Compose की मदद से, पॉलीगॉन से बने शेप बनाए जा सकते हैं. उदाहरण के लिए, इस तरह की आकृतियां बनाई जा सकती हैं:

Compose में कस्टम राउंडेड पॉलीगॉन बनाने के लिए, अपनी app/build.gradle में graphics-shapes डिपेंडेंसी जोड़ें:
implementation "androidx.graphics:graphics-shapes:1.0.1"
इस लाइब्रेरी की मदद से, ऐसे शेप बनाए जा सकते हैं जो पॉलीगॉन से बने होते हैं. पॉलीगोनल शेप में सिर्फ़ सीधी लाइनें और नुकीले कोने होते हैं. हालांकि, इन शेप में गोल कोनों का विकल्प होता है. इससे दो अलग-अलग शेप के बीच आसानी से बदलाव किया जा सकता है. अलग-अलग शेप के बीच मॉर्फ़िंग करना मुश्किल होता है. साथ ही, यह डिज़ाइन के समय की समस्या होती है. हालांकि, यह लाइब्रेरी इन आकृतियों को एक-दूसरे में बदलने की प्रोसेस को आसान बनाती है. इसके लिए, यह एक जैसे पॉलीगोनल स्ट्रक्चर का इस्तेमाल करती है.
पॉलीगॉन बनाना
नीचे दिए गए स्निपेट में, ड्रॉइंग एरिया के बीच में छह पॉइंट वाला एक बुनियादी पॉलीगॉन बनाया गया है:
Box( modifier = Modifier .drawWithCache { val roundedPolygon = RoundedPolygon( numVertices = 6, radius = size.minDimension / 2, centerX = size.width / 2, centerY = size.height / 2 ) val roundedPolygonPath = roundedPolygon.toPath().asComposePath() onDrawBehind { drawPath(roundedPolygonPath, color = Color.Blue) } } .fillMaxSize() )

इस उदाहरण में, लाइब्रेरी एक RoundedPolygon बनाती है. इसमें अनुरोध किए गए आकार को दिखाने वाली ज्यामिति होती है. Compose ऐप्लिकेशन में उस शेप को बनाने के लिए, आपको उससे एक Path ऑब्जेक्ट पाना होगा, ताकि शेप को ऐसे फ़ॉर्म में बदला जा सके जिसे Compose बना सके.
पॉलीगॉन के कोनों को गोल करना
किसी पॉलीगॉन के कोनों को गोल करने के लिए, CornerRounding पैरामीटर का इस्तेमाल करें. इसमें दो पैरामीटर होते हैं, radius और smoothing. हर गोल कोना, एक से तीन क्यूबिक कर्व से बना होता है. इसके बीच के हिस्से में गोलाकार चाप होता है, जबकि दोनों साइड ("फ़्लैंकिंग") कर्व, शेप के किनारे से सेंटर कर्व तक जाते हैं.
दायरा
radius, उस सर्कल की रेडियस होती है जिसका इस्तेमाल वर्टेक्स को गोल करने के लिए किया जाता है.
उदाहरण के लिए, गोल कोनों वाला यह त्रिकोण इस तरह बनाया गया है:

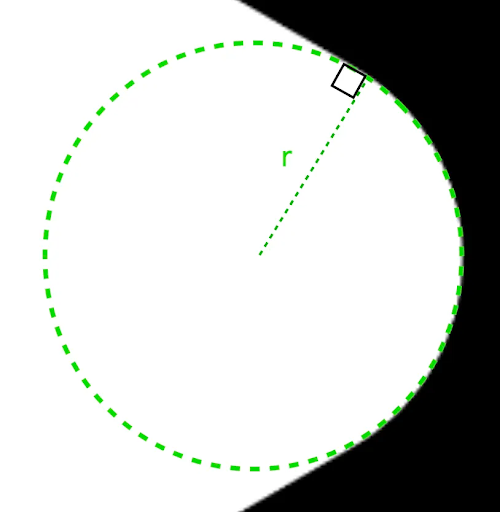
r से, गोल किए गए कोनों के गोलाकार राउंडिंग का साइज़ तय होता है.कोमल करना
स्मूदिंग एक ऐसा फ़ैक्टर है जो यह तय करता है कि कोने के गोलाकार हिस्से से किनारे तक पहुंचने में कितना समय लगता है. स्मूदिंग फ़ैक्टर की वैल्यू 0 (अनस्मूद, CornerRounding की डिफ़ॉल्ट वैल्यू) होने पर, कॉर्नर पूरी तरह से गोल हो जाते हैं. स्मूदिंग फ़ैक्टर की वैल्यू शून्य से ज़्यादा (ज़्यादा से ज़्यादा 1.0) होने पर, कोने को तीन अलग-अलग कर्व से गोल किया जाता है.


