Scaffold
Dans Material Design, un échafaudage est une structure fondamentale qui fournit une plate-forme standardisée pour les interfaces utilisateur complexes. Il rassemble différentes parties de l'UI, telles que les barres d'application et les boutons d'action flottants, pour donner aux applications une apparence cohérente.
Exemple
Le composable Scaffold fournit une API simple que vous pouvez utiliser pour assembler rapidement la structure de votre application conformément aux consignes Material Design.
Scaffold accepte plusieurs composables en tant que paramètres. En voici quelques-uns :
topBar: barre d'application en haut de l'écran.bottomBar: barre d'application en bas de l'écran.floatingActionButton: bouton qui se trouve en bas à droite de l'écran et qui permet d'afficher les actions clés.
Vous pouvez également transmettre le contenu Scaffold comme vous le feriez pour d'autres conteneurs. Il transmet PaddingValues au lambda content que vous devez appliquer au composable racine de votre contenu pour limiter sa taille.
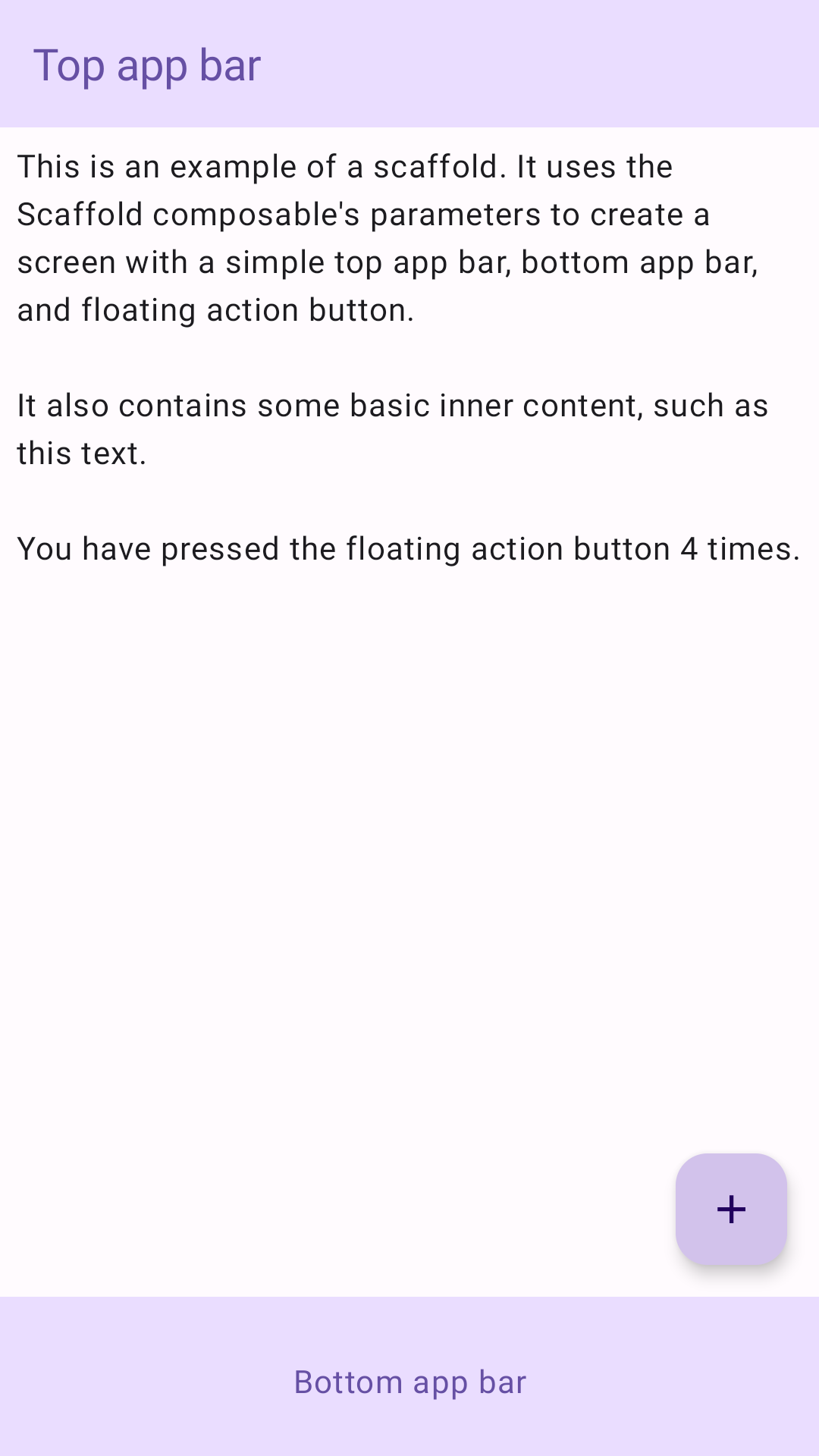
L'exemple suivant montre une implémentation complète de Scaffold. Il contient une barre d'application supérieure, une barre d'application inférieure et un bouton d'action flottant.
@Composable fun ScaffoldExample() { var presses by remember { mutableIntStateOf(0) } Scaffold( topBar = { TopAppBar( colors = topAppBarColors( containerColor = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.primaryContainer, titleContentColor = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.primary, ), title = { Text("Top app bar") } ) }, bottomBar = { BottomAppBar( containerColor = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.primaryContainer, contentColor = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.primary, ) { Text( modifier = Modifier .fillMaxWidth(), textAlign = TextAlign.Center, text = "Bottom app bar", ) } }, floatingActionButton = { FloatingActionButton(onClick = { presses++ }) { Icon(Icons.Default.Add, contentDescription = "Add") } } ) { innerPadding -> Column( modifier = Modifier .padding(innerPadding), verticalArrangement = Arrangement.spacedBy(16.dp), ) { Text( modifier = Modifier.padding(8.dp), text = """ This is an example of a scaffold. It uses the Scaffold composable's parameters to create a screen with a simple top app bar, bottom app bar, and floating action button. It also contains some basic inner content, such as this text. You have pressed the floating action button $presses times. """.trimIndent(), ) } } }
Cette implémentation est la suivante :