将项目配置为使用 Android Game Development Extension。
Android Game Development Extension 会调用 MSBuild 以将 C/C++ 源代码构建到共享库 (.so) 和静态库 (.a) 中。在构建流程中,一项自定义 MSBuild 任务会调用 Gradle 来编译 Java 和 Kotlin 源代码、打包资源,并生成用于部署的 APK 文件。在配置项目时,您必须确保 MSBuild 具有针对 Android 平台进行构建所需的信息。
使用 MSBuild 构建 C/C++
典型的 Android 项目使用 Gradle 构建而成,其中项目内的原生代码由运行 CMake 或 ndk-build 的 Gradle 通道构建。有了适用于 Visual Studio 的 Android Game Development Extension,构建流程颠倒过来。现在,MSBuild 是构建流程的起点。MSBuild 首先为作为扩展程序的一部分在系统上安装的新 Android 平台(例如“Android-x86_64”)构建所有 C/C++ 源代码。MSBuild 随后调用 Gradle 以将包含 C/C++ 逻辑的共享库文件打包到 APK 中。
您应首先在 MSBuild 中复制 CMake 或 ndk-build 中的项目现有构建逻辑。将目标平台设置为以下各项:
- Android-x86
- Android-x86_64
- Android-armeabi-v7a
- Android-arm64-v8a
这些平台全部由 Android Game Development Extension 提供。
设置编译和链接选项
AGDE 在构建应用的 C/C++ 部分时,会使用您选择的 NDK 来确定默认的编译和链接选项。
如果您需要自定义这些编译或链接选项,可以使用“Project Properties”(项目属性)进行设置。您可以在“C/C++”(用于编译)、“Librarian”(用于静态库归档)和“Linker”(用于动态库关联)组中找到最常见的选项。如果您需要传递任何其他自定义选项,可以将其添加到“命令行”部分。例如,如果您使用的是低于 r28 的 NDK,则可能需要设置链接器标志,以使应用支持 16 KB 页面大小。
添加 Android 平台
虽然 Teapot 示例项目包含 Android 平台,但您必须手动将一个 Android 平台添加到现有项目。如要添加一个新平台,请在 Visual Studio 中执行以下操作:
- 依次选择生成 > 配置管理器。
