วิดเจ็ตคอลเล็กชันมีความเชี่ยวชาญในการแสดงองค์ประกอบจำนวนมากประเภทเดียวกัน เช่น คอลเล็กชันรูปภาพจากแอปแกลเลอรี บทความจากแอปข่าว หรือ ข้อความจากแอปการสื่อสาร โดยปกติแล้ว วิดเจ็ตคอลเล็กชันจะมุ่งเน้นที่กรณีการใช้งาน 2 กรณี ได้แก่ การเรียกดูคอลเล็กชันและการเปิดองค์ประกอบของคอลเล็กชันไปยังมุมมองรายละเอียด วิดเจ็ตคอลเล็กชันเลื่อนได้ในแนวตั้ง
วิดเจ็ตเหล่านี้ใช้ RemoteViewsService เพื่อแสดงคอลเล็กชันที่สำรองข้อมูลจากระยะไกล เช่น จากผู้ให้บริการเนื้อหา วิดเจ็ตจะแสดงข้อมูลโดยใช้มุมมองประเภทใดประเภทหนึ่งต่อไปนี้ ซึ่งเรียกว่ามุมมองคอลเล็กชัน
ListView- มุมมองที่แสดงรายการใน รายการที่เลื่อนในแนวตั้ง
GridView- มุมมองที่แสดงรายการใน ตารางกริดแบบเลื่อน 2 มิติ
StackView- มุมมองการ์ดซ้อนกัน คล้ายกับโรโลเดกซ์ ซึ่งผู้ใช้สามารถปัดการ์ดด้านหน้า ขึ้นหรือลงเพื่อดูการ์ดก่อนหน้าหรือถัดไปตามลำดับ
AdapterViewFlipperViewAnimator� ระบบจะแสดงบุตรหลานครั้งละ 1 คนเท่านั้น
เนื่องจากมุมมองคอลเล็กชันเหล่านี้แสดงคอลเล็กชันที่สำรองข้อมูลจากข้อมูลระยะไกล มุมมองจึงใช้ Adapter เพื่อเชื่อมต่ออินเทอร์เฟซผู้ใช้กับข้อมูล Adapter จะเชื่อมโยงรายการแต่ละรายการจากชุดข้อมูล
กับออบเจ็กต์ View แต่ละรายการ
และเนื่องจากมุมมองคอลเล็กชันเหล่านี้ได้รับการสนับสนุนโดยอแดปเตอร์ เฟรมเวิร์ก Android
จึงต้องมีสถาปัตยกรรมเพิ่มเติมเพื่อรองรับการใช้งานในวิดเจ็ต ในบริบทของวิดเจ็ต ระบบจะแทนที่ Adapter ด้วย
RemoteViewsFactory
ซึ่งเป็น Wrapper แบบบางรอบอินเทอร์เฟซ Adapter เมื่อมีการขอสำหรับ
รายการที่เฉพาะเจาะจงในคอลเล็กชัน RemoteViewsFactory จะสร้างและแสดง
รายการสำหรับคอลเล็กชันเป็นออบเจ็กต์ RemoteViews หากต้องการรวมมุมมองคอลเล็กชันในวิดเจ็ต ให้ใช้ RemoteViewsService และ
RemoteViewsFactory
RemoteViewsService เป็นบริการที่ช่วยให้ตัวดัดแปลงระยะไกลขอออบเจ็กต์
RemoteViewsได้ RemoteViewsFactory เป็นอินเทอร์เฟซสำหรับอะแดปเตอร์
ระหว่าง Collection View เช่น ListView, GridView และ
StackView กับข้อมูลพื้นฐานสำหรับมุมมองนั้น จากStackWidget
ตัวอย่าง
ต่อไปนี้คือตัวอย่างโค้ดมาตรฐานเพื่อใช้บริการและ
อินเทอร์เฟซนี้
Kotlin
class StackWidgetService : RemoteViewsService() { override fun onGetViewFactory(intent: Intent): RemoteViewsFactory { return StackRemoteViewsFactory(this.applicationContext, intent) } } class StackRemoteViewsFactory( private val context: Context, intent: Intent ) : RemoteViewsService.RemoteViewsFactory { // See the RemoteViewsFactory API reference for the full list of methods to // implement. }
Java
public class StackWidgetService extends RemoteViewsService { @Override public RemoteViewsFactory onGetViewFactory(Intent intent) { return new StackRemoteViewsFactory(this.getApplicationContext(), intent); } } class StackRemoteViewsFactory implements RemoteViewsService.RemoteViewsFactory { // See the RemoteViewsFactory API reference for the full list of methods to // implement. }
แอปพลิเคชันตัวอย่าง
ข้อมูลโค้ดในส่วนนี้มาจากStackWidget
ตัวอย่างเช่นกัน

StackWidget.ตัวอย่างนี้ประกอบด้วยกองซ้อนของมุมมอง 10 รายการที่แสดงค่า 0 ถึง 9 วิดเจ็ตตัวอย่างมีลักษณะการทำงานหลักดังนี้
ผู้ใช้สามารถปัดมุมมองด้านบนในวิดเจ็ตในแนวตั้งเพื่อแสดงมุมมองถัดไป หรือมุมมองก่อนหน้า นี่คือลักษณะการทำงานในตัวของ