उदाहरण के लिए, नीचे दिए गए स्निपेट में, स्मूदिंग को 0 पर सेट करने और 1 पर सेट करने के बीच का मामूली अंतर दिखाया गया है:
Box( modifier = Modifier .drawWithCache { val roundedPolygon = RoundedPolygon( numVertices = 3, radius = size.minDimension / 2, centerX = size.width / 2, centerY = size.height / 2, rounding = CornerRounding( size.minDimension / 10f, smoothing = 0.1f ) ) val roundedPolygonPath = roundedPolygon.toPath().asComposePath() onDrawBehind { drawPath(roundedPolygonPath, color = Color.Black) } } .size(100.dp) )

साइज़ और पोज़िशन
डिफ़ॉल्ट रूप से, किसी शेप को सेंटर (0, 0) के चारों ओर 1 के रेडियस के साथ बनाया जाता है.
यह रेडियस, उस बहुभुज के सेंटर और बाहरी वर्टेक्स के बीच की दूरी को दिखाता है जिस पर शेप आधारित है. ध्यान दें कि कोनों को गोल करने से, आकार छोटा हो जाता है. ऐसा इसलिए होता है, क्योंकि गोल किए गए कोने, गोल किए जा रहे वर्टिकल की तुलना में सेंटर के ज़्यादा करीब होते हैं. किसी पॉलीगॉन का साइज़ बदलने के लिए, radius वैल्यू को अडजस्ट करें. जगह में बदलाव करने के लिए, पॉलीगॉन के centerX या centerY में बदलाव करें.
इसके अलावा, ऑब्जेक्ट को ट्रांसफ़ॉर्म करके उसका साइज़, पोज़िशन, और रोटेशन बदला जा सकता है. इसके लिए, DrawScope ट्रांसफ़ॉर्मेशन फ़ंक्शन का इस्तेमाल करें. जैसे, DrawScope#translate().
आकृतियों को मॉर्फ़ करना
Morph ऑब्जेक्ट एक नई शेप है. यह दो पॉलीगोनल शेप के बीच ऐनिमेशन दिखाती है. दो शेप के बीच मॉर्फ़ करने के लिए, दो RoundedPolygons और एक Morph ऑब्जेक्ट बनाएं, जो इन दोनों शेप को लेता हो. शुरुआत और आखिर के शेप के बीच का शेप कैलकुलेट करने के लिए, progress की वैल्यू शून्य और एक के बीच दें. इससे शुरुआत (0) और आखिर (1) के शेप के बीच का शेप तय होगा:
Box( modifier = Modifier .drawWithCache { val triangle = RoundedPolygon( numVertices = 3, radius = size.minDimension / 2f, centerX = size.width / 2f, centerY = size.height / 2f, rounding = CornerRounding( size.minDimension / 10f, smoothing = 0.1f ) ) val square = RoundedPolygon( numVertices = 4, radius = size.minDimension / 2f, centerX = size.width / 2f, centerY = size.height / 2f ) val morph = Morph(start = triangle, end = square) val morphPath = morph .toPath(progress = 0.5f).asComposePath() onDrawBehind { drawPath(morphPath, color = Color.Black) } } .fillMaxSize() )
ऊपर दिए गए उदाहरण में, प्रोग्रेस को दोनों शेप (गोल त्रिकोण और वर्ग) के बीच में रखा गया है. इससे यह नतीजा मिलता है:

ज़्यादातर मामलों में, मॉर्फ़िंग को ऐनिमेशन के तौर पर किया जाता है. इसे सिर्फ़ स्टैटिक रेंडरिंग के तौर पर नहीं किया जाता. इन दोनों के बीच ऐनिमेशन बनाने के लिए, Compose में मौजूद स्टैंडर्ड ऐनिमेशन एपीआई का इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है. इससे समय के साथ प्रोग्रेस वैल्यू में बदलाव किया जा सकता है. उदाहरण के लिए, इन दो आकृतियों के बीच के मॉर्फ़ को इस तरह से हमेशा के लिए ऐनिमेट किया जा सकता है:
val infiniteAnimation = rememberInfiniteTransition(label = "infinite animation") val morphProgress = infiniteAnimation.animateFloat( initialValue = 0f, targetValue = 1f, animationSpec = infiniteRepeatable( tween(500), repeatMode = RepeatMode.Reverse ), label = "morph" ) Box( modifier = Modifier .drawWithCache { val triangle = RoundedPolygon( numVertices = 3, radius = size.minDimension / 2f, centerX = size.width / 2f, centerY = size.height / 2f, rounding = CornerRounding( size.minDimension / 10f, smoothing = 0.1f ) ) val square = RoundedPolygon( numVertices = 4, radius = size.minDimension / 2f, centerX = size.width / 2f, centerY = size.height / 2f ) val morph = Morph(start = triangle, end = square) val morphPath = morph .toPath(progress = morphProgress.value) .asComposePath() onDrawBehind { drawPath(morphPath, color = Color.Black) } } .fillMaxSize() )