- 在 Active solution platform 下,选择 <New>。
为新平台输入以下某一项:
- Android-armeabi-v7a
- Android-arm64-v8a
- Android-x86
- Android-x86_64
在从此处复制设置框中,选择其他现有 Android 平台,如果尚无任何 Android 平台,请选择 <Empty>。确保您已启用创建新的项目平台。
添加 Android APK 项
依次选择 Add > New Item > Visual C++ > Android > Android APK,然后点击 Add。在接下来显示的对话框中配置 Android 应用。
- Application Name:简单易懂的 Android 应用名称。
- Application ID:Android 应用的唯一标识符。
- Solution Explorer Location:包含添加的 Android 打包支持文件的虚拟文件夹的位置。默认情况下,这些文件也位于项目中的一个同名文件夹中。您可以通过选中 Put support files in a custom location 复选框并指定自定义位置来自定义位置。虚拟文件夹仍位于 Solution Explorer 中的当前项目下。
让 MSBuild 调用 Gradle 以构建 APK
除非 MSBuild 知道 Gradle 项目的位置,否则它无法调用 Gradle。您可以使用 Gradle Build Directory 属性设置此位置,如图 1 所示。
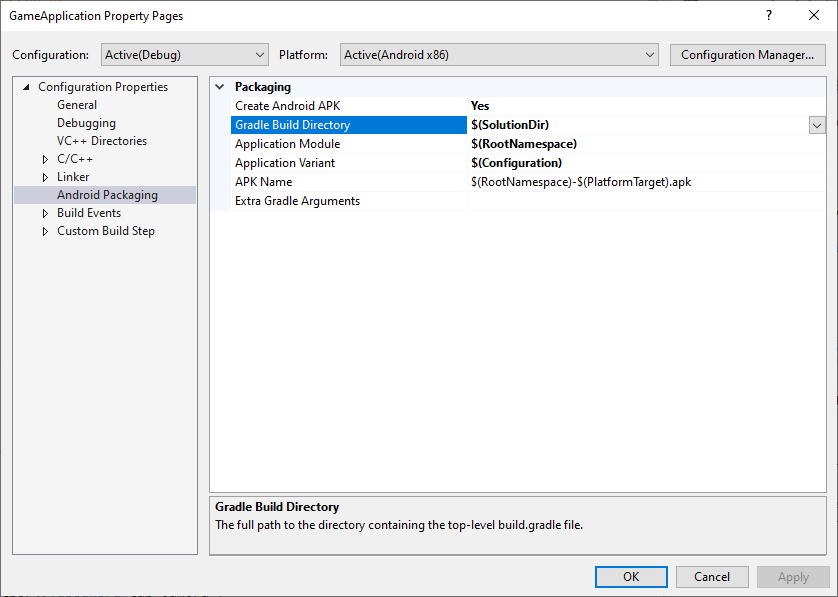
图 1. Gradle Build Directory 属性
此外,还应设置 Application Module、Application Variant 和 APK Name 属性(如上图所示),以使 MSBuild 知道要构建的内容。
- Application Module:Gradle 子项目的名称。这是
settings.gradle文件中设置的主项目。对于直接使用 Android Studio 创建的项目,它通常称为app。 - Application Variant:要构建的 Android 变体。此值应根据 MSBuild 配置进行设置。例如,对于调试 build,应将此值设置为调试变体。如果项目的 MSBuild 配置名称与 Gradle 变体名称相符,则只需使用默认值
$(Configuration)。 - APK Name:生成的 APK 文件的名称,该文件用于在开发计算机上进行调试和性能剖析。此名称会传递给 Gradle,Gradle 构建脚本应遵循此属性(请参阅下一部分中的
