment" android:icon="@drawable/ic_details" android:title="@string/details" /> </menu>
ตัวอย่างเช่น หากเพิ่มเมนูผ่าน onCreateOptionsMenu() ของกิจกรรม คุณสามารถเชื่อมโยงรายการเมนูกับปลายทางได้โดยลบล้าง onOptionsItemSelected() ของกิจกรรมเพื่อเรียก onNavDestinationSelected() ดังที่แสดงในตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้
Kotlin
override fun onOptionsItemSelected(item: MenuItem): Boolean { val navController = findNavController(R.id.nav_host_fragment) return item.onNavDestinationSelected(navController) || super.onOptionsItemSelected(item) }
Java
@Override public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) { NavController navController = Navigation.findNavController(this, R.id.nav_host_fragment); return NavigationUI.onNavDestinationSelected(item, navController) || super.onOptionsItemSelected(item); }
ตอนนี้เมื่อผู้ใช้คลิกรายการเมนู details_page_fragment แอปจะไปยังปลายทางที่เกี่ยวข้องโดยอัตโนมัติด้วย id เดียวกัน
เพิ่มลิ้นชักการนำทาง
ลิ้นชักการนำทางคือแผง UI ที่แสดงเมนูการนำทางหลักของแอป
ลิ้นชักจะปรากฏขึ้นเมื่อผู้ใช้แตะไอคอนลิ้นชัก
![]() ในแถบแอป หรือเมื่อผู้ใช้ปัดนิ้วจากขอบด้านซ้ายของหน้าจอ
ในแถบแอป หรือเมื่อผู้ใช้ปัดนิ้วจากขอบด้านซ้ายของหน้าจอ
ไอคอนลิ้นชักจะแสดงในปลายทางระดับบนสุดทั้งหมดที่ใช้ DrawerLayout
หากต้องการเพิ่มลิ้นชักการนำทาง ให้ประกาศ DrawerLayout เป็นมุมมองรูทก่อน ภายใน DrawerLayout ให้เพิ่มเลย์เอาต์สำหรับเนื้อหา UI หลักและอีกมุมมองที่มีเนื้อหาของลิ้นชักการนำทาง
ตัวอย่างเช่น เลย์เอาต์ต่อไปนี้ใช้ DrawerLayout ที่มีมุมมองย่อย 2 รายการ ได้แก่ NavHostFragment สำหรับแสดงเนื้อหาหลัก และ NavigationView สำหรับแสดงเนื้อหาของลิ้นชักการนำทาง
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!-- Use DrawerLayout as root container for activity -->
<androidx.drawerlayout.widget.DrawerLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:id="@+id/drawer_layout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:fitsSystemWindows="true">
<!-- Layout to contain contents of main body of screen (drawer will slide over this) -->
<androidx.fragment.app.FragmentContainerView
android:name="androidx.navigation.fragment.NavHostFragment"
android:id="@+id/nav_host_fragment"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
app:defaultNavHost="true"
app:navGraph="@navigation/nav_graph" />
<!-- Container for contents of drawer - use NavigationView to make configuration easier -->
<com.google.android.material.navigation.NavigationView
android:id="@+id/nav_view"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_gravity="start"
android:fitsSystemWindows="true" />
</androidx.drawerlayout.widget.DrawerLayout>
