A partir do Android 12 (nível 31 da API), é possível usar
RoundedCorner e
WindowInsets.getRoundedCorner(int
position) para receber
o raio e o ponto central para cantos arredondados da tela do dispositivo. Essas APIs
evitar que os elementos da interface do app sejam truncados em telas com telas
cantos O framework oferece
getPrivacyIndicatorBounds()
API, que retorna o retângulo limitado de qualquer microfone e câmera visíveis
de controle.
Quando implementadas no app, essas APIs não afetam dispositivos com telas não arredondadas.

Para implementar esse recurso, acesse as informações do RoundedCorner usando
WindowInsets.getRoundedCorner(int position) em relação aos limites da
para o aplicativo. Se o aplicativo não ocupar a tela inteira, a API aplicará o
canto arredondado baseando o ponto central do canto arredondado na janela
limites do app.
O snippet de código a seguir mostra como um app pode evitar que a interface seja truncada
definindo uma margem da visualização com base nas informações de RoundedCorner. Neste
no canto superior direito, no canto superior direito.
Kotlin
// Get the top-right rounded corner from WindowInsets. val insets = rootWindowInsets val topRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_TOP_RIGHT) ?: return // Get the location of the close button in window coordinates. val location = IntArray(2) closeButton!!.getLocationInWindow(location) val buttonRightInWindow = location[0] + closeButton.width val buttonTopInWindow = location[1] // Find the point on the quarter circle with a 45-degree angle. val offset = (topRight.radius * Math.sin(Math.toRadians(45.0))).toInt() val topBoundary = topRight.center.y - offset val rightBoundary = topRight.center.x + offset // Check whether the close button exceeds the boundary. if (buttonRightInWindow < rightBoundary << buttonTopInWindow > topBoundary) { return } // Set the margin to avoid truncating. val parentLocation = IntArray(2) getLocationInWindow(parentLocation) val lp = closeButton.layoutParams as FrameLayout.LayoutParams lp.rightMargin = Math.max(buttonRightInWindow - rightBoundary, 0) lp.topMargin = Math.max(topBoundary - buttonTopInWindow, 0) closeButton.layoutParams = lp
Java
// Get the top-right rounded corner from WindowInsets. final WindowInsets insets = getRootWindowInsets(); final RoundedCorner topRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(POSITION_TOP_RIGHT); if (topRight == null) { return; } // Get the location of the close button in window coordinates. int [] location = new int[2]; closeButton.getLocationInWindow(location); final int buttonRightInWindow = location[0] + closeButton.getWidth(); final int buttonTopInWindow = location[1]; // Find the point on the quarter circle with a 45-degree angle. final int offset = (int) (topRight.getRadius() * Math.sin(Math.toRadians(45))); final int topBoundary = topRight.getCenter().y - offset; final int rightBoundary = topRight.getCenter().x + offset; // Check whether the close button exceeds the boundary. if (buttonRightInWindow < rightBoundary << buttonTopInWindow > topBoundary) { return; } // Set the margin to avoid truncating. int [] parentLocation = new int[2]; getLocationInWindow(parentLocation); FrameLayout.LayoutParams lp = (FrameLayout.LayoutParams) closeButton.getLayoutParams(); lp.rightMargin = Math.max(buttonRightInWindow - rightBoundary, 0); lp.topMargin = Math.max(topBoundary - buttonTopInWindow, 0); closeButton.setLayoutParams(lp);
Cuidado com os cortes
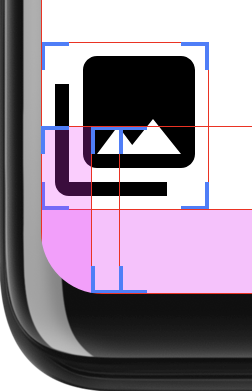
Se a interface preencher toda a tela, cantos arredondados podem causar problemas com o conteúdo. recorte de dados. Por exemplo, a figura 2 mostra um ícone no canto da tela com o layout que está sendo desenhado por trás das barras do sistema:

Para evitar isso, verifique se há cantos arredondados e aplique padding para manter do app fora dos cantos do dispositivo, conforme mostrado exemplo:
Kotlin
class InsetsLayout(context: Context, attrs: AttributeSet) : FrameLayout(context, attrs) { override fun onLayout(changed: Boolean, left: Int, top: Int, right: Int, bottom: Int) { val insets = rootWindowInsets if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.S && insets != null) { applyRoundedCornerPadding(insets) } super.onLayout(changed, left, top, right, bottom) } @RequiresApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.S) private fun applyRoundedCornerPadding(insets: WindowInsets) { val topLeft = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_TOP_LEFT) val topRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_TOP_RIGHT) val bottomLeft = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_BOTTOM_LEFT) val bottomRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_BOTTOM_RIGHT) val leftRadius = max(topLeft?.radius ?: 0, bottomLeft?.radius ?: 0) val topRadius = max(topLeft?.radius ?: 0, topRight?.radius ?: 0) val rightRadius = max(topRight?.radius ?: 0, bottomRight?.radius ?: 0) val bottomRadius = max(bottomLeft?.radius ?: 0, bottomRight?.radius ?: 0) val windowManager = context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE) as WindowManager val windowBounds = windowManager.currentWindowMetrics.bounds