MSBUILD_ANDROID_OUTPUT_APK_NAME属性)。
修改 Gradle 构建脚本
在构建期间,MSBuild 会将以下信息作为项目属性传递给 Gradle 脚本。请更改项目的现有构建脚本(通常名为 build.gradle)以读取这些属性。
MSBUILD_MIN_SDK_VERSION:构建 APK 的最低 SDK 版本(作为字符串)。在项目属性页面上的 Minimum Android SDK Version 框中设置此值,如图 2 所示。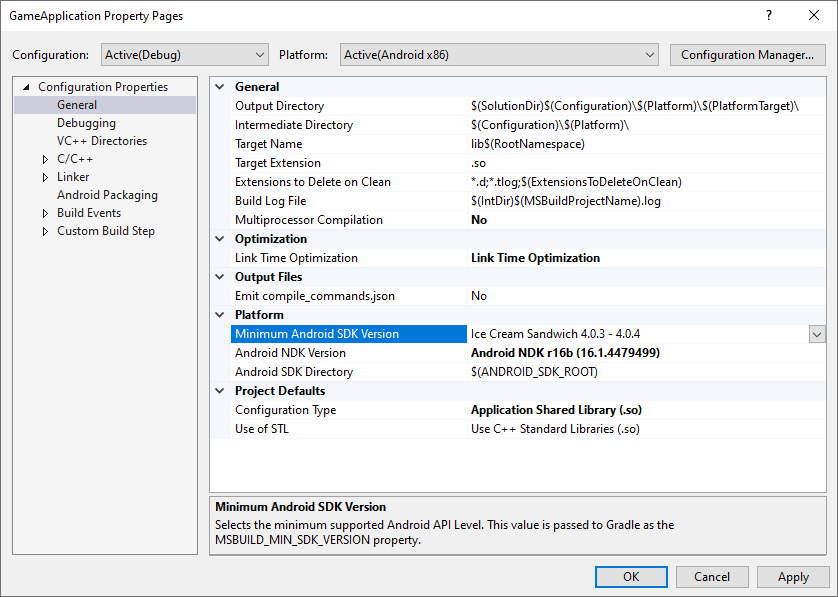
图 2. Minimum Android SDK Version 属性Gradle 构建脚本应将
minSdkVersion或minSdk设置为此字符串值,并在必要时进行toInteger()类型转换。Groovy
android { // ... defaultConfig { applicationId "com.yourcompany.yourapp" minSdkVersion MSBUILD_MIN_SDK_VERSION // Or: minSdk MSBUILD_MIN_SDK_VERSION.toInteger() // ... } // ... }
Kotlin
android { // ... defaultConfig { applicationId = "com.yourcompany.yourapp" minSdkVersion(MSBUILD_MIN_SDK_VERSION) // Or: minSdk = MSBUILD_MIN_SDK_VERSION.toInteger() // ... } // ... }
MSBUILD_ANDROID_OUTPUT_APK_NAME:Gradle 构建的 APK 的预期名称。Android Game Development Extension 将查找与此名称相符的 APK,然后将其部署到连接的设备(用于调试和性能剖析)。在项目属性页面上的 APK Name 框中设置此值,如图 3 所示。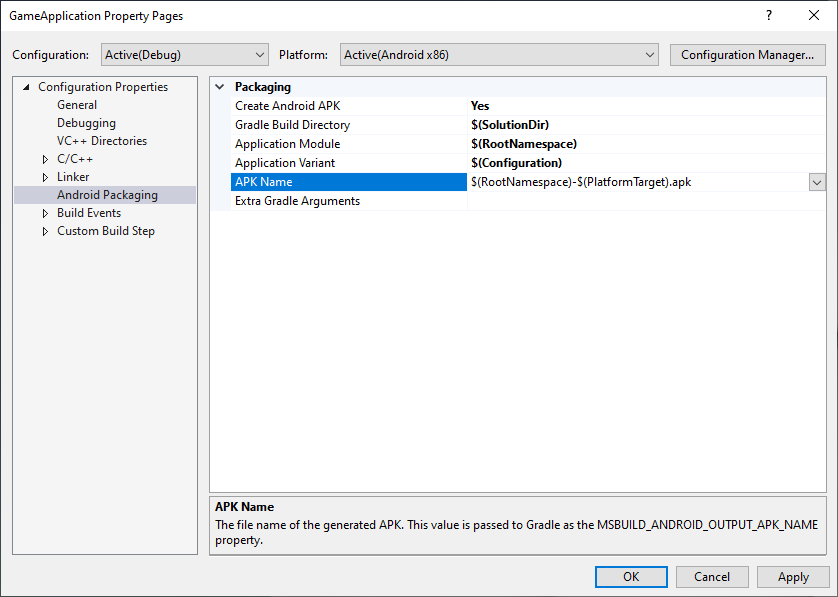
图 3. APK Name 属性Gradle 构建脚本必须遵循此属性。例如,以下示例将所有变体的输出 APK 名称设置为 MSBuild 选择的名称。
Groovy
android { // ... applicationVariants.all { variant -> variant.outputs.all { outputFileName = MSBUILD_ANDROID_OUTPUT_APK_NAME } } // ... }