ถัดไป ให้เชื่อมต่อ DrawerLayout กับกราฟการนำทางโดยส่งไปยัง AppBarConfiguration ดังที่แสดงในตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้
Kotlin
val appBarConfiguration = AppBarConfiguration(navController.graph, drawerLayout)
Java
AppBarConfiguration appBarConfiguration = new AppBarConfiguration.Builder(navController.getGraph()) .setDrawerLayout(drawerLayout) .build();
ถัดไป ในคลาสกิจกรรมหลัก ให้เรียกใช้ setupWithNavController() จากเมธอด onCreate() ของกิจกรรมหลัก ดังที่แสดงด้านล่าง
Kotlin
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) ... val navHostFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.nav_host_fragment) as NavHostFragment val navController = navHostFragment.navController findViewById<NavigationView>(R.id.nav_view) .setupWithNavController(navController) }
Java
@Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); ... NavHostFragment navHostFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.nav_host_fragment); NavController navController = navHostFragment.getNavController(); NavigationView navView = findViewById(R.id.nav_view); NavigationUI.setupWithNavController(navView, navController); }
ตั้งแต่ Navigation 2.4.0-alpha01 เป็นต้นไป ระบบจะบันทึกและกู้คืนสถานะของรายการเมนูแต่ละรายการเมื่อคุณใช้setupWithNavController
การไปยังส่วนต่างๆ ด้านล่าง
NavigationUI ยังจัดการการนําทางด้านล่างได้ด้วย เมื่อผู้ใช้เลือกรายการในเมนู NavController จะเรียกonNavDestinationSelected()และอัปเดตรายการที่เลือกในแถบนำทางด้านล่างโดยอัตโนมัติ
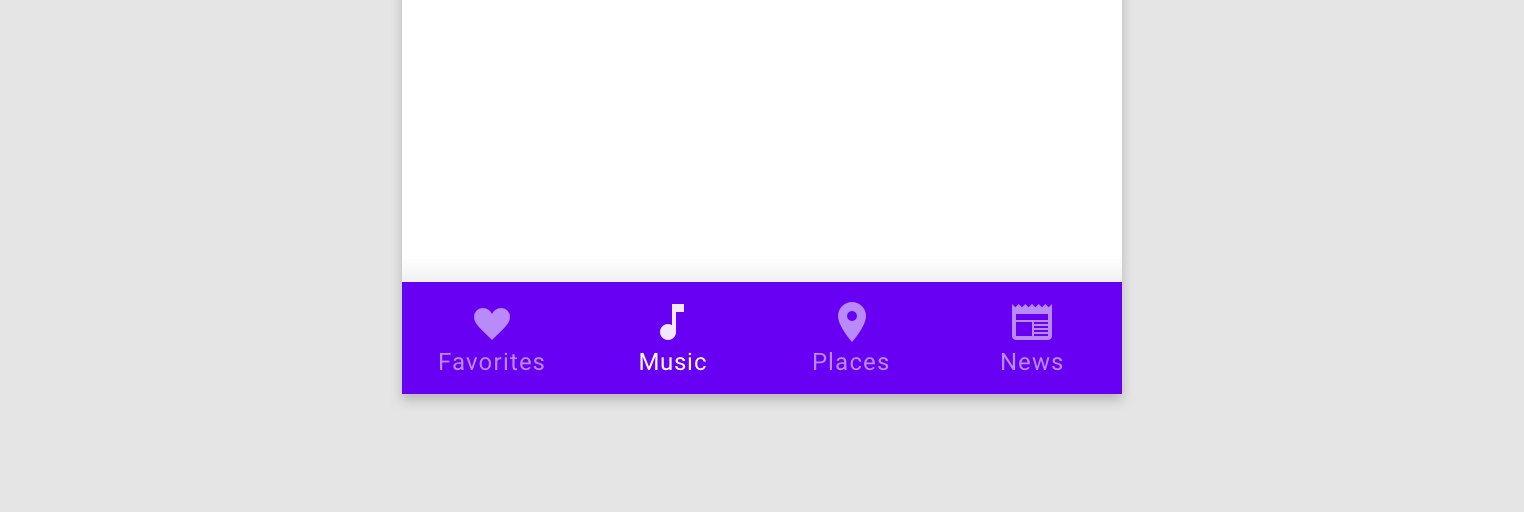
หากต้องการสร้างแถบนำทางด้านล่างในแอป ให้กำหนดแถบในกิจกรรมหลักก่อน ดังที่แสดงด้านล่าง
<LinearLayout> ... <androidx.fragment.app.FragmentContainerView android:id="@+id/nav_host_fragment" ... /> <com.google.android.material.bottomnavigation.BottomNavigationView android:id="@+id/bottom_nav" app:menu="@menu/menu_bottom_nav" /> </LinearLayout>
ถัดไป ในคลาสกิจกรรมหลัก ให้เรียกใช้ setupWithNavController() จากเมธอด onCreate() ของกิจกรรมหลัก ดังที่แสดงด้านล่าง
Kotlin
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) ... val navHostFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.nav_host_fragment) as NavHostFragment val navController = navHostFragment.navController findViewById<BottomNavigationView>(R.id.bottom_nav) .setupWithNavController(navController) }
Java
@Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); ... NavHostFragment navHostFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.nav_host_fragment); NavController navController = navHostFragment.getNavController(); BottomNavigationView bottomNav = findViewById(R.id.bottom_nav); NavigationUI.setupWithNavController(bottomNav, navController); }