val safeArea = Rect( windowBounds.left + leftRadius, windowBounds.top + topRadius, windowBounds.right - rightRadius, windowBounds.bottom - bottomRadius ) val location = intArrayOf(0, 0) getLocationInWindow(location) val leftMargin = location[0] - windowBounds.left val topMargin = location[1] - windowBounds.top val rightMargin = windowBounds.right - right - location[0] val bottomMargin = windowBounds.bottom - bottom - location[1] val layoutBounds = Rect( location[0] + paddingLeft, location[1] + paddingTop, location[0] + width - paddingRight, location[1] + height - paddingBottom ) if (layoutBounds != safeArea && layoutBounds.contains(safeArea)) { setPadding( calculatePadding(leftRadius, leftMargin, paddingLeft), calculatePadding(topRadius, topMargin, paddingTop), calculatePadding(rightRadius, rightMargin, paddingRight), calculatePadding(bottomRadius, bottomMargin, paddingBottom) ) } } private fun calculatePadding(radius1: Int?, radius2: Int?, margin: Int, padding: Int): Int = (max(radius1 ?: 0, radius2 ?: 0) - margin - padding).coerceAtLeast(0) }
Java
public class InsetsLayout extends FrameLayout { public InsetsLayout(@NonNull Context context) { super(context); } public InsetsLayout(@NonNull Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) { super(context, attrs); } @Override protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) { WindowInsets insets = getRootWindowInsets(); if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.S && insets != null) { applyRoundedCornerPadding(insets); } super.onLayout(changed, left, top, right, bottom); } @RequiresApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.S) private void applyRoundedCornerPadding(WindowInsets insets) { RoundedCorner topLeft = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_TOP_LEFT); RoundedCorner topRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_TOP_RIGHT); RoundedCorner bottomLeft = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_BOTTOM_LEFT); RoundedCorner bottomRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_BOTTOM_RIGHT); int radiusTopLeft = 0; int radiusTopRight = 0; int radiusBottomLeft = 0; int radiusBottomRight = 0; if (topLeft != null) radiusTopLeft = topLeft.getRadius(); if (topRight != null) radiusTopRight = topRight.getRadius(); if (bottomLeft != null) radiusBottomLeft = bottomLeft.getRadius(); if (bottomRight != null) radiusBottomRight = bottomRight.getRadius(); int leftRadius = Math.max(radiusTopLeft, radiusBottomLeft); int topRadius = Math.max(radiusTopLeft, radiusTopRight); int rightRadius = Math.max(radiusTopRight, radiusBottomRight); int bottomRadius = Math.max(radiusBottomLeft, radiusBottomRight); WindowManager windowManager = (WindowManager) getContext().getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE); Rect windowBounds = windowManager.getCurrentWindowMetrics().getBounds(); Rect safeArea = new Rect( windowBounds.left + leftRadius, windowBounds.top + topRadius, windowBounds.right - rightRadius, windowBounds.bottom - bottomRadius ); int[] location = {0, 0}; getLocationInWindow(location); int leftMargin = location[0] - windowBounds.left; int topMargin = location[1] - windowBounds.top; int rightMargin = windowBounds.right - getRight() - location[0]; int bottomMargin = windowBounds.bottom - getBottom() - location[1]; Rect layoutBounds = new Rect( location[0] + getPaddingLeft(), location[1] + getPaddingTop(), location[0] + getWidth() - getPaddingRight(), location[1] + getHeight() - getPaddingBottom() ); if (!layoutBounds.equals(safeArea) && layoutBounds.contains(safeArea)) { setPadding( calculatePadding(radiusTopLeft, radiusBottomLeft, leftMargin, getPaddingLeft()), calculatePadding(radiusTopLeft, radiusTopRight, topMargin, getPaddingTop()), calculatePadding(radiusTopRight, radiusBottomRight, rightMargin, getPaddingRight()), calculatePadding(radiusBottomLeft, radiusBottomRight, bottomMargin, getPaddingBottom()) ); } } private int calculatePadding(int radius1, int radius2, int margin, int padding) { return Math.max(Math.max(radius1, radius2) - margin - padding, 0); } }
Esse layout determina se a interface se estende para a área dos cantos arredondados e adiciona padding no local correspondente. A Figura 3 mostra a opção "Show Layout Bounds" desenvolvedor ativada para mostrar o padding sendo aplicado de forma mais clara:
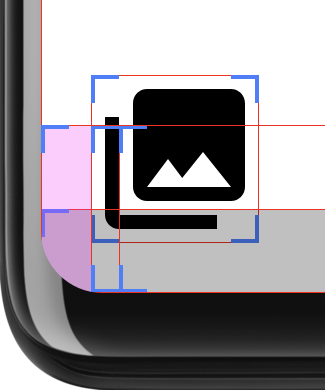
Para fazer essa determinação, o layout calcula dois retângulos: safeArea é
a área dentro dos raios dos cantos arredondados, e layoutBounds é o tamanho
do layout menos o padding. Se layoutArea contiver completamente safeArea, então:
os filhos do layout podem ser cortados. Se esse for o caso, o padding será
adicionado para garantir que o layout permaneça dentro de safeArea.
Ao verificar se layoutBounds inclui safeArea totalmente, você evita adicionar
padding quando o layout não se estende para as bordas da tela. Figura 4.
mostra o layout quando não está desenhado por trás da barra de navegação. Nesse caso,
o layout não se estenda o suficiente para ficar dentro dos cantos arredondados, já que
elas se encaixam na área ocupada pela barra de navegação. Não é necessário preenchimento.