Kotlin
android { // ... applicationVariants.all { variant -> variant.outputs.all { outputFileName = MSBUILD_ANDROID_OUTPUT_APK_NAME } } // ... }
MSBUILD_JNI_LIBS_SRC_DIR:包含 MSBuild 构建的共享库(.so文件)的目录。在项目属性页面上的 Output Directory 框中设置此值,如下所示。默认情况下,此值是 Visual Studio 项目的输出目录属性,如图 4 所示。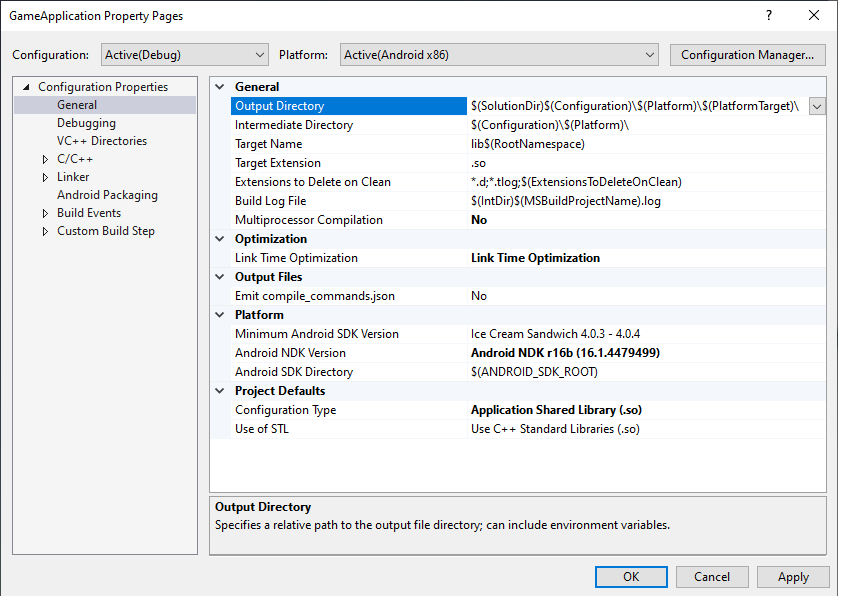
图 4. Output Directory 属性Gradle 应将此文件夹中的共享库文件打包到 APK 内,以便 Android 应用在运行时加载它们。
Groovy
android { // ... sourceSets { main { jniLibs.srcDirs += [MSBUILD_JNI_LIBS_SRC_DIR] } } // ... }
Kotlin
android { // ... sourceSets.getByName("main") { jniLibs.srcDir(MSBUILD_JNI_LIBS_SRC_DIR) } // ... }
此外,由于所有 C/C++ 代码现在都由 MSBuild 构建,因此请移除 Gradle 构建脚本中的
externalNativeBuild部分。这些部分过去用于调用 CMake 或 ndk-build 以编译 C/C++ 代码,但不再需要。MSBUILD_NDK_VERSION:要用于构建项目的 NDK 的版本。在项目属性页面上的 Android NDK Version 框中设置此值,如图 5 所示。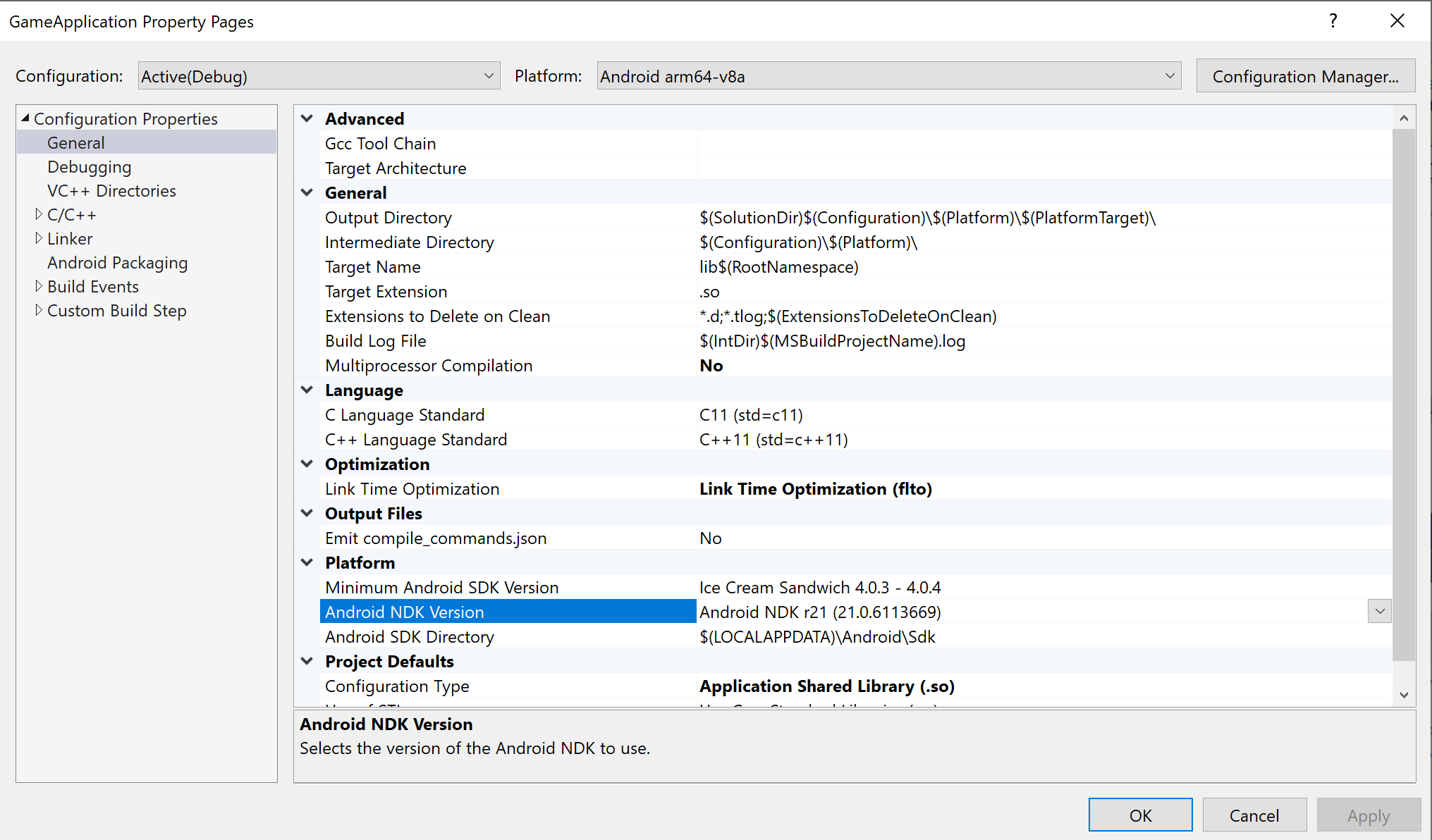
图 5. Android NDK Version 属性Gradle 构建脚本应将
ndkVersion设置为此值,如下所示。Groovy
android { // ... ndkVersion MSBUILD_NDK_VERSION // ... }
Kotlin
android { // ... ndkVersion = MSBUILD_NDK_VERSION // ... }
如需了解详情,请参阅 Android Studio 主题:安装及配置 NDK 和 CMake。