StackViewวิดเจ็ตจะเลื่อนดูมุมมองต่างๆ ตามลำดับโดยอัตโนมัติเหมือนสไลด์โชว์ โดยไม่ต้องมีการโต้ตอบของผู้ใช้ เนื่องจากการตั้งค่า
android:autoAdvanceViewId="@id/stack_view"ในไฟล์res/xml/stackwidgetinfo.xmlการตั้งค่านี้จะมีผลกับรหัสมุมมอง ซึ่งในกรณีนี้คือรหัสมุมมองของมุมมองสแต็กหากผู้ใช้แตะมุมมองด้านบน วิดเจ็ตจะแสดงข้อความ
Toast"แตะมุมมอง n" โดยที่ n คือดัชนี (ตำแหน่ง) ของมุมมองที่แตะ ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับวิธี การใช้งานลักษณะการทำงานได้ที่ส่วนเพิ่มลักษณะการทำงานให้กับแต่ละรายการ
ติดตั้งใช้งานวิดเจ็ตด้วยคอลเล็กชัน
หากต้องการใช้วิดเจ็ตกับคอลเล็กชัน ให้ทำตามขั้นตอนเพื่อใช้วิดเจ็ต แล้วทำตามขั้นตอนเพิ่มเติมอีก 2-3 ขั้นตอน ได้แก่ แก้ไขไฟล์ Manifest เพิ่มมุมมองคอลเล็กชันลงในเลย์เอาต์วิดเจ็ต และแก้ไขAppWidgetProviderคลาสย่อย
ไฟล์ Manifest สำหรับวิดเจ็ตที่มีคอลเล็กชัน
นอกเหนือจากข้อกำหนดที่ระบุไว้ในประกาศวิดเจ็ตใน
ไฟล์ Manifest แล้ว คุณต้องทำให้วิดเจ็ตที่มี
คอลเล็กชันเชื่อมโยงกับ RemoteViewsService ได้ โดยประกาศบริการในไฟล์ Manifest ด้วยสิทธิ์
BIND_REMOTEVIEWS
ซึ่งจะป้องกันไม่ให้แอปพลิเคชันอื่นๆ เข้าถึงข้อมูลของวิดเจ็ตได้อย่างอิสระ
ตัวอย่างเช่น เมื่อสร้างวิดเจ็ตที่ใช้ RemoteViewsService เพื่อป้อนข้อมูลลงใน
มุมมองคอลเล็กชัน รายการในไฟล์ Manifest อาจมีลักษณะดังนี้
<service android:name="MyWidgetService"
android:permission="android.permission.BIND_REMOTEVIEWS" />
ในตัวอย่างนี้ android:name="MyWidgetService" หมายถึงคลาสย่อยของ
RemoteViewsService
เลย์เอาต์สำหรับวิดเจ็ตที่มีคอลเล็กชัน
ข้อกำหนดหลักสำหรับไฟล์ XML ของเลย์เอาต์วิดเจ็ตคือต้องมีมุมมองคอลเล็กชันอย่างใดอย่างหนึ่งต่อไปนี้ ListView, GridView, StackView หรือ AdapterViewFlipper นี่คือไฟล์ widget_layout.xml สำหรับ
StackWidget
ตัวอย่าง
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<StackView
android:id="@+id/stack_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:loopViews="true" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/empty_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:background="@drawable/widget_item_background"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:textStyle="bold"
android:text="@string/empty_view_text"
android:textSize="20sp" />
</FrameLayout>
โปรดทราบว่ามุมมองว่างต้องเป็นองค์ประกอบที่อยู่ระดับเดียวกันกับมุมมองคอลเล็กชันที่มุมมองว่างแสดงสถานะว่าง
นอกจากไฟล์เลย์เอาต์สำหรับวิดเจ็ตทั้งหมดแล้ว ให้สร้างไฟล์เลย์เอาต์อีกไฟล์ที่กำหนดเลย์เอาต์สำหรับแต่ละรายการในคอลเล็กชัน เช่น เลย์เอาต์สำหรับหนังสือแต่ละเล่มในคอลเล็กชันหนังสือ StackWidget ตัวอย่างมี
ไฟล์เลย์เอาต์ของรายการเพียงไฟล์เดียว widget_item.xml เนื่องจากรายการทั้งหมดใช้เลย์เอาต์เดียวกัน
คลาส AppWidgetProvider สำหรับวิดเจ็ตที่มีคอลเล็กชัน
เช่นเดียวกับวิดเจ็ตปกติ โค้ดส่วนใหญ่ในคลาสย่อย AppWidgetProvider
มักจะอยู่ใน
onUpdate()
ความแตกต่างที่สำคัญในการติดตั้งใช้งานสำหรับ onUpdate() เมื่อสร้างวิดเจ็ตที่มีคอลเล็กชันคือคุณต้องเรียกใช้ setRemoteAdapter() ซึ่งจะบอกมุมมองคอลเล็กชันว่าจะรับข้อมูลจากที่ใด
จากนั้น RemoteViewsService จะแสดงผลการติดตั้งใช้งาน RemoteViewsFactory และวิดเจ็ตจะแสดงข้อมูลที่เหมาะสม เมื่อคุณ
เรียกใช้เมธอดนี้ ให้ส่ง Intent ที่ชี้ไปยังการติดตั้งใช้งาน
RemoteViewsService และรหัสวิดเจ็ตที่ระบุวิดเจ็ตที่จะอัปเดต