पॉलीगॉन को क्लिप के तौर पर इस्तेमाल करना
Compose में, कंपोज़ेबल को रेंडर करने के तरीके में बदलाव करने के लिए, clip मॉडिफ़ायर का इस्तेमाल करना आम बात है. साथ ही, क्लिपिंग एरिया के चारों ओर शैडो का फ़ायदा पाने के लिए भी इसका इस्तेमाल किया जाता है:
fun RoundedPolygon.getBounds() = calculateBounds().let { Rect(it[0], it[1], it[2], it[3]) } class RoundedPolygonShape( private val polygon: RoundedPolygon, private var matrix: Matrix = Matrix() ) : Shape { private var path = Path() override fun createOutline( size: Size, layoutDirection: LayoutDirection, density: Density ): Outline { path.rewind() path = polygon.toPath().asComposePath() matrix.reset() val bounds = polygon.getBounds() val maxDimension = max(bounds.width, bounds.height) matrix.scale(size.width / maxDimension, size.height / maxDimension) matrix.translate(-bounds.left, -bounds.top) path.transform(matrix) return Outline.Generic(path) } }
इसके बाद, पॉलीगॉन का इस्तेमाल क्लिप के तौर पर किया जा सकता है. जैसा कि इस स्निपेट में दिखाया गया है:
val hexagon = remember { RoundedPolygon( 6, rounding = CornerRounding(0.2f) ) } val clip = remember(hexagon) { RoundedPolygonShape(polygon = hexagon) } Box( modifier = Modifier .clip(clip) .background(MaterialTheme.colorScheme.secondary) .size(200.dp) ) { Text( "Hello Compose", color = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.onSecondary, modifier = Modifier.align(Alignment.Center) ) }
इस वजह से, ये समस्याएं होती हैं:

यह पहले से रेंडर हो रहे टेक्स्ट से ज़्यादा अलग नहीं दिख सकता. हालांकि, इससे Compose में अन्य सुविधाओं का इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है. उदाहरण के लिए, इस तकनीक का इस्तेमाल किसी इमेज को क्लिप करने और क्लिप किए गए हिस्से के चारों ओर शैडो लगाने के लिए किया जा सकता है:
val hexagon = remember { RoundedPolygon( 6, rounding = CornerRounding(0.2f) ) } val clip = remember(hexagon) { RoundedPolygonShape(polygon = hexagon) } Box( modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize(), contentAlignment = Alignment.Center ) { Image( painter = painterResource(id = R.drawable.dog), contentDescription = "Dog", contentScale = ContentScale.Crop, modifier = Modifier .graphicsLayer { this.shadowElevation = 6.dp.toPx() this.shape = clip this.clip = true this.ambientShadowColor = Color.Black this.spotShadowColor = Color.Black } .size(200.dp) ) }

