搜索是 Android 上的核心用户功能。用户必须能够搜索他们可以使用的任何数据,无论内容是在设备上还是互联网上。为了帮助为用户打造一致的搜索体验,Android 提供了一个搜索框架来帮助您为自己的应用实现搜索功能。
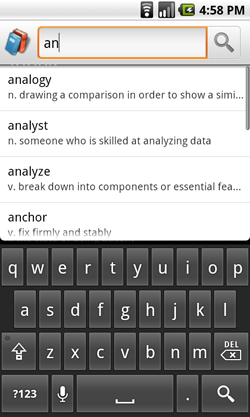
图 1. 包含自定义搜索建议的搜索对话框。
搜索框架提供了两种搜索输入模式:一种是屏幕顶部的搜索对话框,一种是您可以嵌入 activity 布局的搜索微件 (SearchView)。无论是哪种情况,Android 系统都会将搜索查询传递给执行搜索的特定 activity,从而协助您实现搜索功能。您还可以让搜索对话框或搜索微件在用户输入内容时提供搜索建议。图 1 显示了包含可选搜索建议的搜索对话框的示例。
设置搜索对话框或搜索微件后,您可以执行以下操作:
- 启用语音搜索。
- 根据最近的用户查询提供搜索建议。
- 提供与您的应用数据中的实际结果匹配的自定义搜索建议。
- 在系统范围的快速搜索框中提供应用的搜索建议。
注意:搜索框架未提供用于搜索您的数据的 API。要执行搜索,您需要使用适合您的数据的 API。例如,如果您的数据存储在 SQLite 数据库中,请使用 android.database.sqlite API 来执行搜索。
此外,不能保证设备提供专用的搜索按钮,用于在您的应用中调用搜索界面。在使用搜索对话框或自定义界面时,您必须在界面中提供用于激活搜索界面的搜索按钮。如需了解详情,请参阅调用搜索对话框。
以下页面介绍了如何使用 Android 框架来实现搜索功能:
- 创建搜索界面
- 如何设置您的应用以使用搜索对话框或搜索微件。
- 添加近期查询建议
- 如何根据之前使用的查询提供建议。
- 添加自定义建议
- 如何根据您的应用中的自定义数据提供建议,并在系统范围的快速搜索框中提供这些建议。
- 可搜索配置
- 可搜索配置文件的参考文档。其他文档也从特定行为的角度介绍了该配置文件。
保护用户隐私
当您在自己的应用中实现搜索功能时,应采取措施来保护用户的隐私。许多用户认为他们在手机上的活动(包括搜索)是私人信息。为了保护用户隐私,请遵守以下原则:
- 不要将个人信息发送到服务器,但如果必须发送此类信息,不要将其记录下来。
个人信息是指可以识别用户个人身份的任何信息,如用户的姓名、电子邮件地址、结算信息,或可以合理地关联到此类信息的其他数据。如果您的应用在服务器的协助下实现搜索功能,应避免将个人信息与搜索查询一起发送。例如,如果您要搜索某个邮政编码附近的商家,不需要同时发送用户 ID;只需将该邮政编码发送到服务器即可。如果您必须发送个人信息,请避免将其记录下来。如果您必须记录,请非常小心地保护该数据,并尽快将其擦除。
- 为用户提供清除其搜索记录的方法。
搜索框架可帮助您的应用在用户输入内容时提供特定于上下文的建议。有时,这些建议基于先前的搜索或用户在之前的会话中执行的其他操作。用户可能不希望将先前的搜索透露给其他设备用户。如果您的应用提供的建议会透露先前的搜索活动,请实现让用户清除搜索记录的方法。如果您使用
SearchRecentSuggestions,可以调用clearHistory()方法。如果您实现自定义建议,则需要在内容提供程序中提供一种类似的“清除记录”方法,让用户可以执行清除操作。