ตัวอย่างเช่น StackWidget sample จะใช้เมธอด onUpdate()
callback เพื่อตั้งค่า RemoteViewsService เป็นอะแดปเตอร์ระยะไกลสำหรับ
คอลเล็กชันวิดเจ็ตดังนี้
Kotlin
override fun onUpdate( context: Context, appWidgetManager: AppWidgetManager, appWidgetIds: IntArray ) { // Update each of the widgets with the remote adapter. appWidgetIds.forEach { appWidgetId -> // Set up the intent that starts the StackViewService, which // provides the views for this collection. val intent = Intent(context, StackWidgetService::class.java).apply { // Add the widget ID to the intent extras. putExtra(AppWidgetManager.EXTRA_APPWIDGET_ID, appWidgetId) data = Uri.parse(toUri(Intent.URI_INTENT_SCHEME)) } // Instantiate the RemoteViews object for the widget layout. val views = RemoteViews(context.packageName, R.layout.widget_layout).apply { // Set up the RemoteViews object to use a RemoteViews adapter. // This adapter connects to a RemoteViewsService through the // specified intent. // This is how you populate the data. setRemoteAdapter(R.id.stack_view, intent) // The empty view is displayed when the collection has no items. // It must be in the same layout used to instantiate the // RemoteViews object. setEmptyView(R.id.stack_view, R.id.empty_view) } // Do additional processing specific to this widget. appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(appWidgetId, views) } super.onUpdate(context, appWidgetManager, appWidgetIds) }
Java
public void onUpdate(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager, int[] appWidgetIds) { // Update each of the widgets with the remote adapter. for (int i = 0; i < appWidgetIds.length; ++i) { // Set up the intent that starts the StackViewService, which // provides the views for this collection. Intent intent = new Intent(context, StackWidgetService.class); // Add the widget ID to the intent extras. intent.putExtra(AppWidgetManager.EXTRA_APPWIDGET_ID, appWidgetIds[i]); intent.setData(Uri.parse(intent.toUri(Intent.URI_INTENT_SCHEME))); // Instantiate the RemoteViews object for the widget layout. RemoteViews views = new RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(), R.layout.widget_layout); // Set up the RemoteViews object to use a RemoteViews adapter. // This adapter connects to a RemoteViewsService through the specified // intent. // This is how you populate the data. views.setRemoteAdapter(R.id.stack_view, intent); // The empty view is displayed when the collection has no items. // It must be in the same layout used to instantiate the RemoteViews // object. views.setEmptyView(R.id.stack_view, R.id.empty_view); // Do additional processing specific to this widget. appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(appWidgetIds[i], views); } super.onUpdate(context, appWidgetManager, appWidgetIds); }
คงข้อมูลไว้
ดังที่อธิบายไว้ในหน้านี้ คลาสย่อย RemoteViewsService จะมีRemoteViewsFactory ที่ใช้เพื่อแสดงข้อมูลในมุมมองคอลเล็กชันระยะไกล
โดยเฉพาะอย่างยิ่ง ให้ทำตามขั้นตอนต่อไปนี้
คลาสย่อย