ตั้งแต่ Navigation 2.4.0-alpha01 เป็นต้นไป ระบบจะบันทึกและกู้คืนสถานะของรายการเมนูแต่ละรายการเมื่อคุณใช้setupWithNavController
รอรับเหตุการณ์การนําทาง
การโต้ตอบกับ NavController
เป็นวิธีหลักในการไปยังปลายทางต่างๆ NavController
มีหน้าที่รับผิดชอบในการแทนที่เนื้อหาของ NavHost
ด้วยปลายทางใหม่ ในหลายกรณี องค์ประกอบ UI เช่น แถบแอปด้านบนหรือตัวควบคุมการนําทางอื่นๆ ถาวร เช่น BottomNavigationBar จะแสดงอยู่นอก NavHost และต้องได้รับการอัปเดตขณะที่คุณไปยังส่วนต่างๆ
NavController มีอินเทอร์เฟซ OnDestinationChangedListener ที่เรียกใช้เมื่อปลายทางปัจจุบันของ NavController หรืออาร์กิวเมนต์ของ NavController เปลี่ยนแปลง คุณสามารถลงทะเบียนผู้ฟังใหม่ได้ผ่านวิธีaddOnDestinationChangedListener()
โปรดทราบว่าเมื่อเรียกใช้ addOnDestinationChangedListener() ระบบจะส่งปลายทางปัจจุบันไปยังผู้ฟังทันทีหากปลายทางดังกล่าวมีอยู่
NavigationUI ใช้ OnDestinationChangedListener เพื่อทําให้คอมโพเนนต์ UI ทั่วไปเหล่านี้รับรู้การนําทาง อย่างไรก็ตาม โปรดทราบว่าคุณใช้ OnDestinationChangedListener เพียงอย่างเดียวเพื่อให้ UI หรือตรรกะทางธุรกิจที่กําหนดเองรับรู้เหตุการณ์การนําทางได้ด้วย
ตัวอย่างเช่น คุณอาจมีองค์ประกอบ UI ทั่วไปที่ต้องการแสดงในบางพื้นที่ของแอปขณะซ่อนองค์ประกอบเหล่านั้นไว้ในพื้นที่อื่นๆ เมื่อใช้OnDestinationChangedListenerของคุณเอง คุณจะเลือกแสดงหรือซ่อนองค์ประกอบ UI เหล่านี้ได้ตามปลายทางเป้าหมาย ดังที่แสดงในตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้
Kotlin
navController.addOnDestinationChangedListener { _, destination, _ -> if(destination.id == R.id.full_screen_destination) { toolbar.visibility = View.GONE bottomNavigationView.visibility = View.GONE } else { toolbar.visibility = View.VISIBLE bottomNavigationView.visibility = View.VISIBLE } }
Java
navController.addOnDestinationChangedListener(new NavController.OnDestinationChangedListener() { @Override public void onDestinationChanged(@NonNull NavController controller, @NonNull NavDestination destination, @Nullable Bundle arguments) { if(destination.getId() == R.id.full_screen_destination) { toolbar.setVisibility(View.GONE); bottomNavigationView.setVisibility(View.GONE); } else { toolbar.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); bottomNavigationView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); } } });
Listener ที่อิงตามอาร์กิวเมนต์
หรือจะใช้อาร์กิวเมนต์ที่มีค่าเริ่มต้นภายในกราฟการนําทางก็ได้ ซึ่งตัวควบคุม UI ที่เหมาะสมจะใช้เพื่ออัปเดตสถานะได้ ตัวอย่างเช่น แทนที่จะอิงตรรกะใน OnDestinationChangedListener ตามรหัสปลายทางตามตัวอย่างก่อนหน้านี้ เราสามารถสร้างอาร์กิวเมนต์ใน NavGraph ดังนี้