क्लिक करने पर बटन का आकार बदलना
graphics-shape लाइब्रेरी का इस्तेमाल करके, ऐसा बटन बनाया जा सकता है जिसे दबाने पर, वह दो शेप के बीच बदलता है. सबसे पहले, एक MorphPolygonShape बनाएं, जो Shape को बड़ा करे और उसे सही तरीके से फ़िट करने के लिए स्केल और अनुवाद करे. शेप को ऐनिमेट करने के लिए, प्रोग्रेस को पास करने का तरीका देखें:
class MorphPolygonShape( private val morph: Morph, private val percentage: Float ) : Shape { private val matrix = Matrix() override fun createOutline( size: Size, layoutDirection: LayoutDirection, density: Density ): Outline { // Below assumes that you haven't changed the default radius of 1f, nor the centerX and centerY of 0f // By default this stretches the path to the size of the container, if you don't want stretching, use the same size.width for both x and y. matrix.scale(size.width / 2f, size.height / 2f) matrix.translate(1f, 1f) val path = morph.toPath(progress = percentage).asComposePath() path.transform(matrix) return Outline.Generic(path) } }
इस शेप को मॉर्फ़ करने के लिए, दो पॉलीगॉन बनाएं: shapeA और shapeB. Morph बनाएं और उसे याद रखें. इसके बाद, बटन पर क्लिप आउटलाइन के तौर पर मॉर्फ़ लागू करें. इसके लिए, interactionSource on press का इस्तेमाल करें, ताकि ऐनिमेशन को ट्रिगर किया जा सके:
val shapeA = remember { RoundedPolygon( 6, rounding = CornerRounding(0.2f) ) } val shapeB = remember { RoundedPolygon.star( 6, rounding = CornerRounding(0.1f) ) } val morph = remember { Morph(shapeA, shapeB) } val interactionSource = remember { MutableInteractionSource() } val isPressed by interactionSource.collectIsPressedAsState() val animatedProgress = animateFloatAsState( targetValue = if (isPressed) 1f else 0f, label = "progress", animationSpec = spring(dampingRatio = 0.4f, stiffness = Spring.StiffnessMedium) ) Box( modifier = Modifier .size(200.dp) .padding(8.dp) .clip(MorphPolygonShape(morph, animatedProgress.value)) .background(Color(0xFF80DEEA)) .size(200.dp) .clickable(interactionSource = interactionSource, indication = null) { } ) { Text("Hello", modifier = Modifier.align(Alignment.Center)) }
बॉक्स पर टैप करने पर, यह ऐनिमेशन दिखता है:

शेप मॉर्फ़िंग को हमेशा के लिए ऐनिमेट करना
किसी मॉर्फ़ शेप को लगातार ऐनिमेट करने के लिए, rememberInfiniteTransition का इस्तेमाल करें.
यहां एक ऐसी प्रोफ़ाइल फ़ोटो का उदाहरण दिया गया है जिसका आकार समय के साथ बदलता रहता है और जो लगातार घूमती रहती है. इस तरीके में, ऊपर दिखाए गए MorphPolygonShape में मामूली बदलाव किया जाता है:
class CustomRotatingMorphShape( private val morph: Morph, private val percentage: Float, private val rotation: Float ) : Shape { private val matrix = Matrix() override fun createOutline( size: Size, layoutDirection: LayoutDirection, density: Density ): Outline { // Below assumes that you haven't changed the default radius of 1f, nor the centerX and centerY of 0f // By default this stretches the path to the size of the container, if you don't want stretching, use the same size.width for both x and y. matrix.scale(size.width / 2f, size.height / 2f) matrix.translate(1f, 1f) matrix.rotateZ(rotation) val path = morph.toPath(progress = percentage).asComposePath() path.transform(matrix) return Outline.Generic(path) } } @Preview @Composable private fun RotatingScallopedProfilePic() { val shapeA = remember { RoundedPolygon( 12, rounding = CornerRounding(0.2f) ) } val shapeB = remember { RoundedPolygon.star( 12, rounding = CornerRounding(0.2f) ) } val morph = remember { Morph(shapeA, shapeB) } val infiniteTransition = rememberInfiniteTransition("infinite outline movement") val animatedProgress = infiniteTransition.animateFloat( initialValue = 0f, targetValue = 1f, animationSpec = infiniteRepeatable( tween(2000, easing = LinearEasing), repeatMode = RepeatMode.Reverse ), label = "animatedMorphProgress" ) val animatedRotation = infiniteTransition.animateFloat( initialValue = 0f, targetValue = 360f, animationSpec = infiniteRepeatable( tween(6000, easing = LinearEasing), repeatMode = RepeatMode.Reverse ), label = "animatedMorphProgress" ) Box( modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize(), contentAlignment = Alignment.Center ) { Image( painter = painterResource(id = R.drawable.dog), contentDescription = "Dog", contentScale = ContentScale.Crop, modifier = Modifier .clip( CustomRotatingMorphShape( morph, animatedProgress.value, animatedRotation.value ) ) .size(200.dp) ) } }
इस कोड से यह मज़ेदार नतीजा मिलता है:

कस्टम पॉलीगॉन
अगर सामान्य बहुभुजों से बनाए गए आकार, आपके इस्तेमाल के उदाहरण को कवर नहीं करते हैं, तो आपके पास वर्टेक्स की सूची का इस्तेमाल करके, ज़्यादा कस्टम आकार बनाने का विकल्प होता है. उदाहरण के लिए, आपको शायद इस तरह का दिल बनाना हो:

इस शेप के अलग-अलग वर्टेक्स तय करने के लिए, RoundedPolygon
ओवरलोड का इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है. यह x और y कोऑर्डिनेट का फ़्लोट ऐरे लेता है.
दिल के पॉलीगॉन को छोटे-छोटे हिस्सों में बांटने के लिए, ध्यान दें कि पॉइंट तय करने के लिए पोलर कोऑर्डिनेट सिस्टम का इस्तेमाल करना, कार्टेशियन (x,y) कोऑर्डिनेट सिस्टम के मुकाबले ज़्यादा आसान होता है. इसमें 0° दाईं ओर से शुरू होता है और घड़ी की दिशा में आगे बढ़ता है. साथ ही, 270° 12 बजे की पोज़िशन पर होता है:

अब शेप को आसानी से तय किया जा सकता है. इसके लिए, हर पॉइंट पर कोण (𝜭) और केंद्र से रेडियस तय करें:

अब वर्टिकल बनाए जा सकते हैं और उन्हें RoundedPolygon फ़ंक्शन में भेजा जा सकता है:
val vertices = remember { val radius = 1f val radiusSides = 0.8f val innerRadius = .1f floatArrayOf( radialToCartesian(radiusSides, 0f.toRadians()).x, radialToCartesian(radiusSides, 0f.toRadians()).y, radialToCartesian(radius, 90f.toRadians()).x, radialToCartesian(radius, 90f.toRadians()).y, radialToCartesian(radiusSides, 180f.toRadians()).x, radialToCartesian(radiusSides, 180f.toRadians()).y, radialToCartesian(radius, 250f.toRadians()).x, radialToCartesian(radius, 250f.toRadians()).y, radialToCartesian(innerRadius, 270f.toRadians()).x, radialToCartesian(innerRadius, 270f.toRadians()).y, radialToCartesian(radius, 290f.toRadians()).x, radialToCartesian(radius, 290f.toRadians()).y, ) }
इस radialToCartesian फ़ंक्शन का इस्तेमाल करके, वर्टेक्स को कार्टेशियन कोऑर्डिनेट में बदला जाना चाहिए:
internal fun Float.toRadians() = this * PI.toFloat() / 180f internal val PointZero = PointF(0f, 0f) internal fun radialToCartesian( radius: Float, angleRadians: Float, center: PointF = PointZero ) = directionVectorPointF(angleRadians) * radius + center internal fun directionVectorPointF(angleRadians: Float) = PointF(cos(angleRadians), sin(angleRadians))
ऊपर दिए गए कोड से आपको दिल के रॉ वर्टेक्स मिलते हैं. हालांकि, आपको दिल का चुना गया आकार पाने के लिए, कुछ कोनों को गोल करना होगा. 90° और 270° पर मौजूद कोनों को गोल नहीं किया गया है, लेकिन अन्य कोनों को गोल किया गया है. अलग-अलग कोनों को अपनी पसंद के मुताबिक गोल करने के लिए, perVertexRounding पैरामीटर का इस्तेमाल करें:
val rounding = remember { val roundingNormal = 0.6f val roundingNone = 0f listOf( CornerRounding(roundingNormal), CornerRounding(roundingNone), CornerRounding(roundingNormal), CornerRounding(roundingNormal), CornerRounding(roundingNone), CornerRounding(roundingNormal), ) } val polygon = remember(vertices, rounding) { RoundedPolygon( vertices = vertices, perVertexRounding = rounding ) } Box( modifier = Modifier .drawWithCache { val roundedPolygonPath = polygon.toPath().asComposePath() onDrawBehind { scale(size.width * 0.5f, size.width * 0.5f) { translate(size.width * 0.5f, size.height * 0.5f) { drawPath(roundedPolygonPath, color = Color(0xFFF15087)) } } } } .size(400.dp) )
इससे गुलाबी रंग का दिल दिखता है:

अगर ऊपर दिए गए शेप आपकी ज़रूरत के हिसाब से नहीं हैं, तो Path क्लास का इस्तेमाल करके कस्टम शेप बनाएं. इसके अलावा, डिस्क से ImageVector फ़ाइल लोड की जा सकती है. graphics-shapes लाइब्रेरी का इस्तेमाल, किसी भी तरह की शेप बनाने के लिए नहीं किया जाता. इसका इस्तेमाल खास तौर पर, गोल किनारों वाले पॉलीगॉन और उनके बीच मॉर्फ़ ऐनिमेशन बनाने को आसान बनाने के लिए किया जाता है.
अन्य संसाधन
ज़्यादा जानकारी और उदाहरणों के लिए, ये संसाधन देखें:
- ब्लॉग: आने वाले समय में क्या-क्या हो सकता है - शेप
- ब्लॉग: Android में शेप मॉर्फ़िंग
- Shapes Github डेमो