RemoteViewsServiceRemoteViewsServiceเป็นบริการที่อะแดปเตอร์ระยะไกลสามารถขอRemoteViewsได้ใน
RemoteViewsServiceคลาสย่อย ให้รวมคลาสที่ใช้RemoteViewsFactoryอินเทอร์เฟซRemoteViewsFactoryคืออินเทอร์เฟซสำหรับ อแดปเตอร์ระหว่างมุมมองการรวบรวมข้อมูลระยะไกล เช่นListView,GridView,StackViewกับข้อมูลพื้นฐานสำหรับมุมมองนั้น การติดตั้งใช้งานของคุณมีหน้าที่สร้างออบเจ็กต์RemoteViewsสำหรับแต่ละรายการในชุดข้อมูล อินเทอร์เฟซนี้เป็น Wrapper แบบบางรอบAdapter
คุณไม่สามารถพึ่งพาอินสแตนซ์เดียวของบริการหรือข้อมูลใดๆ ที่มีอยู่เพื่อ
คงอยู่ อย่าจัดเก็บข้อมูลใน RemoteViewsService เว้นแต่จะเป็นข้อมูลแบบคงที่ หากต้องการให้ข้อมูลของวิดเจ็ตคงอยู่ แนวทางที่ดีที่สุดคือการใช้
ContentProvider ที่มีข้อมูล
คงอยู่หลังจากวงจรของกระบวนการ ตัวอย่างเช่น วิดเจ็ตร้านขายของชำสามารถจัดเก็บสถานะของรายการในลิสต์ซื้อของชำแต่ละรายการไว้ในตำแหน่งที่ถาวร เช่น ฐานข้อมูล SQL
เนื้อหาหลักของRemoteViewsServiceการติดตั้งใช้งานคือRemoteViewsFactory ซึ่งอธิบายไว้ในส่วนต่อไปนี้
อินเทอร์เฟซ RemoteViewsFactory
คลาสที่กำหนดเองซึ่งใช้RemoteViewsFactoryอินเทอร์เฟซจะให้ข้อมูลแก่
วิดเจ็ตสำหรับรายการในคอลเล็กชัน โดยการ
รวมไฟล์เลย์เอาต์ XML ของรายการวิดเจ็ตกับแหล่งข้อมูล แหล่งข้อมูลนี้อาจเป็นอะไรก็ได้ตั้งแต่ฐานข้อมูลไปจนถึงอาร์เรย์อย่างง่าย ในStackWidget
ตัวอย่าง แหล่งข้อมูลคืออาร์เรย์ของ WidgetItems RemoteViewsFactory
ทําหน้าที่เป็นอแดปเตอร์เพื่อเชื่อมข้อมูลกับมุมมองการรวบรวมข้อมูลระยะไกล
วิธีที่สำคัญที่สุด 2 วิธีที่คุณต้องใช้สำหรับคลาสย่อย RemoteViewsFactory คือ
onCreate() และ
getViewAt()
ระบบจะเรียกใช้ onCreate() เมื่อสร้างโรงงานเป็นครั้งแรก
ส่วนนี้คือที่ที่คุณตั้งค่าการเชื่อมต่อหรือเคอร์เซอร์กับแหล่งข้อมูล ตัวอย่างเช่น ตัวอย่าง StackWidget ใช้ onCreate() เพื่อเริ่มต้นอาร์เรย์ของออบเจ็กต์ WidgetItem เมื่อวิดเจ็ตทำงานอยู่ ระบบจะเข้าถึงออบเจ็กต์เหล่านี้โดยใช้ตำแหน่งดัชนีในอาร์เรย์และแสดงข้อความที่ออบเจ็กต์มี
ต่อไปนี้เป็นตัวอย่างจากStackWidgetตัวอย่างRemoteViewsFactory
การใช้งานที่แสดงส่วนต่างๆ ของเมธอด onCreate()
Kotlin
private const val REMOTE_VIEW_COUNT: Int = 10 class StackRemoteViewsFactory( private val context: Context ) : RemoteViewsService.RemoteViewsFactory { private lateinit var widgetItems: List<WidgetItem> override fun onCreate() { // In onCreate(), set up any connections or cursors to your data // source. Heavy lifting, such as downloading or creating content, // must be deferred to onDataSetChanged() or getViewAt(). Taking // more than 20 seconds on this call results in an ANR. widgetItems = List(REMOTE_VIEW_COUNT) { index -> WidgetItem("$index!") } ... } ... }
Java
class StackRemoteViewsFactory implements RemoteViewsService.RemoteViewsFactory { private static final int REMOTE_VIEW_COUNT = 10; private List<WidgetItem> widgetItems = new ArrayList<WidgetItem>(); public void onCreate() { // In onCreate(), setup any connections or cursors to your data // source. Heavy lifting, such as downloading or creating content, // must be deferred to onDataSetChanged() or getViewAt(). Taking // more than 20 seconds on this call results in an ANR. for (int i = 0; i < REMOTE_VIEW_COUNT; i++) { widgetItems.add(new WidgetItem(i + "!")); } ... } ...