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <navigation xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" android:id="@+id/navigation\_graph" app:startDestination="@id/fragmentOne"> <fragment android:id="@+id/fragmentOne" android:name="com.example.android.navigation.FragmentOne" android:label="FragmentOne"> <action android:id="@+id/action\_fragmentOne\_to\_fragmentTwo" app:destination="@id/fragmentTwo" /> </fragment> <fragment android:id="@+id/fragmentTwo" android:name="com.example.android.navigation.FragmentTwo" android:label="FragmentTwo"> <argument android:name="ShowAppBar" android:defaultValue="true" /> </fragment> </navigation>
อาร์กิวเมนต์นี้ไม่ได้ใช้เมื่อไปยังปลายทาง แต่ใช้เป็นวิธีแนบข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมไปยังปลายทางโดยใช้ defaultValue ในกรณีนี้ ค่าจะระบุว่าควรแสดงแถบแอปหรือไม่เมื่ออยู่ในปลายทางนี้
ตอนนี้เราเพิ่ม OnDestinationChangedListener ใน Activity ได้แล้ว โดยทำดังนี้
Kotlin
navController.addOnDestinationChangedListener { _, _, arguments -> appBar.isVisible = arguments?.getBoolean("ShowAppBar", false) == true }
Java
navController.addOnDestinationChangedListener( new NavController.OnDestinationChangedListener() { @Override public void onDestinationChanged( @NonNull NavController controller, @NonNull NavDestination destination, @Nullable Bundle arguments ) { boolean showAppBar = false; if (arguments != null) { showAppBar = arguments.getBoolean("ShowAppBar", false); } if(showAppBar) { appBar.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); } else { appBar.setVisibility(View.GONE); } } } );
NavController
จะเรียกใช้การเรียกกลับนี้ทุกครั้งที่มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงปลายทางการนำทาง ตอนนี้Activityจะอัปเดตสถานะหรือระดับการมองเห็นของคอมโพเนนต์ UI ที่ตนเป็นเจ้าของตามอาร์กิวเมนต์ที่ได้รับในคอลแบ็กได้แล้ว
ข้อดีอย่างหนึ่งของแนวทางนี้คือ Activity จะมองเห็นเฉพาะอาร์กิวเมนต์ในกราฟการนำทาง และไม่ทราบว่าFragmentแต่ละรายมีบทบาทและความรับผิดชอบอย่างไร ในทํานองเดียวกัน แต่ละส่วนจะไม่ทราบว่าActivity นั้นอยู่ที่ไหนและคอมโพเนนต์ UI ที่เป็นเจ้าของ
แหล่งข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการนําทางได้ที่แหล่งข้อมูลต่อไปนี้
ตัวอย่าง
- ตัวอย่างการนําทางพื้นฐานของคอมโพเนนต์สถาปัตยกรรม Android
- ตัวอย่างการนำทางขั้นสูงของคอมโพเนนต์สถาปัตยกรรม Android
Codelabs
บล็อกโพสต์
วิดีโอ
- แนวทางปฏิบัติแนะนำ 10 ข้อสำหรับการเปลี่ยนไปใช้กิจกรรมเดียว
- กิจกรรมเดี่ยว: เหตุผล โอกาส และวิธี (Android Dev Summit ปี 2018)
- Android Jetpack: จัดการการนําทาง UI ด้วยตัวควบคุมการนําทาง (Google I/O ปี 2018)