เมธอด RemoteViewsFactory getViewAt() จะแสดงผลออบเจ็กต์ RemoteViews
ที่สอดคล้องกับข้อมูลที่ position ที่ระบุในชุดข้อมูล ต่อไปนี้เป็น
ตัวอย่างจากStackWidgetของตัวอย่างRemoteViewsFactory
Kotlin
override fun getViewAt(position: Int): RemoteViews { // Construct a remote views item based on the widget item XML file // and set the text based on the position. return RemoteViews(context.packageName, R.layout.widget_item).apply { setTextViewText(R.id.widget_item, widgetItems[position].text) } }
Java
public RemoteViews getViewAt(int position) { // Construct a remote views item based on the widget item XML file // and set the text based on the position. RemoteViews views = new RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(), R.layout.widget_item); views.setTextViewText(R.id.widget_item, widgetItems.get(position).text); return views; }
เพิ่มลักษณะการทำงานให้กับแต่ละรายการ
ส่วนก่อนหน้าแสดงวิธีเชื่อมโยงข้อมูลกับคอลเล็กชันวิดเจ็ต แต่จะเกิดอะไรขึ้นหากคุณต้องการเพิ่มลักษณะการทำงานแบบไดนามิกลงในรายการแต่ละรายการใน มุมมองคอลเล็กชัน
ตามที่อธิบายไว้ในจัดการเหตุการณ์ด้วยonUpdate()
คลาส โดยปกติคุณจะใช้
setOnClickPendingIntent() เพื่อตั้งค่าลักษณะการคลิกของออบเจ็กต์ เช่น เพื่อ
ทําให้ปุ่มเปิดActivity แต่
ไม่อนุญาตให้ใช้วิธีนี้กับมุมมองย่อยในรายการคอลเล็กชันแต่ละรายการ
เช่น คุณสามารถใช้ setOnClickPendingIntent() เพื่อตั้งค่าปุ่มส่วนกลาง
ในวิดเจ็ต Gmail ที่เปิดแอปได้ แต่จะใช้กับ
รายการในรายการแต่ละรายการไม่ได้
แต่หากต้องการเพิ่มลักษณะการคลิกให้กับแต่ละรายการในคอลเล็กชัน ให้ใช้
setOnClickFillInIntent() ซึ่งเกี่ยวข้องกับการตั้งค่าเทมเพลต PendingIntent สำหรับ
มุมมองคอลเล็กชัน แล้วตั้งค่า Intent ที่เติมในแต่ละรายการใน
คอลเล็กชันผ่าน RemoteViewsFactory
ส่วนนี้ใช้ตัวอย่าง StackWidget เพื่ออธิบายวิธีเพิ่มลักษณะการทำงานให้กับ
รายการแต่ละรายการ ในStackWidgetตัวอย่าง หากผู้ใช้แตะมุมมองด้านบน
วิดเจ็ตจะแสดงข้อความ Toast "แตะมุมมอง n" โดย n คือ
ดัชนี (ตำแหน่ง) ของมุมมองที่แตะ โดยมีวิธีการดังนี้
StackWidgetProviderซึ่งเป็นคลาสย่อยของAppWidgetProviderจะสร้าง PendingIntent ด้วยการดำเนินการที่กำหนดเองชื่อTOAST_ACTIONเมื่อผู้ใช้แตะมุมมอง ระบบจะเรียกใช้ Intent และออกอากาศ
TOAST_ACTIONการออกอากาศนี้จะถูกสกัดกั้นโดยเมธอด
onReceive()ของคลาสStackWidgetProviderและวิดเจ็ตจะแสดงข้อความToastสำหรับมุมมองที่แตะ ข้อมูลสำหรับรายการในคอลเล็กชันมาจากRemoteViewsFactoryผ่านRemoteViewsService
ตั้งค่าเทมเพลตความตั้งใจที่รอดำเนินการ
StackWidgetProvider (คลาสย่อยของ AppWidgetProvider)
ตั้งค่า PendingIntent รายการแต่ละรายการในคอลเล็กชันจะตั้งค่า PendingIntent ของตัวเองไม่ได้
แต่คอลเล็กชันโดยรวมจะตั้งค่าเทมเพลต PendingIntent
และแต่ละรายการจะตั้งค่า Fill-In Intent เพื่อสร้างลักษณะการทำงานที่ไม่ซ้ำกัน
ในแต่ละรายการ
คลาสนี้ยังได้รับการออกอากาศที่ส่งเมื่อผู้ใช้แตะมุมมองด้วย
โดยจะประมวลผลเหตุการณ์นี้ในเมธอด onReceive() หาก
การดำเนินการของ Intent คือ TOAST_ACTION วิดเจ็ตจะแสดงข้อความ Toast สำหรับมุมมองปัจจุบัน
Kotlin
const val TOAST_ACTION = "com.example.android.stackwidget.TOAST_ACTION" const val EXTRA_ITEM = "com.example.android.stackwidget.EXTRA_ITEM" class StackWidgetProvider : AppWidgetProvider() { ... // Called when the BroadcastReceiver receives an Intent broadcast. // Checks whether the intent's action is TOAST_ACTION. If it is, the // widget displays a Toast message for the current item. override fun onReceive(context: Context, intent: Intent) { val mgr: AppWidgetManager = AppWidgetManager.getInstance(context) if (intent.action == TOAST_ACTION) { val appWidgetId: Int = intent.getIntExtra( AppWidgetManager.EXTRA_APPWIDGET_ID, AppWidgetManager.INVALID_APPWIDGET_ID ) // EXTRA_ITEM represents a custom value provided by the Intent // passed to the setOnClickFillInIntent() method to indicate the // position of the clicked item. See StackRemoteViewsFactory in // Set the fill-in Intent for details. val viewIndex: Int = intent.getIntExtra(EXTRA_ITEM, 0) Toast.makeText(context, "Touched view $viewIndex", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() } super.onReceive(context, intent) } override fun onUpdate( context: Context, appWidgetManager: AppWidgetManager, appWidgetIds: IntArray ) { // Update each of the widgets with the remote adapter. appWidgetIds.forEach { appWidgetId -> // Sets up the intent that points to the StackViewService that // provides the views for this collection. val intent = Intent(context, StackWidgetService::class.java).apply { putExtra(AppWidgetManager.EXTRA_APPWIDGET_ID, appWidgetId) // When intents are compared, the extras are ignored, so embed // the extra sinto the data so that the extras are not ignored. data = Uri.parse(toUri(Intent.URI_INTENT_SCHEME)) } val rv = RemoteViews(context.packageName, R.layout.widget_layout).apply { setRemoteAdapter(R.id.stack_view, intent) // The empty view is displayed when the collection has no items. // It must be a sibling of the collection view. setEmptyView(R.id.stack_view, R.id.empty_view) } // This section makes it possible for items to have individualized // behavior. It does this by setting up a pending intent template. // Individuals items of a collection can't set up their own pending // intents. Instead, the collection as a whole sets up a pending // intent template, and the individual items set a fillInIntent // to create unique behavior on an item-by-item basis. val toastPendingIntent: PendingIntent = Intent( context, StackWidgetProvider::class.java ).run { // Set the action for the intent. // When the user touches a particular view, it has the effect of // broadcasting TOAST_ACTION. action = TOAST_ACTION putExtra(AppWidgetManager.EXTRA_APPWIDGET_ID, appWidgetId) data = Uri.parse(toUri(Intent.URI_INTENT_SCHEME)) PendingIntent.getBroadcast(context, 0, this, PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT) } rv.setPendingIntentTemplate(R.id.stack_view, toastPendingIntent) appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(appWidgetId, rv) } super.onUpdate(context, appWidgetManager, appWidgetIds) } }
Java
public class StackWidgetProvider extends AppWidgetProvider { public static final String TOAST_ACTION = "com.example.android.stackwidget.TOAST_ACTION"; public static final String EXTRA_ITEM = "com.example.android.stackwidget.EXTRA_ITEM"; ... // Called when the BroadcastReceiver receives an Intent broadcast. // Checks whether the intent's action is TOAST_ACTION. If it is, the // widget displays a Toast message for the current item. @Override public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) { AppWidgetManager mgr = AppWidgetManager.getInstance(context); if (intent.getAction().equals(TOAST_ACTION)) { int appWidgetId = intent.getIntExtra(AppWidgetManager.EXTRA_APPWIDGET_ID, AppWidgetManager.INVALID_APPWIDGET_ID); // EXTRA_ITEM represents a custom value provided by the Intent // passed to the setOnClickFillInIntent() method to indicate the // position of the clicked item. See StackRemoteViewsFactory in // Set the fill-in Intent for details. int viewIndex = intent.getIntExtra(EXTRA_ITEM, 0); Toast.makeText(context, "Touched view " + viewIndex, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } super.onReceive(context, intent); } @Override public void onUpdate(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager, int[] appWidgetIds) { // Update each of the widgets with the remote adapter. for (int i = 0; i < appWidgetIds.length; ++i) { // Sets up the intent that points to the StackViewService that // provides the views for this collection. Intent intent = new Intent(context, StackWidgetService.class); intent.putExtra(AppWidgetManager.EXTRA_APPWIDGET_ID, appWidgetIds[i]); // When intents are compared, the extras are ignored, so embed // the extras into the data so that the extras are not // ignored. intent.setData(Uri.parse(intent.toUri(Intent.URI_INTENT_SCHEME))); RemoteViews rv = new RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(), R.layout.widget_layout); rv.setRemoteAdapter(appWidgetIds[i], R.id.stack_view, intent); // The empty view is displayed when the collection has no items. It // must be a sibling of the collection view. rv.setEmptyView(R.id.stack_view, R.id.empty_view); // This section makes it possible for items to have individualized // behavior. It does this by setting up a pending intent template. // Individuals items of a collection can't set up their own pending // intents. Instead, the collection as a whole sets up a pending // intent template, and the individual items set a fillInIntent // to create unique behavior on an item-by-item basis. Intent toastIntent = new Intent(context, StackWidgetProvider.class); // Set the action for the intent. // When the user touches a particular view, it has the effect of // broadcasting TOAST_ACTION. toastIntent.setAction(StackWidgetProvider.TOAST_ACTION); toastIntent.putExtra(AppWidgetManager.EXTRA_APPWIDGET_ID, appWidgetIds[i]); intent.setData(Uri.parse(intent.toUri(Intent.URI_INTENT_SCHEME))); PendingIntent toastPendingIntent = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(context, 0, toastIntent, PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT); rv.setPendingIntentTemplate(R.id.stack_view, toastPendingIntent); appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(appWidgetIds[i], rv); } super.onUpdate(context, appWidgetManager, appWidgetIds); } }
ตั้งค่าความตั้งใจในการกรอกข้อมูล
RemoteViewsFactory ต้องตั้งค่าความตั้งใจในการเติมข้อความในแต่ละรายการในคอลเล็กชัน ซึ่งจะช่วยให้แยกความแตกต่างของการดำเนินการเมื่อคลิกแต่ละรายการได้ จากนั้นระบบจะรวมความตั้งใจในการกรอกข้อมูลกับเทมเพลต PendingIntent เพื่อกำหนดความตั้งใจสุดท้ายที่จะดำเนินการเมื่อมีการแตะรายการ
Kotlin
private const val REMOTE_VIEW_COUNT: Int = 10 class StackRemoteViewsFactory( private val context: Context, intent: Intent ) : RemoteViewsService.RemoteViewsFactory { private lateinit var widgetItems: List<WidgetItem> private val appWidgetId: Int = intent.getIntExtra( AppWidgetManager.EXTRA_APPWIDGET_ID, AppWidgetManager.INVALID_APPWIDGET_ID ) override fun onCreate() { // In onCreate(), set up any connections or cursors to your data source. // Heavy lifting, such as downloading or creating content, must be // deferred to onDataSetChanged() or getViewAt(). Taking more than 20 // seconds on this call results in an ANR. widgetItems = List(REMOTE_VIEW_COUNT) { index -> WidgetItem("$index!") } ... } ... override fun getViewAt(position: Int): RemoteViews { // Construct a remote views item based on the widget item XML file // and set the text based on the position. return RemoteViews(context.packageName, R.layout.widget_item).apply { setTextViewText(R.id.widget_item, widgetItems[position].text) // Set a fill-intent to fill in the pending intent template. // that is set on the collection view in StackWidgetProvider. val fillInIntent = Intent().apply { Bundle().also { extras -> extras.putInt(EXTRA_ITEM, position) putExtras(extras) } } // Make it possible to distinguish the individual on-click // action of a given item. setOnClickFillInIntent(R.id.widget_item, fillInIntent) ... } } ... }
Java
public class StackWidgetService extends RemoteViewsService { @Override public RemoteViewsFactory onGetViewFactory(Intent intent) { return new StackRemoteViewsFactory(this.getApplicationContext(), intent); } } class StackRemoteViewsFactory implements RemoteViewsService.RemoteViewsFactory { private static final int count = 10; private List<WidgetItem> widgetItems = new ArrayList<WidgetItem>(); private Context context; private int appWidgetId; public StackRemoteViewsFactory(Context context, Intent intent) { this.context = context; appWidgetId = intent.getIntExtra(AppWidgetManager.EXTRA_APPWIDGET_ID, AppWidgetManager.INVALID_APPWIDGET_ID); } // Initialize the data set. public void onCreate() { // In onCreate(), set up any connections or cursors to your data // source. Heavy lifting, such as downloading or creating // content, must be deferred to onDataSetChanged() or // getViewAt(). Taking more than 20 seconds on this call results // in an ANR. for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { widgetItems.add(new WidgetItem(i + "!")); } ... } // Given the position (index) of a WidgetItem in the array, use the // item's text value in combination with the widget item XML file to // construct a RemoteViews object. public RemoteViews getViewAt(int position) { // Position always ranges from 0 to getCount() - 1. // Construct a RemoteViews item based on the widget item XML // file and set the text based on the position. RemoteViews rv = new RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(), R.layout.widget_item); rv.setTextViewText(R.id.widget_item, widgetItems.get(position).text); // Set a fill-intent to fill in the pending // intent template that is set on the collection view in // StackWidgetProvider. Bundle extras = new Bundle(); extras.putInt(StackWidgetProvider.EXTRA_ITEM, position); Intent fillInIntent = new Intent(); fillInIntent.putExtras(extras); // Make it possible to distinguish the individual on-click // action of a given item. rv.setOnClickFillInIntent(R.id.widget_item, fillInIntent); // Return the RemoteViews object. return rv; } ... }
อัปเดตข้อมูลคอลเล็กชันอยู่เสมอ
รูปที่ 2 แสดงขั้นตอนการอัปเดตในวิดเจ็ตที่ใช้คอลเล็กชัน โดยจะแสดง
วิธีที่โค้ดวิดเจ็ตโต้ตอบกับ RemoteViewsFactory และวิธี
ทริกเกอร์การอัปเดต
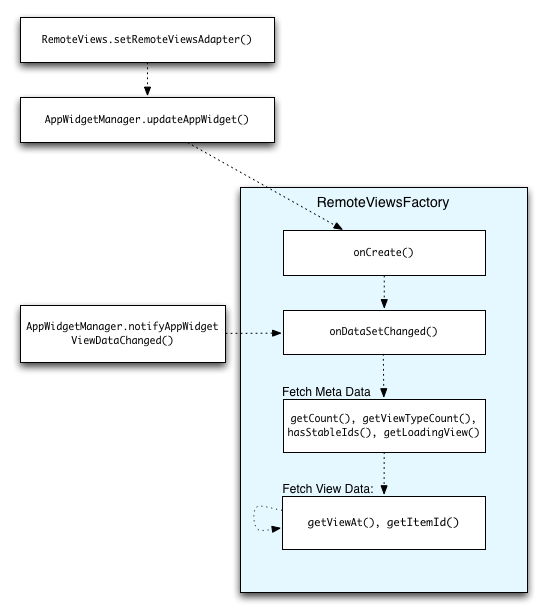
RemoteViewsFactory ระหว่างการอัปเดตวิดเจ็ตที่ใช้คอลเล็กชันจะแสดงเนื้อหาล่าสุดแก่ผู้ใช้ได้ เช่น วิดเจ็ต Gmail จะแสดงภาพรวมของกล่องจดหมายให้ผู้ใช้ หากต้องการให้เป็นไปได้ ให้ทริกเกอร์RemoteViewsFactoryและมุมมองการรวบรวมเพื่อดึงและแสดงข้อมูลใหม่
โดยใช้
AppWidgetManager เพื่อเรียก
notifyAppWidgetViewDataChanged() การเรียกนี้จะทำให้เกิดการเรียกกลับไปยังเมธอด
onDataSetChanged()
ของออบเจ็กต์ RemoteViewsFactory ซึ่งช่วยให้คุณดึงข้อมูลใหม่ได้
คุณสามารถดำเนินการที่ต้องใช้การประมวลผลจำนวนมากแบบพร้อมกันภายใน
onDataSetChanged()ได้ คุณมั่นใจได้ว่าการเรียกนี้จะเสร็จสมบูรณ์
ก่อนที่จะดึงข้อมูลเมตาหรือข้อมูลการดูจาก RemoteViewsFactory นอกจากนี้ คุณยังสามารถดำเนินการที่ต้องใช้การประมวลผลสูงภายในเมธอด getViewAt()
ได้ด้วย หากการเรียกนี้ใช้เวลานาน ระบบจะแสดงมุมมองการโหลดที่ระบุโดยเมธอด
getLoadingView()
ของออบเจ็กต์ RemoteViewsFactory ในตำแหน่งที่สอดคล้องกันของมุมมองคอลเล็กชัน
จนกว่าจะมีการส่งคืน
ใช้ RemoteCollectionItems เพื่อส่งต่อคอลเล็กชันโดยตรง
Android 12 (API ระดับ 31) เพิ่มเมธอด setRemoteAdapter(int viewId,
RemoteViews.RemoteCollectionItems
items)
ซึ่งช่วยให้แอปส่งต่อคอลเล็กชันได้โดยตรงเมื่อเติมข้อมูลใน
มุมมองคอลเล็กชัน หากตั้งค่าอะแดปเตอร์โดยใช้วิธีนี้ คุณไม่จำเป็นต้อง
ใช้ RemoteViewsFactory และไม่จำเป็นต้องเรียกใช้
notifyAppWidgetViewDataChanged()
นอกจากจะช่วยให้การป้อนข้อมูลในอแดปเตอร์ง่ายขึ้นแล้ว วิธีนี้ยังช่วย
ลดเวลาในการตอบสนองสำหรับการป้อนข้อมูลรายการใหม่เมื่อผู้ใช้เลื่อนลงในรายการเพื่อ
ดูรายการใหม่ เราขอแนะนำให้ใช้วิธีนี้ในการตั้งค่าอแดปเตอร์ตราบใดที่ชุดรายการคอลเล็กชันของคุณมีขนาดค่อนข้างเล็ก อย่างไรก็ตาม วิธีนี้ใช้ได้ไม่ดีนักหากคอลเล็กชันมี Bitmaps จำนวนมากที่ส่งไปยัง setImageViewBitmap
หากคอลเล็กชันไม่ได้ใช้ชุดเลย์เอาต์ที่คงที่ (กล่าวคือ หากบางรายการปรากฏเฉพาะบางครั้ง) ให้ใช้ setViewTypeCount เพื่อระบุจำนวนเลย์เอาต์ที่ไม่ซ้ำกันสูงสุดที่คอลเล็กชันจะมีได้ ซึ่งช่วยให้
อแดปเตอร์นำกลับมาใช้ใหม่ได้ในการอัปเดตวิดเจ็ตแอป
ตัวอย่างวิธีใช้คอลเล็กชัน RemoteViews แบบง่ายมีดังนี้
Kotlin
val itemLayouts = listOf( R.layout.item_type_1, R.layout.item_type_2, ... ) remoteView.setRemoteAdapter( R.id.list_view, RemoteViews.RemoteCollectionItems.Builder() .addItem(/* id= */ ID_1, RemoteViews(context.packageName, R.layout.item_type_1)) .addItem(/* id= */ ID_2, RemoteViews(context.packageName, R.layout.item_type_2)) ... .setViewTypeCount(itemLayouts.count()) .build() )
Java
List<Integer> itemLayouts = Arrays.asList( R.layout.item_type_1, R.layout.item_type_2, ... ); remoteView.setRemoteAdapter( R.id.list_view, new RemoteViews.RemoteCollectionItems.Builder() .addItem(/* id= */ ID_1, new RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(), R.layout.item_type_1)) .addItem(/* id= */ ID_2, new RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(), R.layout.item_type_2)) ... .setViewTypeCount(itemLayouts.size()) .build() );

